Displaying items by tag: marine science
Terrifying Nemo - New Study on Impact of Boat Engine Noise on Fish Finds Clownfish Severely Bothered
Everyone who has ever seen the Pixar film Finding Nemo knows what a clownfish looks like, but a new study gives some alarming insight into their response to human behaviour.
A study by international scientists on the impact of motorboat engine noise found that clownfish are so bothered by it that they will hide, skip meals and even attack domino damselfish and other neighbours.
The erratic behaviour is the result of hormonal changes caused by the engine noise, the researchers from France, Chile and Britain state.
Working on the reefs around Moorea in French Polynesia, the scientists exposed 40 pairs of clownfish to recordings of natural reef sounds or motorboat noise for up to two days.
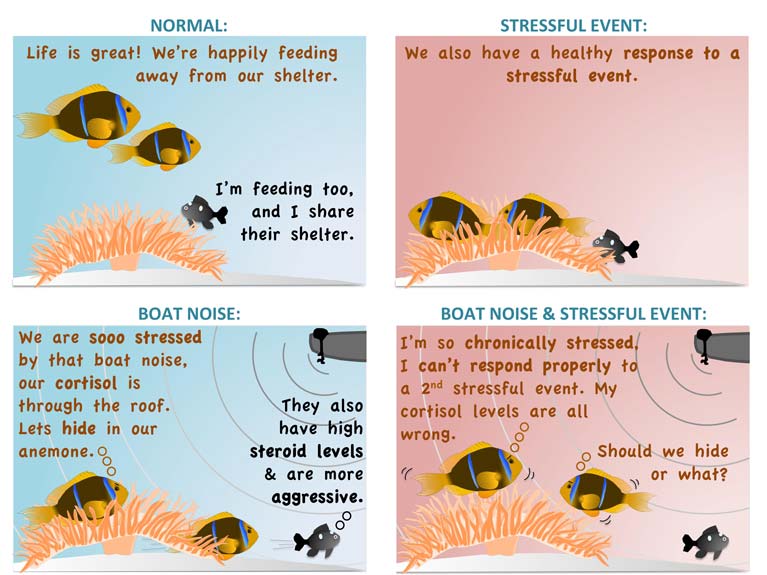
The engine reverberations caused clownfish to “hide in the protective tentacles of their host anemone, move less into open water to feed, and to be more aggressive towards domino damselfish that also reside in the anemone”, they found.
They also found that anemonefish which were also affected by the noise were “unable to respond appropriately to a second stressor, putting them at greater risk from threats such as predators and climate change”.
The study found noise-exposed fish had elevated levels of the stress hormone, cortisol.
They also had higher levels of the reproductive hormones testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone, which corresponded with observed behavioural changes.
“These measurable hormones offer a window into complex behaviours and could be used to develop new noise-mitigation tools,” the scientists state.
Associate professor Suzanne Mills at the École Pratique des Hautes Études (EPHE) PSL Université Paris in France, who is lead author, noted that the high cortisol levels after two days of exposure suggest that clownfish become “chronically stressed by motorboat noise”.
“This compromises the stress response system, leaving clownfish unable to mount appropriate responses to further stressful events. If these stressful events include a predator, motorboat noise could have grave implications,” she said.
“Our new findings highlight the need to control man-made noise in marine protected habitats,” she said.
The paper, entitled Hormonal and behavioural effects of motorboat noise on wild coral reef fish, is published in the journal Environmental Pollution.
Ocean's Ability to Capture Atmospheric Carbon "Drastically Underestimated", Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Study Finds
The ocean’s biological “carbon pump” has been “drastically underestimated in its ability to capture carbon from the atmosphere, a new study has found writes Lorna Siggins
Scientists with the US Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have found that the depth of the sunlit area where photosynthesis takes place varies significantly throughout the ocean.
A paper published by WHOI geochemist Ken Buesseler in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences explains that this matters because the phytoplankton’s ability to take up carbon depends on the amount of sunlight that’s able to penetrate the ocean’s upper layer.
