Displaying items by tag: Dun Laoghaire Combined Clubs
Dun Laoghaire Yacht Clubs 'Welcome' 250m Limit on Cruise Ship Berth
Dun Laoghaire's Combined Clubs (DLCC) say in a joint statement that 'Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company lost its application to develop a facility for super-sized cruise ships'. The clubs have 'welcomed' yesterday's decision of An Bord Pleanala to limit any proposed development to accommodate a maximum size of cruise ship to 250m.
The DLCC represents the Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club, Dublin Bay Sailing Club, Royal Irish Yacht Club, Royal St. George Yacht Club, Royal Alfred Yacht Club and the National Yacht Club.
DLCC convenor Liam Owens says 'This removal of the threat of the supersized cruise ships secures the future of this premier location for the benefit of all Dun Laoghaire residents, watersports users, walkers and all those visitors and locals who value this historic amenity'
'We welcome the decision of An Bord Pleanala to limit cruise ships to 250m, similar to those ships already being accommodated in the Harbour and to which we have no objection', Owens says.
The DLCC statement 'regrets that the Board has overruled its Inspector’s conclusions that the proposed development was contrary to the National Ports Policy, and that the economic case for the development was not sustained'.
The statement contonues: 'We are very pleased that Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council, the future owners of the Harbour concurs with and has included a similar limitation in its Development Plan. We look forward to working with DLRCC to develop a National Watersports Centre in Dun Laoghaire Harbour as specified in the DLRCC’s Development Plan for the benefit of all'.
An Bord Pleanala is currently in process of hearing submissions - for and against - about the future of a proposed superliner berth in Dun Laoghaire which would change the harbour out of all recognition for recreational purposes, but could provide Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company with a new income stream, though only after massive investment.
Meanwhile, Dun Laoghaire/Rathdown County Council agreed on October 22nd in a requirement of their Development Plan that the harbour – which they will control in the future if proposed legislation can be completed and put in place – will be limited to berthing liners of not more than 250 metres in length. W M Nixon returns this morning to the continuing saga of Dun Laoghaire Harbour’s future.
It was only a snippet of news in the stream of maritime information which pours steadily through the Afloat.ie website, no more than a Tweet from Cllr Melissa Halpin on October 22nd confirming the 250 metre length limit’s approval. She was responding to Afloat’s review of ideas in an Opinion piece in The Irish Times by Dermot Reidy of Dun Laoghaire Combined Clubs, an active umbrella group which has put forward a detailed submission to An Bord Pleanala. And the DLCC’s proposals, as Councillor Victor Boyhan was delighted to report yesterday, also received the full support of the Council at their weekly meeting, this time on Thursday, October 29th. [see webcast of Special Meeting of the County Council on the Development Plan here – Ed]
The oral hearing will resume for its final public session on Monday 2nd November after taking a week’s break from October 23rd following the hearing of detailed submissions from many sources since October 14th. But it was typical of the way that so many organisations are involved – or would wish to be involved – in the future of Dun Laoghaire Harbour, that even as An Bord Pleanala was still taking evidence, the local council finally responded to the growing pressure from the Save Our Seafront group led by local politicians such as Richard Boyd Barrett TD and Cllrs Melissa Halpin and Victor Boyhan, and considered a motion to restrict the size of cruise liners which will be allowed to use Dun Laoghaire Harbour in the future.
It could be that it’s only a straw in the wind, for as Richard Boyd Barrett so tellingly explained to the hugely-significant protest meeting in the Kingston Hotel on September 7th, while there is a Government aspiration to transfer control of the administration of Dun Laoghaire Harbour to the local council, various legislative sleights-of-hand and some political and business manoeuvrings could still mean that in the end, the Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company’s commercial imperatives – real or imagined – could be the final controller of the agenda, with Dun Laoghaire/Rathdown County Council only in titular control.
Nevertheless, the DL/RCC’s new Development Plan’s inclusion of the stipulation that cruise liners coming to the harbour should not exceed 250 metres in length is a huge improvement on the unlovely 360 metre floating tenements which are currently envisaged in the Harbour Company’s plan. And when we actually get around to considering the sort of ship this will involve, and how she can be accommodated at a re-configured version of either St Michael’s Wharf or Carlisle Pier without any intrusive new structures in mid-harbour, then we realize we are indeed looking at something hopeful.

