Displaying items by tag: book review
'Irish Shipping Ltd- A Fleet History' Launched in Rosslare Harbour
#IrishShipping - A new publication 'Irish Shipping Ltd. – A Fleet History' as previously reported on Afloat.ie was launched recently with an official reception held in Rosslare Harbour.
More than 250 people attended the inaugural launch in the Hotel Rosslare which overlooks the ferryport. The publication was well received by the general public and critics alike and former ISL employee Capt. Jim O' Leary officially launched the long awaited publication.
It is anticipated that this book will be a great source of reference as well as telling the story of a very special shipping company. The promotional tour of the book continues with a launch taking place today in the Port of Cork Company's Boardroom at 6pm.
Also this week the National Maritime Museum of Ireland in Dun Laoghaire will be the venue on Thursday starting at 4pm. Appropriately another former ISL employee, Operations Manager Mr. Bill Lynch FICS, FCILT is to launch the book and again all are welcome to attend.
'Irish Shipping Ltd. – A Fleet History' involved around 5 years of research by the authors Brian Cleare, Leo Coy and brothers, Brian and John Boyce. They established the Rosslare Maritime Enthusiasts in 2004 and the group decided to proceed with the book venture following exhibitions on Irish Shipping Ltd in Rosslare Harbour and the National Maritime College of Ireland in Cork Harbour which attracted a combined attendance of over 2,500 people.
This is the RME's third publication, following the titles: 'Images of Rosslare Harbour' and 'The Ships of Rosslare Harbour'. They have received widespread respect in their field and much praise from renowned authorities in the maritime history sphere including the World Ships Society. Amongst the group are dedicated maritime historians, retired and serving seafarers, and local history experts.
In October 2012 the group established the Rosslare Maritime Heritage Centre which as reported is open to public on weekends.
Book Launch Tour: ‘Irish Shipping Ltd –A Fleet History’
#IrishShipping - The eagerly awaited publication 'Irish Shipping Ltd-A Fleet History' which traces every ship of the former state-owned shipping company, will be celebrated with an inaugural book launch this Friday in Rosslare Harbour, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The launch of the publication which covers the fleet from its humble beginnings in 1941 to its sad demise in 1984, is to be held in the Hotel Rosslare (22 Nov.) at 8pm.
All are welcome to the launch venue which appropriately overlooks the ferryport from where ISL's ferry division Irish Continental Line (ICL) ran routes to France. Among the ferries they run was the St. Killian which was notably lengthened in 1982.
Further book launches and signings are to take place next week, firstly in the Port of Cork Company's Boardroom on Tuesday (26 Nov.) at 6pm.
Two days later the book's promotional tour heads for another nautically apt venue, the National Maritime Museum of Ireland (NMMI) in Dun Laoghaire on Thursday (28 Nov.) at 4pm. The launch will be performed by the former Operations Manager in Irish Shipping, Mr. Bill Lynch FICS, FCILT, and again all are welcome to attend.
The authors, Brian Cleare, Leo Coy and brothers, Brian and John Boyce have spent the last five years researching and gathering material about the fleet that were mostly cargoships, bulk-carriers and a handful of oil tankers. All ships were named with the prefix 'Irish' followed by a species of tree, i.e. Irish Pine.
With over four hundred photographs, the publication is lavishly illustrated in covering every vessel of the fleet. Many of the photographs have never been published before.
This fine hardback (354pages) is priced €30.00 and will be an invaluable source of reference for many years to come. No doubt this new book will generate interest from former ISL seafarers, shore-staff and researchers. In addition to all those who hold dearly the importance of an Irish flagged merchant fleet and this unique period in our maritime history.
The authors as previously reported are also behind the Rosslare Harbour Maritime Heritage Centre and they will be holding additional launches nationwide, details made available upon confirmation. To keep track of book launches and of the centre visit the Rosslare Maritime Enthusiasts facebook page.
Irish Ferries – An Ambitious Voyage: History Recorded in New Book
#AmbitiousVoyage - Irish Ferries and the story of its involvement in the development of passenger and freight ferry services between Ireland, UK and Continental Europe is the subject of a new book entitled 'Irish Ferries – An Ambitious Voyage' .
The book distributed by Easons and on sale through bookshops around Ireland was written by noted marine historians Miles Cowsill and Justin Merrigan. The book is produced by Isle of Man based Ferry Publications.