By taking account of the depth of the “euphotic”, or sunlit zone, and his fellow authors found that about twice as much carbon sinks into the ocean per year than previously estimated.
The paper relies on previous studies of the carbon pump, including his own.
“Is the amount of carbon sinking in the ocean going up or down?"
“If you look at the same data in a new way, you get a very different view of the ocean’s role in processing carbon, hence its role in regulating climate,” Buesseler has said.
“Using the new metrics, we will be able to refine the models to not just tell us how the ocean looks today, but how it will look in the future,” he says.
“Is the amount of carbon sinking in the ocean going up or down? That number affects the climate of the world we live in.”
Buesseler and his co-authors call on their fellow oceanographers to consider their data in context of the actual boundary of the euphotic zone.
“If we’re going to call something a euphotic zone, we need to define that,” he says. “So we’re insisting on a more formal definition so that we can compare sites.”
Rather than taking measurements at fixed depths, the authors used chlorophyll sensors —indicating the presence of phytoplankton— to rapidly assess the depth of the sunlit region. They also suggest using the signature from a naturally-occuring thorium isotope to estimate the rate at which carbon particles are sinking.
Buesseler is a principal investigator with WHOI’s Ocean Twilight Zone project, which focuses on what he calls the “little-understood but vastly important mid-ocean region”.
Buesseler and colleagues have already called on the international marine research community to intensify studies of the twilight zone during the upcoming United Nations Decade of the Ocean (2021-2030).
Increased understanding of the twilight zone ecosystem and its role in regulating climate will lead to global policy to protect the area from exploitation, he and his colleagues state.
Co-authors of the paper include: Phillip Boyd of University of Tasmania, Australia; Erin Black of Dalhousie University, Nova Scotia, and Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, New York; and David Siegel, University of California, Santa Barbara.
This work was funded by WHOI’s Ocean Twilight Zone project; NASA; the Ocean Frontier Institute at Dalhousie University; and the Australian Research Council.
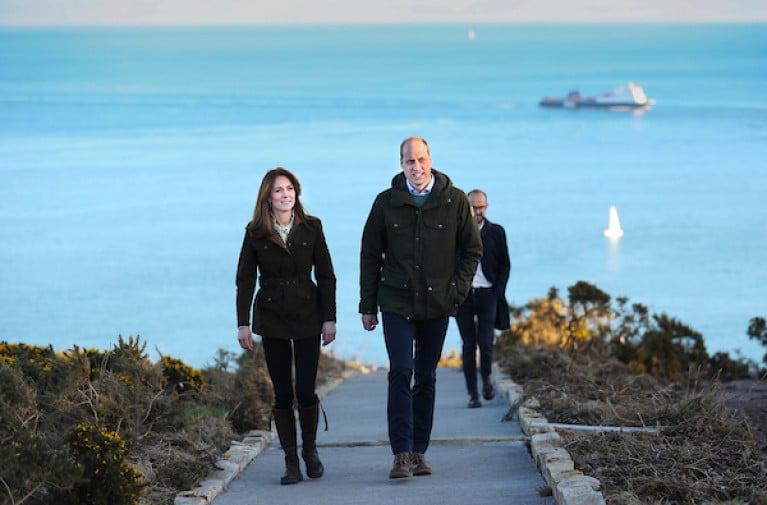
The vital role of the ocean, climate change, and actions to safeguard it for future generations were the focus of conversations between The Duke and Duchess of Cambridge and the Marine Institute during the royal couple’s first official visit to Ireland.
Dr Paul Connolly, CEO of the Marine Institute, Ireland’s state agency for marine research, technology development and innovation, along with All-Ireland Ocean Youth Ambassador, Eimear Manning, met with The Duke and Duchess at Howth, North County Dublin, today.
