Displaying items by tag: Achill Island
The past weekend’s good weather tempted a group of jet-skiers who subsequently ran into difficulty in Clew Bay, as The Irish Times reports.
Achill Island RNLI launched its lifeboat on Saturday evening (25 April) to reports of three men on personal water craft needing assistance between Newport in Rosmoney — waters considered treacherous for even the most experienced of mariners.
All three were towed to Rosmoney with a locally owned RIB in an operation that also involed the Irish Coast Guard and An Garda Síochána.
Gardai also mounted further patrols of Lough Derg, where earlier this month they had exercised their emergency powers to warn inland waterways users to stay at home as measures to control coronavirus remain in place.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Achill Island Beach Rated Among The Best In The World
Keem Bay on Achill Island has made the grade among the 50 best beaches in the world, according to a top travel website.
And as The Irish Post reports, the Co Mayo coastal beauty spot was ranked among the best even of that number, placing just outside the top 10 of Big 7 Travel’s selection.
Keeping company with the gorgeous turquoise waters of the Adriatic and eastern Mediterranean, the West Indies and other breathtaking tropical paradises, we think that’s good going for the Wild Atlantic Way.
One of the world’s largest sharks had become a regular visitor to an Achill Island beach, as Independent.ie reports.
Local tourist officials have recorded almost daily sightings of the 20-plus-foot basking shark in the waters of Keem Bay over the last month.
And has word of got out, visitor numbers on the Co Mayo island are growing among those hoping to get a glimpse of the gargantuan fish.
The second biggest fish in the seas behind the whale shark — and the largest in the North Atlantic — basking sharks are regulars in Irish waters.
Indeed, number of the gentle marine wildlife giants have reached such figures that experts have referred to the waters off the West Coast in the summer months as a ‘shark ark’.
Independent.ie has more on the story HERE.
Kitesurfers Clash On Achill Island In ‘Battle For The Lake’ This Weekend
#Kitesurfing - Independent.ie has the lowdown on this weekend’s Battle for the Lake kitesurfing extravaganza on Achill Island.
Keel Lough is the venue for the finale of the 2018 IKSA tour that will see many of the same competitors that wowed the crowds during the Battle for the Bay on Dollymount Strand this past summer.
Also bringing his skills to this eighth Battle for the Lake is Kevin Langeree, Red Bull’s King of the Air, who will be giving demonstrations on the lough and even DJing for fans after dark.
Indeed its the festival atmosphere around the competition that’s as much of a draw to Mayo from today (Friday 28 September), with a packed music and comedy lineup — even fire dancers to light up the nights.
Independent.ie has more on the story HERE.
Training For Achill Islanders In Seal Rescue Protocol
#MarineWildlife - Islanders’ attempts to rescue a seal pup stranded on Achill in Co Mayo recently were sadly not successful.
But the incident has galvanised a local group set up amid growing concerns over marine wildlife strandings, who will train with a team from Seal Rescue Ireland in January on potential lifesaving measures, as the Mayo News reports.
“We’re getting these trainers down just so people know what to do in these situations,” said Achill resident Sorsha Kennedy. “It’s okay for them to be on the shore, they may just be resting, but people don’t know that.”
Kennedy was part of a group that attempted to rescue a baby seal washed up on rocks at Keel Beach in late November.
The pup unfortunately died in transit to Seal Rescue Ireland’s base across the country in Courtown.
“It’s a terribly long stressful journey for an animal already in distress,“ said John Nikolai, who discovered the seal while walking his dog. “It’s such a pity there isn’t another sanctuary closer in the west.”
The Mayo News has more on the story, while Afloat.ie reported recently on other seal rescue efforts around the Irish coast.
Achill Reaffirms its Status as Ireland’s Largest Island with the Help of Mayo Sailing Club
The Michael Davitt Bridge that connects Achill Island to the mainland was officially opened by leading Irish land reformer Michael Davitt on 31st August 1887, making 2017 its 130th anniversary. Construction began on a replacement Michael Davitt Bridge in 1948, and was completed a year later writes Daria Blackwell
The third Michael Davitt Bridge, which was commissioned in 2008, was a design based on a Spanish Calatrava architectural model. This swing bridge weighs 390 tons, yet it is operated manually. It’s illuminated by LED lighting integrated into the bridge design, and in the long winter nights of West Mayo, this adds to its sense of permanence.