The 150 page hard-back production traces the path that the Irish Ferries organisation has taken from its very earliest days operating services on the Irish Sea between Ireland and Britain under the B&I Line flag.
Detailed and comprehensive, the book goes on to chronicle the development of direct ferry services between Ireland and France and the role played by Irish Continental Line before that company and B&I line came together in the early-1990s to form the enlarged enterprise known today as Irish Ferries.
Covered in some detail is the ship building and modernisation programme carried out by the company which resulted in the commissioning of four new vessels for the company's Dublin-Holyhead and Rosslare-Pembroke Dock routes, including the cruise ferry 'Ulysses' which, at the time of its launch, was the world's largest car ferry.
Amply illustrated with pictures drawn from various private and company archives, the book is one that will appeal to all involved in shipping and maritime history.
Become A Book Investor of New Title: Irish Shipping Ltd – A Fleet History
#NewBook - A new book tracing every ship in Irish Shipping Ltd is due to be published in October.
The publication 'Irish Shipping Ltd-A Fleet History' is to cover the fleet from its humble beginnings in 1941 to its sad demise in 1984.
The authors, Brian Cleare, Leo Coy and brothers, Brian and John Boyce have done many years of research and gathered together over four hundred photographs covering every ship in the fleet. Many of the photographs have never been published before.
This fine hardback publication, with more than 500 pages will be a superb source of reference for many years to come.
After an initial launch in County Wexford, the authors will visit the ports of Cork, Dublin and Waterford to further promote the book.
As is usual with such a publication initial production costs are expected to be high. The authors are inviting one hundred people the exciting opportunity to become "investors" in the project.
For €100, each "investor" will receive a special, limited edition of the book. Their name will appear in ALL of the 1000 + books printed.
Each book will be signed by the authors and will have a special hand drawn sketch of an Irish Shipping Ltd vessel signed by the artist. In addition, each of these 100 books will have a special dust jacket and will be numbered 1 – 100.
If you would like to register your interest please contact the Rosslare Maritime Enthusiasts:
John Boyce 086 3934251 email: [email protected] Brian Cleare 086 1075057 email: [email protected]
Leo Coy 086 3103417 email: [email protected]
Please note that the last date for registration is less than a week away!... next Saturday 21st September
Mountains to Sea DLR Book Festival 2013 to Include Maritime Venues
#BookFestival – This year's Mountains to Sea dlr Book Festival 2013 starts today and continues through the week till next Sunday (8 Sept), writes Jehan Ashmore.
Among the venues showcasing the many events organised by Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown County Council (DLRCoCo) they are to include the National Maritime Museum of Ireland (NMMI) and Royal St. Georges Yacht Club.
So take a note of the busy festival programme (PDF) with an exciting and varied line up of authors, workshops and events for you. Keep up to date on Facebook and Twitter or by calling into the festival box office in the Pavilion Theatre on Marine Road.
The festival's publicity image features the Dun Laoghaire Harbour mouth entrance (all 232 metres wide) which is 'stacked' full of literary works. With such large books!... facing opposite Dun Laoghaire waterfront, it's little wonder that the county's major new Central Library & Cultural Centre headquarters currently under construction is to be considerable larger!... than the existing library.
The new facility will have a performance space with seating for 100 people, an art gallery, education workshop space and café. To read more about the new library (click here also for YouTube) to see the building develop in fast motion sequence.
The new structure stands next to the NMMI maritime museum housed in the former Mariners Church, where as previously reported is the Dun Laoghaire & the 1913 Lockout Exhibition.
This commemorative exhibition includes unique historic photos of Dun Laoghaire that dates back a century ago. The exhibition runs to 18th January 2014.
Mariners’ Church featured in New Life for Churches in Ireland
#MARINERS CHURCH – NEW LIFE for Churches in Ireland – Good Practice in Conversion and Reuse is the title of a new multi-authored publication. Among the diverse range of 17 case studies is the former Mariners' Church, Dun Laoghaire, which as the National Maritime Museum of Ireland was officially reopened in June by President Michael D. Higgins.
At the reopening President Higgins said "This magnificent old Mariners' Church is one of the few large mariner churches in the world. It is a beautiful building...it is great to raise awareness of our maritime heritage".
Writing about the former Church of Ireland place of worship, Peter Pearson details the history of the building erected in 1836 to the designs of Joseph Welland for the benefit of the many sailors who were based on Royal Navy vessels in the then new Kingstown Harbour.