During a coastal walk of Howth Head, Dr Connolly spoke with Their Royal Highnesses on several subjects that are central to the work of the Marine Institute including the importance of the oceans to coastal communities and climate adaptation. The Marine Institute, through the BlueFish Project, is working with coastal communities in Ireland and Wales on the importance of the ocean to their livelihoods and the impacts of a changing climate.
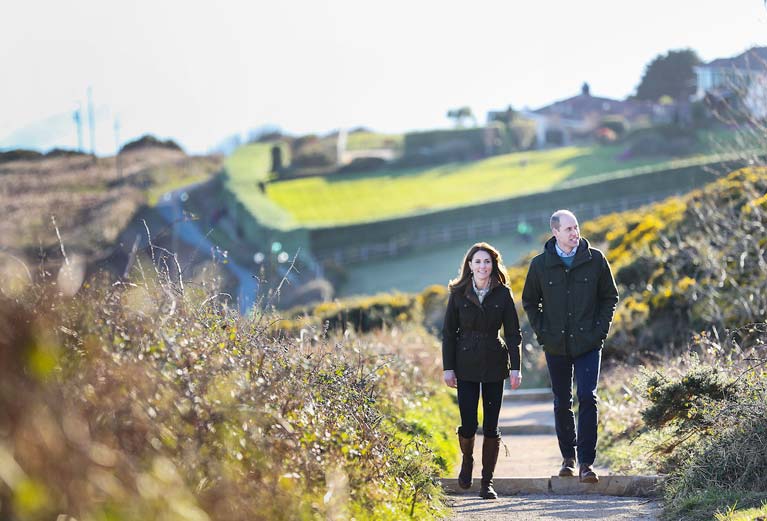 The Royal couple take a stroll on the Hill of Howth, a village and outer suburb of Dublin Photo: Julien Behal
The Royal couple take a stroll on the Hill of Howth, a village and outer suburb of Dublin Photo: Julien Behal
Other topics of conversation included Ireland’s role in exploring and mapping the seabed, international collaboration on ocean research, and the Marine Institute’s role in empowering Ireland and its people to safeguard and harness our ocean wealth.
Eimear Manning is one of 23 All-Atlantic Ocean Youth Ambassadors who are supported by the All-Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance (AORA). She is also an environmental education specialist delivering programmes for a variety of environmental and youth-focused charities and Non-Governmental Organisations.
She spoke with The Duke and Duchess of Cambridge about ways to engage with communities, schools and businesses to introduce behavioural change initiatives and programmes for the marine environment. Working with All-Atlantic Ocean Youth Ambassadors across the globe, she strives to promote sustainable development and stewardship of the Atlantic Ocean.
The Marine Institute’s work aligns with The Royal Foundation of The Duke and Duchess of Cambridge and its aim to unite people to tackle some of today’s biggest challenges.
In January 2020, Prince William launched the Earthshot Prize, an ambitious set of challenges to inspire a decade of action to repair the planet. These challenges will seek answers to the biggest issues currently facing the planet, including climate and energy, nature and biodiversity, oceans, air pollution and fresh water.
2020 signals a ‘super year’ for the environment with crucial summits including the COP26 Climate Change Conference in the UK and the Convention on Biodiversity in China and the UN Ocean Conference. This year, European Maritime Day takes place in Cork City, Ireland, with a two-day event (14-15 May) during which Europe’s maritime community meet to discuss and forge joint action on maritime affairs and sustainable blue growth.
Dr Paul Connolly, CEO of the Marine Institute said, “I was delighted to meet with Their Royal Highnesses, The Duke and Duchess of Cambridge, to talk about shared interests in protecting our oceans and adapting to a changing climate.”
“Our oceans are fundamental to life on earth. They unite us – yet they face a multitude of challenges. Our focus in the Marine Institute is to further our understanding of our changing ocean. Our enhanced knowledge and services help us to observe these patterns of change and identify the steps to safeguard our marine ecosystems for future generations.”