 The Michael Davitt bridge at Achill Sound has an air of permanence about it, but that small central span can be opened, albeit with difficulty
The Michael Davitt bridge at Achill Sound has an air of permanence about it, but that small central span can be opened, albeit with difficulty
And the fact is, the 2008 bridge has been rarely opened since it was built. It had been too difficult to close, so it was decided that it would be better not to open it in the first place. The sheltered theoretically-available through-transit by boats with a high air-draft via narrow and tidal Achill Sound, while not actively discouraged, was certainly not promoted as a passage-making option.
This caused a dilemma for the islanders, for when it comes to Government grant aid, an island is not an “island” if connected by a fixed bridge. A long battle with the State has been ongoing since, with the Achill islanders demanding that the bridge be shown to be openable again, and this finally happened this past weekend.
 Achill Island is big country, a challenging island to sail round
Achill Island is big country, a challenging island to sail round
To mark the connection choices that Achill maintains with the mainland, a Maritime and Heritage Festival celebrating the past and present of the Achill Parish was held on Sunday the 3rd of September. As part of the festival, the bridge was scheduled to open at 5:00 pm to allow a parade of ships to pass through at high water.
Mayo Sailing Club was invited to take part. Members of the Club accepted the invitation and seized the opportunity to go one step further and circumnavigate Achill Island. Wallace Clark had written about it in Sailing Round Ireland and several members of MSC were inspired to attempt the challenge, as it had not been done in recent memory.
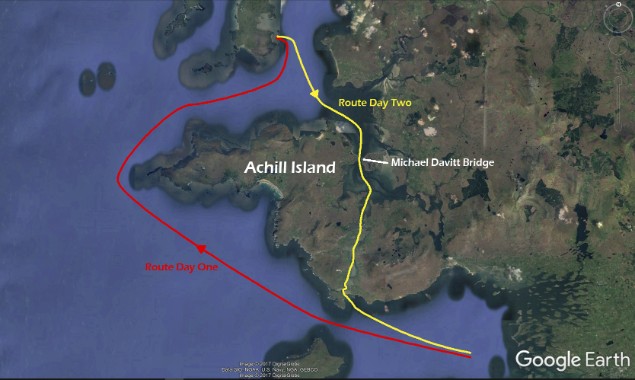 The route taken by the Mayo Sailing Club fleet at the weekend
The route taken by the Mayo Sailing Club fleet at the weekend
The currents in Achill Sound run strong and swift, and shoaling is common. Mayo Sailing Club Vice Commodore Duncan Sclare organized yachts to sail from Rosmoney in a clockwise manner so they’d have a rising tide coming south through Achill Sound and still have enough water to exit the Sound beyond Corraun back into Clew Bay to return to their moorings in Rosmoney.
Navigational calculations were meticulously plotted, tides accounted for, fishermen consulted, and charts checked, as the fleet prepared to set off on the Saturday from Rosmoney. Five yachts set off on the circumnavigation. This was no small feat, as conditions on Saturday were demanding. A rough, wet and boisterous rounding of notorious Achill Head was in store for the fleet, which was subjected to 40+ knots of gusts of wind tearing down Slievemor, the second highest peak on Achill Island at 671 metres. They sought shelter for the night and holed up securely at anchor in Blacksod Bay, where good company and cold beer went down well in the pub.
 The Mayo SC fleet safely through the bridge despite the fog, and already on their way south as the tide is ebbing. Photo: Alex Blackwell
The Mayo SC fleet safely through the bridge despite the fog, and already on their way south as the tide is ebbing. Photo: Alex Blackwell
They set off in the morning to arrive at the bridge just before its scheduled opening, but a thick fog enveloped Achill and Achilbeg. Yet the project continued, even though two deeper draft vessels ran aground on the way in and had to await the incoming tide to continue on. When the time came, all five of the Achill circumnavigators succeeded in passing though the bridge, dressed for the occasion. A sixth member joined the fleet, passing under the bridge from the south and returning with the fleet, accompanied by Coast Guard vessels, rowers, and ribs, and a flotilla of the famous traditional Achill yawls making spectacular transits under sail.
