Displaying items by tag: Howth
Howth Plans Big Event for 2012 ICRA Nationals
ICRA – the 2011 Club of the Year – laid out its stall until 2014 at the eighth annual conference in Dun Laoghaire at the weekend and the momentum is already building at Howth Yacht Club (HYC) who stage the 2012 National Championships at the beginning of next season.
The country's biggest yacht club has a potential sponsor in the wings and Saturday's conference also heard from the Club's Norbert Reilly that HYC is adding feeder events around the two day championships from May 25/27 to double the attraction of the North Dublin venue.
The Corby Cup will be sailed the weekend prior to the Nationals (19-20 May) and the Irish sea offshore body, ISORA, will stage a feeder race from Conwy in Wales to Howth. Both initiatives will encourage UK boats to travel to Dublin for the ICRA series.
Typically the ICRA event attracts over 100 boats in four different classes.

In spite of a dip in the size of the Cruiser fleet in Howth in recent years local boats are still taking some of the big prizes nationally with Reilly's Crazy Horse the 2011 Volvo Dun Laoghaire and DBSC Cruiser Challenge winner and Pat Kelly's J109 Storm picking up the weekend conference's top 'Boat of the Year' prize.
Ashore there are plans to make the event family oriented and a 'ladies lunch' is also planned.
The weekend's ICRA conference decided to do away with the crew limit rule for the seven race series in Howth as the association focuses on getting more crews out on the water to enjoy cruiser racing.
The ICRA Nationals goes West for a return visit to Tralee Bay Sailing Club in June 2013 and in 2014 the National Championships will be staged by the Royal Irish Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire.
In the normal cycle of things 'the ICRAs' should be heading to the south coast again in 2015 but so far, the conference heard, the association is open to offers.
The 2012 ICRA Notice of Race for the Howth Championships will be available on Afloat.ie shortly
Howth Autumn League Race Three Results
Welsh Kayaker Sets New Irish Sea Crossing Record
According to Canoe & Kayak, last Saturday 2 October Anglesey man John Willacy crossed from Soldier's Point in Holyhead to Howth in Dublin - a distance of 55.8 nautical miles - in 11 hours 19 minutes and 59 seconds.
It's not the first open sea kayaking record set by Willacy, who last year broke the record for circumnavigation of the Isle of Man in 12 hours 38 minutes.
Lack of Wind Forces Cancellation of Howth Autumn League
This morning's second race of the WD 40 sponsored Howth Yacht Club Autumn League was cancelled due to lack of wind.
Howth Lifeboat Shows True Colours
Howth Lifeboat at 1800 hrs the night before the big match - inspite of our photograph we are assured that any Kerry sailors in difficulty on the Irish Sea this weekend will be treated the same as everyone else.
Meanwhile the last manager to lead Dublin into All-Ireland SFC battle has given his blessing to Pat Gilroy's troops as they seek to snare pre-match favourites Kerry and bring Sam back to the capital for the first time in 16 years.Dr Pat O'Neill has savoured the buzz around the city this week and feels "very confident" that the current team can emulate the All-Ireland achievement of his 1995 heroes. Up the Dubs!