Arctic Researchers Network for Ireland
The Marine Institute in collaboration with the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade launched the Network of Arctic Researchers in Ireland (NARI) last Friday.
NARI aims to create, maintain and develop an informal all-island network of Arctic researchers in Ireland to facilitate the collaboration of scientific activities linked to the Arctic, and to provide independent scientific advice to the public and policymakers.
Irish sailors have voyaged to both the Arctic and Antarctic in recent times. Last Summer Gary McMahon's restored Ilen project went to Greenland and the Arctic circle. Jamie Young’s Frers 49 exploration yacht Killary Flyer from Ireland's west coast travelled to the Arctic in 2013 and 2019. And this year Round the World Sailor Damian Foxall led a mission to Antarctica.
According to the IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere, the extent of Arctic sea ice is declining and is getting thinner. Glaciers and ice sheets in polar and mountain regions are also losing mass, contributing to an increasing rate of sea-level rise, together with expansion of the warmer ocean. Sea level rise will increase the frequency of extreme sea-level events and warming oceans are disrupting marine ecosystems.
With significant demand for greatly enhanced knowledge and services to observe the changes in our oceans, NARI aims to enhance collaboration and promote Irish-based Arctic research activities, seek international polar cooperation and support the next generation of Arctic scientists.
President of NARI, Dr Audrey Morley of National University of Ireland, Galway said, “The coordination of research efforts on a regional, national and international scale is becoming increasingly urgent in order to address the emerging environmental and societal pressures on the Arctic region, which are of global significance. NARI will support a greater scientific understanding of the Arctic region and its role in the Earth system.”
Dr Audrey Morley will be leading a survey on the Marine Institute’s marine research vessel the RV Celtic Explorer later this year to improve our understanding of marine essential climate variables in the Nordic Seas. The Marine Institute is providing ship-time funding for this research survey and funding Dr Audrey Morley’s Post-Doctoral Fellowship (Decoding Arctic Climate Change: From Archive to Insight) in support of improving our understanding of Arctic climate change and ecosystems.
Dr Paul Connolly, CEO of the Marine Institute said, “As an Arctic neighbour, Ireland is exposed to the effects of a warming ocean, such as rising sea levels, increasing storm intensity and changing marine ecosystems. Scientists based in Ireland can make a real and meaningful contribution to Arctic research, and help to develop and implement adaptation responses from local to global scales. The Marine Institute is delighted to be supporting a network which will foster impactful research into the causes, manifestations and impact of Arctic change.”
Since 2018, the Embassy of Ireland in Oslo and the Marine Institute have sponsored early career researchers to attend the Arctic Frontiers Emerging Leaders. It is an annual program held in Tromsø, Norway, which brings together approximately 30 young scientists and professionals from around the world with interests in Arctic security, Arctic economy and Arctic environment.
 The Marine Institute and Dept Foreign Affairs have launched an informal Arctic researchers network
The Marine Institute and Dept Foreign Affairs have launched an informal Arctic researchers network
Ciara Delaney, Regional Director at the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, said: “The Department of Foreign Affairs is delighted to host today’s round-table meeting of Irish-based Arctic researchers. Given the impact of climate change and the increasing relevance of strategic developments in the Arctic, the Arctic region is of growing importance to Ireland. A previous roundtable meeting in 2019 demonstrated considerable interest for the establishment of a national network of researchers to identify and take forward areas of common interest on Arctic issues. Building on this initiative, we are delighted to officially launch the new Network, together with the Marine Institute of Ireland. I hope that NARI can contribute to developing a strong, research-led, evidence base for Ireland’s growing engagement with the Arctic region.”
The new all-island network (NARI) brings together multidisciplinary scientists from the National University of Ireland Galway, the University of Limerick, the National Maritime College of Ireland, Cork Institute of Technology, Queens University Belfast, National University of Ireland Maynooth, University College Dublin, Trinity College Dublin and University College Cork.