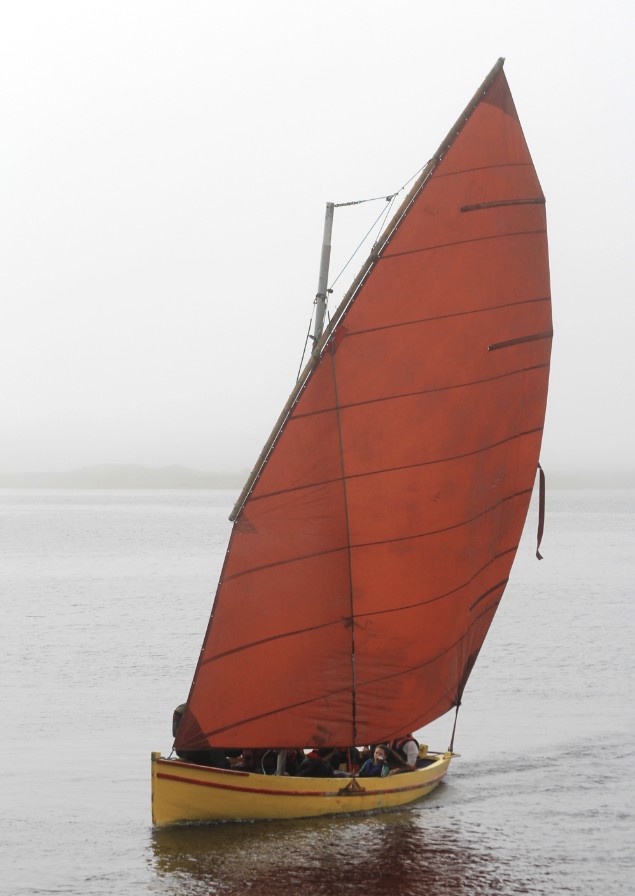 Last boat through – an Achill yawl sweeps towards the narrow gap at good speed with the sluicing tide under her…... Photo: Alex Blackwell
Last boat through – an Achill yawl sweeps towards the narrow gap at good speed with the sluicing tide under her…... Photo: Alex Blackwell
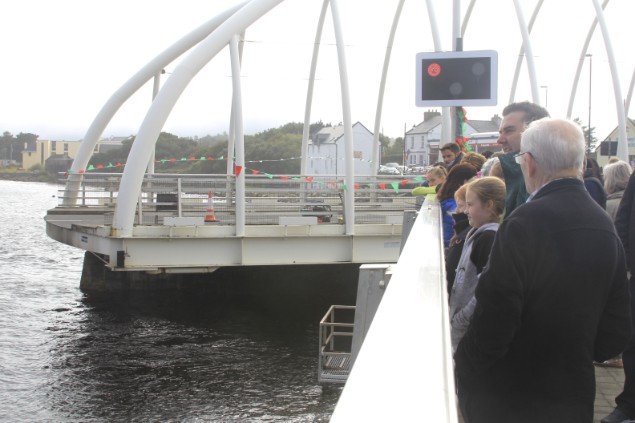 …..and almost immediately the bridge closes again………Photo: Alex Blackwell
…..and almost immediately the bridge closes again………Photo: Alex Blackwell
 ....with the MSC fleet still in fog as they disappear down the Sound………..Photo: Alex Blackwell
....with the MSC fleet still in fog as they disappear down the Sound………..Photo: Alex Blackwell
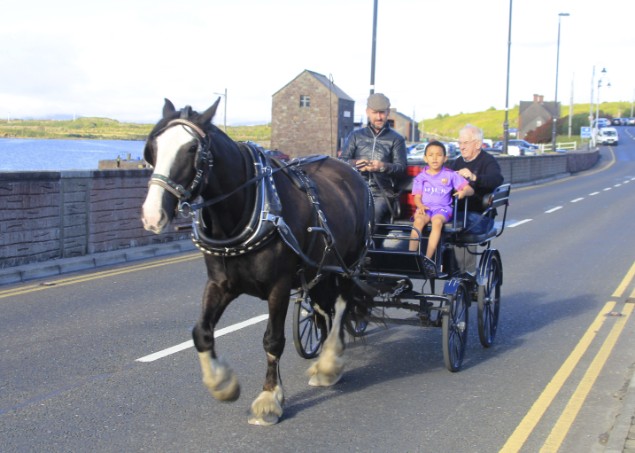 …..but back at the reinstated bridge, the sun is out, and shore transport becomes dominant once more. Photo: Alex Blackwell The crowd cheered from the bridge as each vessel passed through, and the Achill yawls then had a race in the Sound close south of the bridge in front of Alice’s Restaurant, complete with loudspeaker commentary as the evening weather finally improved for the fog to lift, and let sunshine illuminate the spectacular landscape. The day’s events were recorded by Henry McGlade for the TV show “The Irish at Home and Abroad” for an episode due to be shown on Sky TV in early October.
…..but back at the reinstated bridge, the sun is out, and shore transport becomes dominant once more. Photo: Alex Blackwell The crowd cheered from the bridge as each vessel passed through, and the Achill yawls then had a race in the Sound close south of the bridge in front of Alice’s Restaurant, complete with loudspeaker commentary as the evening weather finally improved for the fog to lift, and let sunshine illuminate the spectacular landscape. The day’s events were recorded by Henry McGlade for the TV show “The Irish at Home and Abroad” for an episode due to be shown on Sky TV in early October.