Accompanying the case study are photographs including those taken by Jehan Ashmore on the day of the reopening to illustrate the building which underwent substantial conservation and renovation work (between 2005-2011) by James Slattery Architects.
Asides the Mariners' Church there are further case studies from throughout the island of Ireland, amongst them Elmwood Hall in Belfast, Carlingford Heritage Centre, Triskel Christ Church, Cork and St. Werburgh's Church, where last month the book had its Dublin launch.
Also featured are more modest but nevertheless important schemes, followed by a section featuring projects where work is underway but not complete. Schemes include the conversion of churches for domestic as well as cultural, commercial and community use. Each of these case studies are underpinned by an analysis of our ecclesiastical heritage, a flow chart to stimulate discussion on underused churches and an explanation of conservation principles and statutory responsibilities.
The 144-page publication is produced by the Ulster Historic Churches Trust and edited by Paul Harron. Among the other contributors are Edward McParland, Grainne Shaffrey, Patrick Shaffrey, Michael O'Boyle and Alistair Rowan. The book has a wealth of full colour photographs, drawings and illustrative material throughout.
Retail prices are €15 / £12 (softback) and €20 / £18 (hardback) and they can be purchased from the following stockists:
DUN LAOGHAIRE: Maritime Museum Gift Shop, National Maritime Museum of Ireland, Mariners'Church, Haigh Terrace (note: Open 11am-5pm Everyday)
DUBLIN: RIAI Bookshop / Irish Georgian Society (both on Merrion Square), Dublin Civic Trust, Castle St. (beside Dublin Castle) and St. Michan's Church office
BELFAST: Good Book Shop, Donegall St. (beside St Anne's Cathedral)
or available through Amazon.
ISBN: 978-0-9573791-1-4
Poolbeg Yacht Club to host Lecture on "Captain Bligh"
#LECTURE – Captain Bligh is the topic of the next lecture organised by the Dublin Bay Old Gaffers Association, held in the Poolbeg Yacht & Boat Club, Dublin Port on 20 November.
The illustrated talk (8pm) is to be presented by Sean Cullen, Senior Hydrographer, INFOMAR and whose predecessor was the Irish National Seabed Survey.
In addition limited copies of a new stunning publication "Warships, U-Boats & Liners - A Guide to Shipwrecks Mapped in Irish Waters" will be made available to purchase. The book which was launched today, showcases some of the more spectacular and important shipwrecks in Irish waters.
All are welcome to attend the DBOGA lecture programme noting there will be a door contribution for the RNLI.
Ordeal By Ice - Ships of the Antarctic by Rorke Bryan
It is hard to believe that for almost three centuries, explorers have been captivated by Antarctica, bewitched by her unbelievably tranquil yet savage cold. Can you imagine trying to survive in -83 °C & 250 km winds? Imagine a wind so cold it can freeze exposed skin instantly? Or having to face the gruelling voyage through the Southern Ocean broaching in 98-ft waves with frozen decks, insufficient wet wool clothing, horrible food, being guided by the stars through rocks, reefs, icebergs? Strangely, few ships were lost in these poorly charted waters. But many men starved en route or were lost in blizzards & never heard of again. Twenty-two of Shackleton's crew lived for five months under their upturned ship on Elephant Island. Yet Shackleton's famous recruiting poster 'return uncertain' attracted 100s of volunteers! These were brave men.
This extraordinary and lavishly-illustrated book is the first to explore all expeditions to the Antarctic & lead us on remarkable voyages of discovery. Ordeal By Ice is published to commemorate the 100th Anniversary of Scott and Amundsen's journeys to the South Pole in November 1911.
Cook's voyage in 1771 from Plymouth on Adventure completed the first West-East circumnavigation. However, ten crew were eaten by cannibals at Queen Charlotte Sound. Corkman Edward Bransfield sighted Antartica in 1820. But it was Scott's voyage with Discovery 1901-1904 that raised public awareness of the Blue Continent. In 1907-09 Shackleton's Nimrod Expedition nearly reached the South Pole 3 years before Amundsen. Scott's Discovery was the first ship built for Antarctic exploration, however it leaked & rolled badly & was poorly insulated. Had Charles Bonner not accidentally fallen to his death from the mast of Discovery waving goodbye to New Zealand, Tom Crean might never have joined Shackleton. He noted Shackleton's mood improved with the temperature of his cabin!