Marine Institute’s 'Explorers Education Programme' Arrives in Dun Laoghaire Harbour
The children from Glenageary Killiney National School (GKNS) are participating in the Marine Institute's Pilot Explorers Education Programme™, hosted by the Irish National Sailing & Powerboat School in Dun Laoghaire this Friday. The programme complements the national school curriculum, presenting children with a deeper understanding of the impact of our ocean, climate change, conservation and a deeper understanding of living things that abound our shores. This programme is a pilot programme funded by the Marine Institute.
‘The children of 5th class in GKNS are delighted and excited to be taking part in this pilot programme, especially this year, as it is very relevant to our attempts to achieve the Green School Biodiversity Flag’ reports Ms Yates, class teacher of fifth class.
The children will participate in a sea safari on the beaches of Salthill and Sea Point in Dun Laoghaire examining marine life and studying the conservation aspects of the shoreline. They will discuss and debate ocean literacy and plan individual and group projects on their findings.
Fifth class hope to participate in The Marine Institute's Explorers Super Hero Pop Art & Creative Writing Competition which was launched by the Marine Institute on the 27 January and is open to all primary schools.
Marine Scientist Running in General Election Criticises "Unrealistic" Green Party Plan to Designate Up to 50 Per Cent of Irish Territorial Waters as Protected
A marine scientist running for the Social Democrats in the general election has described as “unrealistic” a Green Party proposal to designate 50 per cent of Irish territorial waters as marine protected areas writes Lorna Siggins
Wicklow councillor Jennifer Whitmore, who formerly worked for the Marine Institute before spending time in Australia, said her party aims to establish marine protected areas (MPAs) based on “scientific evidence and local community consultation”.
These MPAs would include “no-take zones”, while her party also favours developing a blue carbon strategy for identifying and protecting Ireland’s blue carbon sites, such as seagrass, kelp beds and salt marshes.
The Social Democrats are one of several parties seeking a ban on supertrawlers in Irish waters as part of election manifestos. Sinn Féin has prioritised a ban on supertrawlers but wants to see it extended to an EU-level restriction.
The Green Party also wants to ban offshore salmon farming and switch to “closed-loop” onshore salmon farms. It proposes that all processing plants and fishing vessels over an “agreed size” should be certified as sustainable by the Marine Stewardship Council, and it is seeking a ban on the practice of pair trawling.
The Green Party proposes to end oil and gas exploration and has set ambitious targets for offshore renewable energy.
Fine Gael has committed to ending licensing for oil exploration, and taking a phased approach to gas, while Solidarity-People Before Profit had spearheaded legislation to ban oil and gas exploration. The latter party also wants a ban on supertrawlers and support for conservation and sustainable commercial fishing. At local level, People Before Profit helped to establish the Save our Seafront campaign in Dun Laoghaire in 2002 to oppose commercialisation of the coastal rim.
Fine Gael has one of the lengthiest policies on the marine sector in its manifesto, much of which is drawn from the Government’s “Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth” strategy, including a commitment to “investigating the practicalities and merits” of establishing an offshore maritime area as Ireland’s seventh national park.
Fianna Fáíl priorities safeguarding Ireland’s interest in future EU-UK discussions on fishing, and promises to seek EU “Brexit contingency” funding for fishermen. It also promises to introduce an “Oceans Act “ to protect marine biodiversity and commits to reviewing the contentious Sea Fisheries and Maritime Jurisdiction Act.
Labour promises to set up maritime conservation zones and expand the Naval Service, while Aontú wants to retain the “status quo” in fishing as part of its rural policy.
The Irish Times writes, that a catastrophic storm during high tide will leave thousands of homes, businesses and landmark buildings in Dublin under water is inevitable over the coming decades, one of the country’s foremost climate change experts has warned.
Prof Peter Thorne said Ireland had been lucky to “dodge a bullet” until now during major storm events – because they have struck during low or neap tides – but it was only a matter of time until the elements combined for a devastating surge.