 The evening sunshine strengthens as the fog continues to lift, and yawl racing gets under way in the Sound. Photo: Alex Blackwell
The evening sunshine strengthens as the fog continues to lift, and yawl racing gets under way in the Sound. Photo: Alex Blackwell
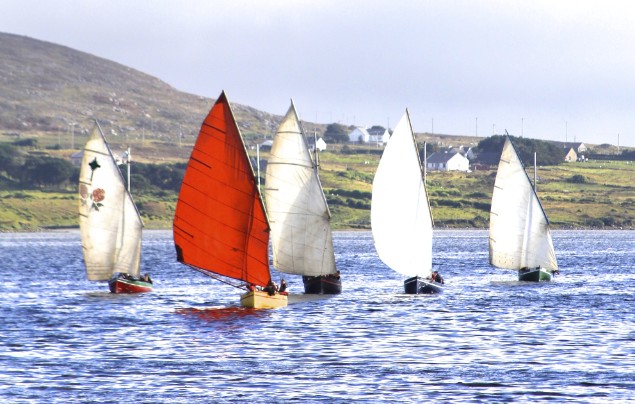 Achill yawl racing at its best – this is going to be a cracker of a finish. Photo: Alex Blackwell
Achill yawl racing at its best – this is going to be a cracker of a finish. Photo: Alex Blackwell
But by the time the weather improved, Mayo SC fleet were well on their way, their movements dictated by the now rapidly falling tide, and it wasn’t until they were out on Clew Bay itself that the visibility began to clear properly for them, and the familiar sight of the peak of Croagh Patrick showed above the fog’s grey blanket.
Back in Mayo SC’s hospitable clubhouse at Rosmoney, Former MSC Commodore Rory Casey of the First 31.7 As Lathair commented: "One of the best sailing weekends I've ever had - we had a bit of everything. Why do we have to travel to the ends of the world, when we have this adventure sailing here on our doorstep?"
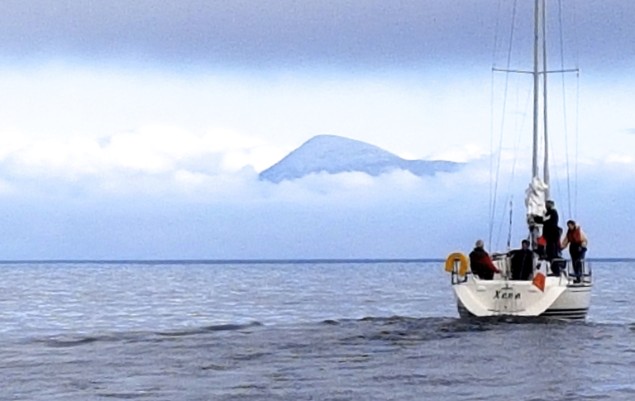 Out on the open waters of Clew Bay, it took longer for the fog to lift, but the MSC fleet got the reassuring sight of Croagh Patrick above the fog blanket as they headed for home after a successful weekend circumnavigation of Achill Island. Photo: Rory Casey
Out on the open waters of Clew Bay, it took longer for the fog to lift, but the MSC fleet got the reassuring sight of Croagh Patrick above the fog blanket as they headed for home after a successful weekend circumnavigation of Achill Island. Photo: Rory Casey
Vice Commodore Duncan Sclare, who made the circuit on one of the smaller boats, the Achilles 30 Freebird, summed it up: "On this circumnavigation of Ireland’s largest island, we experienced it all: Flat calm, Atlantic seas, howling winds, rain, sunshine, fog, tricky navigation, an unopenable bridge that opened, and great company. A voyage that will be remembered a lifetime."
The Mayo Sailing Club boats whose crews now cherish very special memories of the first weekend of September 2017 in proving that Achill is indisputably an island were: Freebird, As Lathair, Xena, Misty, Enya, and Eabha Marie.
Achill Beach Returns After More Than 30 Years
#CoastalNotes - A beach on Achill Island lost to storms 33 years ago has returned after a freak Easter tide.
And locals at Dooagh are celebrating the return of their 300-metre sandy strand that in more recent years has been bare rock, as the Guardian reports.
It’s believed a wintry cold snap in mid April, with winds from the north, led to the surprise sandy deposit — one that’s already boosted tourism in the area, part of the Wild Atlantic Way coastal route.
The Guardian has more on the story HERE.