Charles Larsen's ship Antarctic got caught in ice & her crew were marooned on an ice floe. On his expedition to Antarctica, Douglas Mawson brought a Vimy Vickers monoplane with an air-tractor sledge. Wilhelm Filchner was forbidden by the Kaiser to go to the South Pole. There was mutiny when his ship became trapped in ice for the winter. Bellingshausen sighted the Antarctic in 1820, three days before Edward Bransfield but his voyage was not translated into English until 1945.
Rorke Bryan has been fascinated by the Antarctic since he was 8 years old & saw Scott of the Antarctic in The Metropole Cinema in Dublin. The son of a merchant mariner, he studied Natural Sciences in Trinity College Dublin and then he joined the British Antarctic Survey in the Falklands and spent three years at Base T on Adelaide Island. His work has brought him all over the world. He loves polar & maritime expeditions as well as sailing in the Baltic, climbing & cross-country ski-ing. He is married with a son and daughter who are following in their father's footsteps. Rorke divides his time between Canada & Galway & Sweden.
Book Review – Not all Elementary, My Dear Watson
#YACHT DESIGN – If weight, breadth, height and thickness are your primary concerns in evaluating a new book, then this is for you writes WM Nixon. If very high production values, with quality printing, impressive layouts, and the visionary use of a wide range of historic photos are high on your priorities, then this will get your approval. If an inspired text, elucidating many formerly tangled matters of interest in sailing and design history, and all set in a clearly in a comprehensive context which provides a superb socio-economic historical analysis of an important part of Scotland at the height of its maritime, engineering, scientific and industrial glory, then you'll delight in this. But if one of your special pleasures is browsing through a comparative display of properly presented sets of yacht designs, then you'll be disappointed – the few drawings shown in this otherwise magnificent book are little more than sketches used to illustrate changing design trends.
It may well be that the team involved in producing this masterpiece plan to bring out a book of Watson designs in due course – ideally, it might be of broader scope, taking in the designs of all the main Scottish yacht designers. Certainly if the large and varied selection of the more significant designs created by Watson himself, or together with his team as head of a busy drawing office, were included in this volume, then we'd have to think of having neat mini forklift trucks and strong lecterns available for all readers. As it is, it's a bonny baby, chiming in at a smidgin under 3 kilos, or 6lbs 8 ozs if you're in a maternity ward, and it's to the credit of those involved that they've kept it down to this weight, which permits an attractive posting and package service anywhere in the world.
So wherever you are, go for it. This book is right up there with the legendary Royal Cork history in terms of breadth and quality, and in terms of information in many arcane but relevant topics, it's in a league of its own. George Lennox Watson was a multi-talented individual who was the personal expression of Scottish creative and practical genius at its fullest flower. Anyone who thinks only of Glasgow as the place where they invented the deep fried Mars bar will find this work by Martin Black a surprise and a delight, and a cause for admiration of the huge technological and educational advances made by the people of southwest Scotland in the 19th and early 20th Centuries.
Watson died young, aged 53 in 1904. Yet although he was cut off in his prime, such was his contribution to design development at a time of rapid change that, years later, when the great Olin Stephens was asked who he reckoned was the greatest yacht designer of all time, the response was brief: "Watson, of course".
Because it was a magnet for those interested in industry and innovation, Glasgow in its expanding years was one of those places where the emerging Victorian middle classes were soon making their mark. New professions being delineated, and their areas and methods of work codified. Doctors were of course already on the scene, but rapid specialization in medicine saw new disciplines emerging within healthcare. Architects had their functions clarified, as did civil engineers, surveyors and a host of other new professions such as accountancy.
George Lennox Watson, born 1851, came from a well-established medical family, but his own interest was in the design side of the maritime world, and after a brief time as apprentice in the drawing office of a shipbuilding firm, he established his own yacht design office in 1873. He was still a very young man, and far from yacht design being comfortably established as a worthy profession in its own right, until he set up his firm virtually all yacht designers had been employed as in-house developer of design ideas, the employees of boatyards. The idea of a designer setting up his own office and acting as intermediary between owners and several yachtyards was novel – indeed, Watson may have been the first in the world.
