Displaying items by tag: Marina Operators
Irish Marina Operators Association
Irish Marina Operators Association (IMOA), c/o Irish Federation of Marine Industries, Confederation House, 84–86 Lower Baggot Street, Dublin 2. Tel: 01 605 1621, fax: 01 638 1621, email: [email protected]
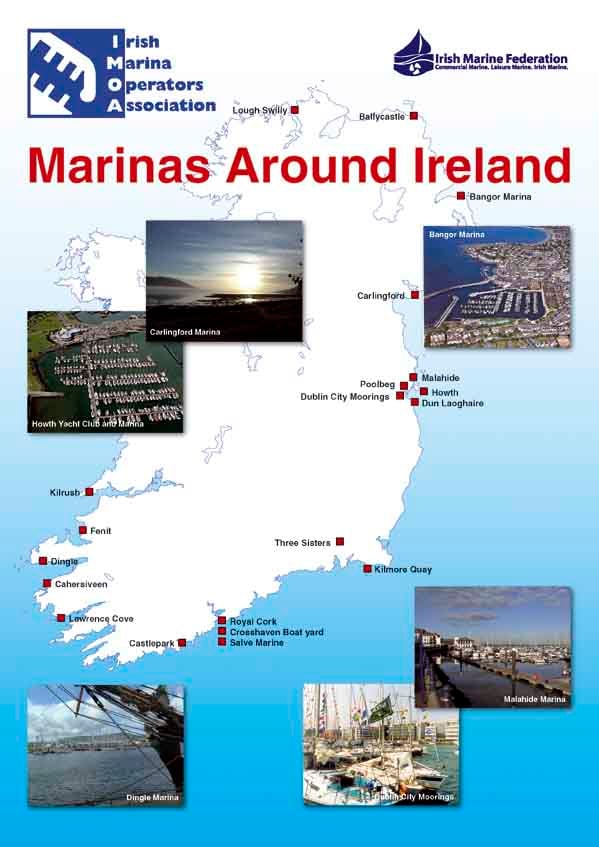
The Irish Marina Operators Association was founded in May 2003 and represents 23 of the coastal marinas around our shores. The IMOA is a self managing special interest group within the Irish Marine Federation, the trade association affiliated to IBEC representing the marine industry in Ireland. The IMOA elects its own representative board of directors, the chairman automatically having a seat on the main IMF board.
The objectives of the IMOA are to provide a forum for discussion within the marina industry in Ireland and to represent the views of the marina operators to government in regard to legislation, regulation, training, insurance and health and safety issues.
The IMOA is an effective lobbying body and has achieved some success in relation to approved waste management plans for marinas and also with the new Development and Foreshore Act. The objectives of the IMOA are to ensure that Ireland’s marina industry develops in a sustainable way and will eventually provide for a necklace of marinas around our coastline.
In the future the IMOA will seek to have our marina infrastructure effectively marketed overseas as part of an integrated marine leisure tourism campaign.
Regional Contacts
Chairman – Mr Damien Offer, Malahide Marina. Tel: 01 845 4129, email: [email protected]
East – Mr Hal Bleakley, Dun Laoghaire Marina. Tel: 01 2020 040, email: [email protected]
South – Mr Wietza Buwalda, Salve Marina. Tel: 021 483 1145, email: [email protected]
South West – Mr Brian Farrell, Dingle Marina. Tel: 066 9151629, email: [email protected]
West – Mr John Hehir, Kilrush Creek Marina. Tel: 065 9052072, email: [email protected]
North West – Ms Nancy Doherty, Lough Swilly Marina. Tel: 074 9360008, email: [email protected]
North – Mr Andrew Jaggers, Bangor Marina. Tel: 028 91453297, email: [email protected]




























