The Maynooth University academic, who was lead author on the fifth assessment report of the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, and is aged 40, said he expected a major high tide flood event in his lifetime.
In the capital this would mean water from Dublin Bay surging into the Liffey while it was in full flow from the Wicklow mountains.
More on this story by clicking here.
Peter Heffernan Says Farewell to the Marine Institute
Dr Heffernan has served as the CEO of the Marine Institute since 1993 and has held a highly successful role in building and leading the organisation. The semi-state agency has grown from a staff of one to 230, which now incorporates the Institute’s headquarters in Co Galway, the Newport Research Facility in Co Mayo and the Irish Maritime Development Office (IMDO) in Dublin.
Chairman of the Marine Institute Dr John Killeen said, “As CEO, Dr Heffernan has overseen tremendous growth. He has played a fundamental role in developing Ireland’s ocean research capacity, increasing collaboration in marine research and innovation in Europe, as well as driving sustainable development across a range of maritime sectors. Dr Heffernan leaves a lasting-legacy and has set the Institute on course to become a global leader in ocean knowledge. On behalf of the Board and Marine Institute staff, I thank Dr Heffernan for his dedication, strategic direction and leadership as CEO and wish him all the best as he begins a new voyage.”
As CEO of the Institute, Dr Heffernan has overseen the arrival of Ireland’s two purpose-built marine research vessels, the RV Celtic Voyager in 1997 and the RV Celtic Explorer in 2003. The RV Celtic Voyager has provided a platform for scientists to undertake essential fisheries research, environmental monitoring, seabed mapping, oceanographic work, data buoy maintenance and student training. The RV Celtic Explorer has played a vital role in Ireland’s fisheries research, placing Ireland in a much stronger position to propose effective conservation measures for fish stocks and support the sustainability of the Irish fishing industry. A new state-of-the-art marine research vessel is also scheduled for completion in 2022, which will mark a major milestone in the Marine Institute’s effort to provide world-class marine scientific advice and services.
In 2009, Dr Peter Heffernan instigated the development of the Inter-Department Marine Coordination Group (MCG). Chaired by the Minister for Agriculture, Food and Marine, the group brought together representatives of departments with an involvement in marine and maritime issues to coordinate inter-departmental action. The MCG produced Ireland’s first integrated marine plan for Ireland Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth in 2012 which set out two targets - increase the value of Ireland’s ocean wealth to 2.4% of GDP by 2030 and double the turnover from our ocean economy (from €3.2 billion) to exceed €6.4 billion by 2020. In 2018, Ireland’s ocean economy is estimated to have a turnover of €6.2 billion and GVA estimated at €4.2 billion equivalent to 2% of GDP.
In 2013, Dr Heffernan acted as an inspiration and Irish EU Presidency ambassador for the creation of the Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance (AORA) with the signing of the Galway Statement on Atlantic Ocean Cooperation between Canada, the European Union and the United States of America. Six years on and AORA has been recognised as an outstanding success story in the Atlantic area and an exemplar of international science diplomacy. To date, AORA has achieved an investment from Horizon 2020 EU funding of more than €140 million to support research in the Atlantic Ocean.
Ireland is now considered a world leader in the field of seabed mapping through the expertise of the Geological Survey Ireland and the Marine Institute. The Irish National Seabed Survey (INSS), which began in 1999 remains one of the largest seabed mapping projects ever undertaken in the world. Now known as the INFOMAR programme and scheduled for completion in 2026, Ireland will become the first nation in the world to have comprehensively mapped its entire seabed territory.
Research and Innovation are central to the role and mission of the Marine Institute. A Marine Knowledge, Research and Innovation Strategy for Ireland, ‘Sea Change’ was prepared by the Marine Institute and launched in 2007. A new National Marine Research and Innovation Strategy 2021 was also prepared by the Marine Institute in 2017, to help ensure Ireland maintains its position at the forefront of marine research in Europe.