It wasn't easy, and as he struggled to establish his firm, and in developing his knowledge of what makes a sailing boat fast, his painstaking and pioneering research was inevitably rather basic. Thus in his early days he tended to be conservative in outlook – he couldn't afford a flop, and he opposed any changes in rating rules which might make his research and his designs obsolete. But the interesting thing is that as the firm of G. L. Watson acquired a sound reputation in the hard-nosed world of Glasgow business, and the toffee-nosed world of big time international yachting, he became more innovative, indeed positively adventurous.
The late 1880s and early 1890s were the times of the most rapid change. The Watson office went from producing narrow-gutted straight-stemmed heavy cutters, briefly through a period of clipper-bowed lovelies, and then very quickly into boats which became personified by the extraordinarily beautiful Britannia, the 121ft cutter design by Watson and built on the Clyde by Henderson for the Prince of Wales, with Willie Jameson of Portmarnock in north Dublin in the honorary but key role of Owner's Representative throughout the building. Jameson was to be the successful amateur sailing master on Brittania for several seasons, and his friendship with Watson flourished until the letter's untimely death a decade later.
Britannia was a first class racer all her life, until George V – who loved the boat with a passion – decreed she should be scuttled on his death, and she was sunk south of the Isle of Wight in 1936. Her near sister Valkyrie II was owned by Lord Dunraven of Adare in County Limerick, whose enormous wealth is credited in this book to his business acumen in buying a hugely successful coal-field in South Wales. I'd been under the impression his acumen lay in marrying a young lady of Wales whose dowry included land which later turned out to be a coalfield, but no matter.
Be that as it may, Valkyrie didn't last as long as Britannia, she was sunk as a result of an epic collision (sadly, one man was killed) while racing in the Clyde in 1894 . But the point is, how is it that Watson's office, having been designing fast but very traditional and ancient-looking racing cutters up until 1890 and later, were suddenly in 1892 proposing these sleek very new-style boats, and seeing them launched in 1893? These wonderful yachts, which still seem modern to us, with their sweet easily driven normal hulls, elegant bows (dismised as "spoons" by conservatives at the time), and virtually separate deep keels. How come?

The sinking in the Clyde of Valkyrie II after a collision with Satanita in 1894
By this time the Watson office was a thriving concern, partly thanks to a huge business within it creating enormous steam yachts for the mega-rich on both sides of the Atlantic. With the need to churn out acres of design to meet many needs, innovative young designers were employed as draftsmen in what was a hotbed of creativity and novelty, and they were thus enabled to provide Watson with some very advanced concepts for his approval and development.
Thus some would argue that the prime mover in the Watson office's relatively sudden and very significant shift to more clearly delineated shallower hulls, and the initially much-derided spoon bows, was primarily a young draftsman employee called Alfred Mylne, who later, of course, established himself as a leading designer in his own right. But in 1892, he was still just an employee - anything that came out of the office had to be signed off by Watson himself.
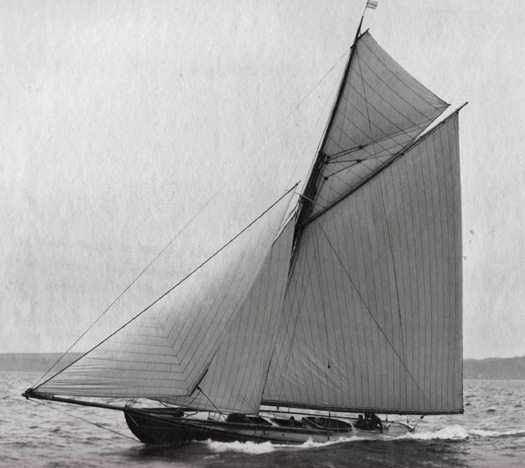

The 10 Rater Dora of 1891 marked a significant change in the shape of Watson's yachts
Though it may have been the 18-year-old Mylne who saw through the change with the first spoon bows for the new 2.5 Rater Ornsay in 1891, and more importantly, the much larger 10 Rater Dora which, like Ornsay, was additionally innovative in having a centreplate, it is a bit unfair of some partisan sailing folk in Scotland to claim that the sensational Britannia and Valkyrie in 1893 were actually designed by Alfred Mylne. However, this book does make the point that after his own work overload became evident in 1895, Watson entrusted all the design work on smaller yachts to Mylne, whom he regarded as his protégée.