Crude Oil ‘Tar Balls’ Mar Achill Beach
#CoastalNotes - Achill Island has been blemished by ‘tar balls’ that washed up on its Blue-Flagged Keel Beach during the week, as The Irish Times reports.
Appearing as black stones from a distance, the blobs of crude oil are soft and extremely sticky to the touch.
But despite being the result of oil leaks at sea, such tar balls are considered relatively harmless, according to the Irish Coast Guard.
The news comes less than a month after Fingal County Council warned of palm oil ‘fatbergs’ washed up on a Skerries beach.
Similar fatty deposits were found on beaches in Mayo last November.
Coast-To-Coast Cycle To Raise Funds For Achill Island Lifeboat
#RNLI - A coast-to-coast cycle starting in England and finishing in Co Mayo next month will raise funds for Achill Island RNLI.
Jane McNeela and Ursula Murray from Preston will undertake the Coast to Coast Bicycle Ride as part of the RNLI’s Mayday fundraising campaign.
The duo will leave Preston in Lancashire on Saturday 9 May and will spend the next five days cycling westbound across Ireland and deep into Mayo.
Friends for 13 years, the cyclists share a love for adventure and the great outdoors. Their previous endeavours include climbing the highest three peaks in the UK, fire walking and cycling from London to Paris.
But their latest endeavour has a personal twist, as McNeela is already familiar with the West of Ireland, having family connections in the Mayo town of Ballycroy.
The programme begins with a 120-mile cycle from Preston to Holyhead in Wales on Saturday 9 May and then, after a ferry trip to Dublin Port, another cycle to their hotel in Dublin.
On the Sunday they will cycle to Mullingar, while on the Monday they will move on to Strokestown and from there onwards to Swinford on Tuesday. On Wednesday they will cycle to Tiernaur. On Thursday, they will take on the final leg of the journey when they cycle to Achill Island’s bridge before finishing up at Achill Island’s lifeboat station in Kildavnet.
Plans are afoot for a group of cyclists to support the duo on their final trip from Tiernaur to Achill on Thursday 14 May.
Following their mammoth trek, a presentation night will be held in Patten’s Lounge Bar in Derreens, Achill on Friday 15 May to show the RNLI’s appreciation for the efforts of the women and their supportive husbands, Mark and Greg.
Speaking ahead of their adventure, McNeela said: "We decided to take on this challenge for Achill Island RNLI because of an incident in the sea in Achill when my 13-year-old daughter got into difficulties because of a strong current.
"Though panic set in, prompt action by her friend saved the day before we needed to call on the RNLI but it made me realise how invaluable the lifesaving charity it is and it was reassuring to know that there was a lifeboat station in Achill if we had needed to make the call that day."
Anthony McNamara, chair of Achill Island RNLI's fundraising branch, said all at the station were "delighted that Jane and Ursula have chosen Achill Island RNLI to benefit from their coast-to-coast bicycle ride and we would encourage cyclists to join them in their final leg or offer support at any of the places they will stop in on their way to Achill.
"Our lifeboat crew relies on the generosity of the public to help them to continue to save lives at sea. From crew kit to training and fuel for our lifeboats, every penny and cent raised by this cycle will help us to continue to rescue people every day."
Achill Islanders Not So 'Keem' On Viewing Platform Plans
#IslandNews - A glass-floored viewing platform jutting out over the Atlantic Ocean on Achill Island has got officials excited about its potential to attract tourism.
But locals are concerned that the project could mar the area's special views with an eyesore.
As the Mayo News reported last month, funding has been secured to develop the so-called 'Signature Discovery Point' at Keem Beach on Ireland's largest coastal island.
Keem Beach is one of 35 locations along the Wild Atlantic Way in Co Mayo that will share in the €257 million funding pot.
And the ambitious plans for the area – that also features as part of the new Galway-Mayo Blueway – include a viewing platform over the waves and rocky shore near the old coastguard station, along the lines of the Grand Canyon Skywalk.
But the reaction among the Achill community has been mixed, with support for the initiative by development company Comhlacht Forbartha Áitiúil Acla tempered by comments from local sculptor Ronan Halpin, who expressed concerns over the "visual intrusion" and "sustainability" of such a unique engineering project.
“Keem Bay is one the most beautiful and unspoilt places in our country. Its isolation and seclusion are a major part of its inherent charm," he added. "The proposal to build a glass walkway at the top of Moiteóg would seem to fly in the face of all this natural beauty and majesty."
The Mayo News has much more on the story HERE.





































