Penfold Wins J24 Euro Title in Last Race Decider
Top of the table was 'Reloaded' (Mark Penfold), sailing under US colours, with 34 points, three ahead of the leading European entry 'Il Riccio' (Ian Southworth/Chris McLaughlin) which takes the European Championship trophy.
With the exception of their discard of a 20th in the fifth race, 'Reloaded' was consistently in the top four in most races and had one bullet, while closest rivals 'Il Riccio' had two bullets and only a 9th to discard.
That they had some 28 points to spare over the third placed 'Serco' (Bob Turner) emphasised their dominance over the series. The German champion 'Rotoman' (Kai Mares) was only a point behind in 4th place and won the final race of the regatta while Stuart Jardine, the oldest helm in the championship, had the distinction of winning three races, including the first two races of the final day. Another German boat 'Hungriger Wolf' (Johann Huhn) had six top ten results to earn 6th overall.
Local boat Jibberish (O'Kelly/Wormald/Walsh) enjoyed its best result when finishing second behind 'Stouche' (Jardine) in the seventh race while German entry 'JJone' (Frithjof Schade) was looking at the same transom in the eighth race. The Southworth/McLaughlin crew topped the fleet in the penultimate race followed by the Hungarian boat 'Naviscon' (Farkas Litkey) while 'Serco' took second behind 'Rotoman' in the final race.
Needing to beat their US rivals by several places in the last race to take 1st overall, 'Il Riccio' could only manage an 8th to 'Reloaded's' 5th.
The leading Irish crew was 'Hard on Port' (Flor O'Driscoll, HYC) in 10th overall with 'Jamais Encore' (John-Patrick McCaldin, Lough Erne YC) next best in 17th.
J24 Euros Open in Howth, Strong Winds Cancel Practise Race
The BMW J/24 European Championships were officially opened last night with a ceremony on the forecourt in front of the Howth Yacht Club clubhouse on the podium erected by the sponsor but a practise race scheduled for this afternoon was cancelled due to strong winds.
Last night's openning ceremony featured two top-of-the range BMW vehicles and a motorcycle and a backdrop with the highly appropriate phrase of 'Joy is Plain Sailing' in front of the national flags of the nine competing nations.
With an audience of competitors, supporters and club members, the speakers on the podium were introduced by the 'Master of Ceremonies', Club and Championship Press Officer Graham Smith.
First to speak was Derek Bothwell, Chairman of the Championship Organising Committee, and then the Commodore Roger Cagney addressed the large crowd who has assembled on the forecourt and balcony. They were followed by John Ives, Managing Director of BMW Ireland, the title sponsors, who spoke about BMW's global involvement in sailing, and then Niamh McCutcheon, President of the Irish Sailing Association, spoke on behalf of the ISA and the Irish Sports Council who supported the event.
Jim Farmer, President of the World Council of the International J/24 Class Association, spoke next, and the final speaker was the Mayor of Fingal, Cllr.Gerry McGuire, who welcomed all the overseas visitors to the county and officially declared the Championship open.
Team Echo Win Dublin Match Race Event
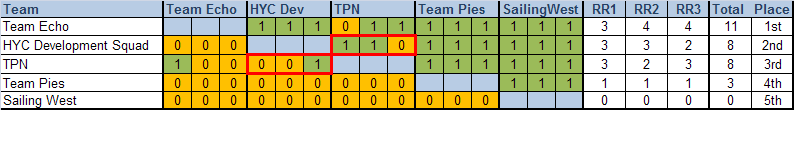
After a three round robin series organised by Howth Yacht Club, visting Team Echo, from Poole in Dorest, won Dublin's 2011 Match Racing Open. The team made up of Mark Lees, Toby Yeabsley, Mark Yeabsley and Peter Austin convincingly won the Investwise sponsored series, sailed in J80s with 11 wins and one loss.
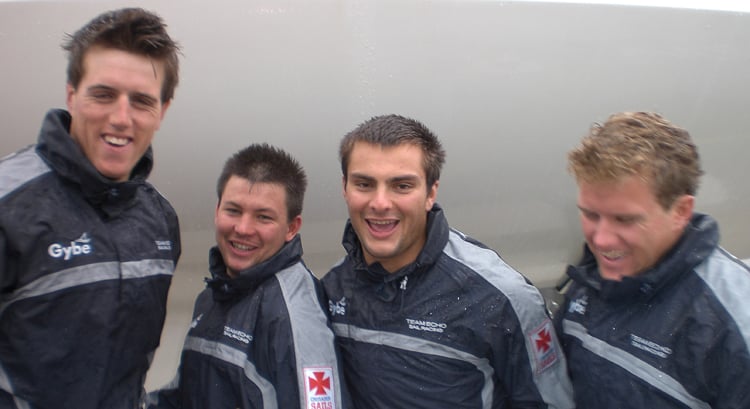

Team Echo won the Dublin Match Racing Open
In the second race an unfortunate incident where bowman Peter Austin cut his leg disrupted the usual momentum of the team. an Irish Match racer kindly stepped in as a substitute for the remainder of racing one the first day and regular mainsheet trimmer Toby Yeabsley stepped in as bowman while Peter went to be treated in hospital.
A tie break was required to split the home clubs team - consisting of evelopment squad members skippered by Ryan Scott - from Peter Bayly and Team PN, with the HYC Development Squad taking second 2 wins to 1. Peter showed glimpses of what he can do, the only skipper to take a race form the British team.
Alistair Kissane and Team Pies finished fourth and Audrey Adamson with SailingWest Ladies finished fifth.
Dun Laoghaire's Jay Bourke Wins Etchells Title
It was tight in points at the top end of the Etchells Nationals in Howth in the last weekend of August.
After a protest was resolved Jay Bourke's Northside Dragon from the Royal St. George Yacht Club won on countback from Royal Corinthian visitor Palaver with Dan O'Grady's Kootamundra third.
The top 3 Overall ...
1st Northside Dragon J Bourke RStGYC 10 pts
2nd Palaver D Franks Royal Corinthian YC 10 pts
3rd Kootamundra D O'Grady HYC 12 pts
Squall Puts Paid to First Race of Star Europeans in Dun Laoghaire
Howth Race Officer David Lovegrove opted to send the 27-boat fleet back ashore ahead of the gale that was followed by torrential rain and squalls, a decision, say Royal St. George YC organsiers, that met with the approval of competitors from 17 nations.

Dun Laoghaire's Max Treacy and Anthony Shanks before racing was cancelled yesterday. Photo: Gareth Craig.
By 4pm though the gales and rain had dsisappered and sunny ideal 10-knot conditions returned to Dun Laoghaire, unfortunately just too late for the Stars to resume racing.
Fresh to strong conditions are expected to continue for the early part of the week. Two races are scheduled for tomorrow, starting at 11.30am.
Greath Craig's pics are below and more on the Afloat gallery here.






































