The detail on all this and much more can be followed with interest and pleasure, thanks to the complete nature and thoroughness of this book, which does justice to a remarkable man. Watson was immersed in all aspects of design and business – his mantra was: "Straight is the line of duty, curved is the line of beauty'. It's a different spin on the comment by Gaudi, the eccentric architect of the fantastic Sagrada Familia cathedral in Barcelona, that "straight lines are for mankind, curves are of God".
On the business of yacht design, Watson commented: "The designing of cruising-sailing yachts provides a man with bread, that of racers with bread and butter, and that of steam yachts with bread, butter – and jam". But in addition to his main lines of work, Watson had a mission – creating effective lifeboats for the Royal National Lifeboat Institution, which he did for free. This work started in 1887, and by the time the designer died seventeen years later (of heart failure exacerbated by chronic rheumatoid arthritis) the Watson name was synonymous with the best lifeboats in the world, and he had seen the RNLI through, from rowing boats to rowing/sailing boats and then on to motor-powered lifeboats – a motor-powered prototype was being tested in 1904, the year of his death.
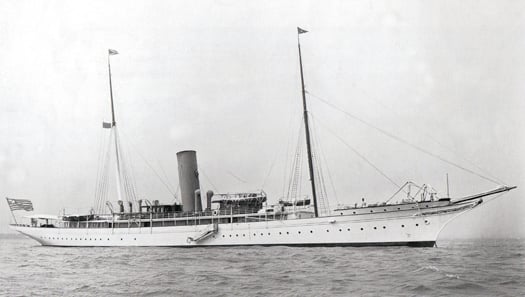
The jam on the bread and butter – in financial terms, the main part of Watson's business at its height was the design of elegant steam yachts for multimillionaires on both sides of the Atlantic. This is the 1266 ton Warrior designed for F W Vanderbilt in 1903
George Lennox Watson was a great and a good man, and this book is as much a worthy tribute to him as a man, as it is to his extraordinary talents as a yacht designer. The maritime community worldwide will be grateful to Hal Sisk, who has brought together the creative team to publish this extraordinary volume, and to Martin Black whose research and dedication have given us an exceptional insight into one of the giants of the already distant world of the late 19th and early 20th Centuries.
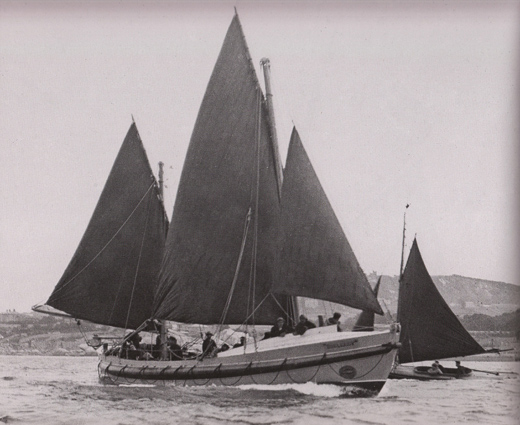

The personal mission. From 1887 until his death in 1904, G L Watson worked unpaid as the designer for the RNLI. This is Dunleary, the Kingstown (Dun Laoghaire) No 2 Watson Sailing Lifeboat, built by Hollwey of Dublin in 1898. She was in service until 1914, and saved 24 lives
G L WATSON
The Art and Science of yacht Design.
By Martin Black. 496 pages, fully illustrated, including many previously unpublished photos.
Published by Peggy Bawn Press, c/o Copper Reed Studio,
94 Henry St.,
Limerick
www.peggybawnpress.com
€89 inc p & p worldwide.
New Book On Titanic Captain Edward John Smith to Be Launched
· A detailed family history of the Captain, dispelling myths & gathering further stories to his tale
· His movements on that fateful night are tracked, explaining his actions and motives in detail
· Includes a wealth of previously unpublished and little known material
· Reveals the fascinating career of this seasoned captain, listing his White Star voyages in depth
· Original research drawing on ship's logs, crew lists, newspapers and first-hand accounts
· April 15th 2012 is the 100th Anniversary of the sinking of the Titanic
· Both author and Titanic Captain were born in Stoke-on –Trent in Staffordshire
· Seventy black & white illustrations are included







































