The Marine Institute has achieved an outstanding success rate of over 40% in funding bids to the European Union’s Horizon 2020 programme. The total funding approved to date under this programme has now surpassed the €8m target, 18 months ahead of schedule. The work of the Marine Institute has seen significant collaborations with industry and other research centres and universities in Ireland, Europe and international stakeholders, strengthening Ireland’s ability in providing a foundation for applied research and innovation.
Dr Heffernan was recently selected as a member of the European Commission’s Mission Board for Healthy Oceans, Seas, Coastal and Inland Waters, one of five major research missions of Horizon Europe, the EU Research and Innovation programme (2021 – 2027). Dr Heffernan will be one of 15 experts on the Mission Board which will identify the first possible specific missions on healthy oceans by the end of 2019.
Two centuries after the “white continent” was recorded officially for the first time by an expedition led by Irishman Edward Bransfield, Kerry round-the-world offshore racer Damian Foxall plans to explore Antarctica by sail.
Kerry-born Foxall will be accompanied on his “Team South” expeditions – which are open to the public - by marine biologists Lucy Hunt and Niall McAllister.
As The Irish Independent reports in its Review section today, the three highly accomplished sailors and scientists from Cork and Kerry will take their background in environmental education, research and adventure to head to Antarctica, to experience first-hand the impact of climate change and witness the fragile ecosystem inhabited by penguins, albatrosses, whales and seals.
"I look forward to stepping foot on the continent for the first time"
“Having been involved in over ten round-the-world races, I have seen the southern ocean and the world in a way that few get to experience - icebergs, albatross and forgotten sub-Antarctic islands,” Foxall says.
“ I look forward to stepping foot on the continent for the first time and to sharing this unique privilege with my team and our guests,” he says.
The trio will work with Quixote Expeditions, skippering the 65ft ketch, Ocean Tramp. The Antarctic expedition company has an ethos of community collaboration, education, scientific research and minimal footprint.
When not offshore racing,Foxall is a passionate adventurer and advocate for ocean health, while Niall MacAllister, who runs marine wildlife expeditions and sail training in west Cork, has recently been skippering on the research sailing sloop, Song of the Whale, for a series of marine mammal research programmes.
Lucy Hunt created the ocean health education programme for the Volvo Ocean Race 2017/18 and is now working on the new programme for 2021/22 Ocean Race, while directing her Sea Synergy marine education and awareness centre in her native Waterville, Co Kerry.
The trio has linked in with ornithologist and Antarctic guide Jim Wilson and polar explorer enthusiast Eugene Furlong, who are involved in the project to commemorate Edward Bransfield in his native Ballinacurra, Co Cork, in January 2020.
Team South expeditions start at 9,000 US dollars per person for two weeks, excluding flights. Photographers and film crews are among early bookings, and there is availability on some legs for equally curious citizen scientists and adventurous types, who won’t need much sailing experience.
The five consecutive expeditions start in December and end in March, and the last leg of the journey includes sailing the Antarctic Peninsula before crossing the Drake passage to the Falkland Islands.
A free berth is awarded each trip to a research scientist throughout the southern summer season which runs from November to March. More details are here
Read more about Team South and about Edward Bransfield who put Antarctica on the map in The Irish Independent here
Citizen science pinpointed the first samples of a rare kelp in Irish waters, and now NUI Galway researchers are hoping that sea swimmers, divers and kayakers may help to find more writes Lorna Siggins
Samples of golden kelp (Laminaria ochroleuca), which is normally found in France, Spain and Britain, were identified for the first time almost a year ago in north Mayo.
The small population was discovered in Scots Port cove on the north-west facing Belmullet coastline, and recognised by Dr Kathryn Schoenrock of NUI Galway’s (NUIG) Ryan Institute.
The dominant kelp species found in Irish waters is Cuvie (Laminaria Hyperborea), and five main types of kelp provide important habitats for marine life.
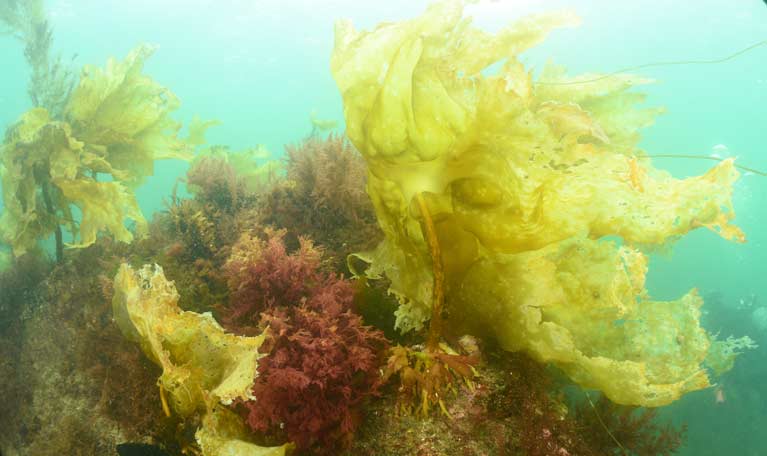 Photo of sample of golden kelp found for first time last year in Irish waters in north Mayo - NUI Galway researchers appealing to citizen scientists to help locate more examples. Photo: Dr Kathryn Schoenrock, NUI Galway
Photo of sample of golden kelp found for first time last year in Irish waters in north Mayo - NUI Galway researchers appealing to citizen scientists to help locate more examples. Photo: Dr Kathryn Schoenrock, NUI Galway
“Golden kelp, which harbours less biodiversity, is a really important species in Spain and Portugal,” Dr Schoenrock explained.
“We would have expected to find the first samples here on Ireland’s south-east coast, given the proximity to Britain, France and Spain,” she says.
Scots Port is located 1,040 kilometres away from the nearest golden kelp population in Britain, and 1,630 kilometres away from the nearest population in France.
Genetic analyses would suggest that the Co Mayo population is more diverse than the British, resembling the richness described for populations in the Iberian peninsula, Dr Schoenrock said.
“The fact that it was found in a small enclosed cove in north Mayo may be a result of a Portuguese or Spanish vessel sheltering nearby,” she says.
“However, it can drift long distances and it could be more prevalent than we know.”
The samples found by citizen science participants in a Searsearch Ireland and Porcupine survey trip were collected by Dr Stacy A Krueger-Hadfield for genetic analysis at the University of Alabama at Birmingham in North America.
The discovery was the subject of a study which had recently been published in the scientific journal, Marine Biodiversity Records.
Dr Schoenrock said that citizen science initiatives like Seasearch Ireland and Coastwatch are an “excellent way to involve local communities that have a vested interest in the health of these ecosystems”.
“In conjunction with existing research bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), National Parks and Wildlife Services, and the Marine Institute, we need more programmes that can sustain long term ecological research of shallow marine systems over many years,” she said.
Seasearch Ireland national co-ordinator Tony O’Callaghan said that its participants had collected over 50,000 records of over 1,000 species.
He said the data set is “the best continuous record collected since the last major state-funded study of Ireland’s inshore marine environment, the Biomar survey, which was in the 90s.”
This project is funded under the EPA Research Programme 2014-2020.
Given that golden kelp has much lower biodiversity than native kelp forests, it is more suitable kelp to harvest, Dr Schoenrock noted.
“It can grow to a larger size and it doesn’t dominate habitats yet in Ireland,” she said.
State approval in November 2017 of a license to harvest native kelp by mechanical means in Bantry Bay has aroused opposition on environmental grounds in West Cork and resulted in ongoing litigation.






































