Photo imaging of a maxi-size 360 metre cruise liner in the proposed berth in mid-harbour in Dun Laoghaire, which would involved building a new 435 metre pier jutting far into what is currently clear water.
There are many 250 metre modern high quality cruise liners afloat today, and they occupy a sweet part of the upper end niche market which would provide the possibility of bringing Dun Laoghaire the kind of discerning cruise line passengers who might do the local economy a bit of real good over and above the basic income paid to the Harbour Company as berthing fees.
But by contrast, in the case of a giant liner of 360 metres, the berthing fees are pretty much the only income that will accrue to the local economy, as tenement cruise liner folk are not big spenders ashore, in fact many of them plan to do their entire cruise without spending one cent extra on the money they laid out to buy their ticket in the first place.
Such giant ships can be comfortably, conveniently and economically accommodated in Dublin Port, where the European Development Bank has just approved a €100 million loan to further develop the giant cruise liner berthing. All of which makes it even more absurd that Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company should be thinking of hunting in the same over-fished pool, when there is a different and well-stocked pool for which their harbour and town’s unique appeal will provide a juicy and successful bait.
And on top of that, for our maritime enthusiasts, setting the length limit at 250 metres is something very special, for it takes us right into consideration of one of the finest ships ever built in Ireland - the wonderful Canberra, the last and possibly the greatest ocean liner ever built by Harland & Wolff in Belfast. She may have been launched as long ago as 1958 – on St Patrick’s Day, no less – yet although she ended her active and very varied career in 1997, she still looks as modern as tomorrow, and her handy overall length of 250 metres – 820ft since you ask – made her ideal for a cruise liner to interesting places after she’d been taken off her original route from London to Australia.
The Canberra
She also served as a troopship in the Falklands War of 1982, where her duties included a visit to South Georgia where she would have been anchored close to Sir Ernest Shackleton’s grave. But eventually, after many years of further popular service as a cruise liner, for all that much of her technology was way ahead of its time, the poor old Canberra just got worn out, for she’d been busy since the day she left Belfast Lough – and in 1997 she was sold to Pakistan to be scrapped on the beach, which she resisted to the end – the word is this unique vessel took an awful lot of breaking up.

The hard life. Canberra in South Georgia while on troopship duties during the Falklands war of 1982
Invitably, modern 250 metre cruise liners do not quite have the timless elegance of the Canberra, as accountants and financial officers rule their concept as much as naval architects. But nevertheless they are of a more comprehensible and manageable size than the excessive 360 metre behemoths which would destroy the character of Dun Laoghaire Harbour, and provided the Harbour Master felt it could be done without impairing the basic character of the harbour, I feel we should be at least receptive to the idea of 250 metre vessels coming in, for it’s a huge step for the County Council to have made the decision to set this size limit.

The Lirica is a modern 250 metre cruise liner, and although obviously more voluminous than Canberra, nevertheless it is possible that she could be berthed in Dun Laoghaire without massive waterfront infrastructural change being required.
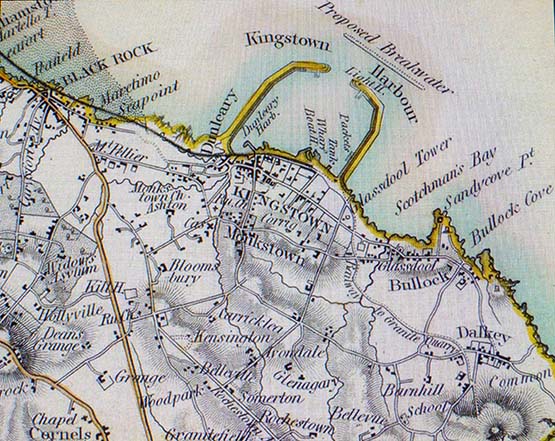
Meanwhile, the battle goes on to try and create a truly meaningful relationship between Dun Laoghaire township and its harbour, for as we’ve pointed out here before, when they started planning an Asylum Harbour back in the early 1800s, it was moved forward primarily by considerations of facilitating government power and function, and there was no real consideration of the requirements of ordinary mortals.
Thus the most basic initial thinking behind the new harbour was that it could provide refuge when required for troopships and naval vessels. So no thought whatever was given to the notion that personnel on board such vessels should have any contact with the shore, which at that time was virtually empty in any case, as the only local settlement of any kind, the little harbour of Dun Leary, was seen as being outside and irrelevant to the new harbour.
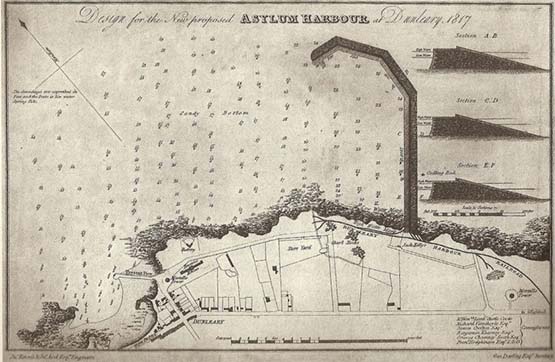
The beginnings. The initial plan for the new Asylum Harbour was a singe pier to provide protection from southeasterlies. It was well to the east of the little local port of Dun Leary, and a new road – ultimately George’s Street - was sketched in through uninhabited countryside to take travellers direct from Dunleary to the next local village of Dalkey while keeping them at some distance from the new harbour
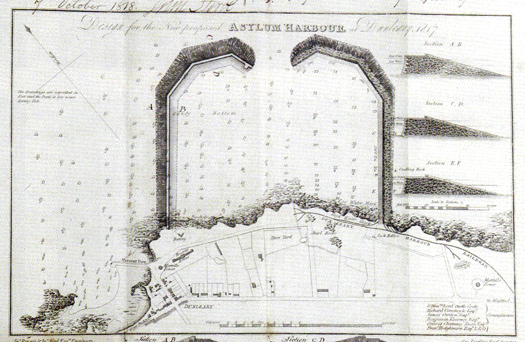
A second plan for the new harbour included a west pier, but it still excluded Dunleary itself.
But as the new harbour took shape, superbly constructed in Dalkey granite to be a sort of “instant historic monument”, inevitably shoreside development took place as well. After the place had been named Kingstown following a Royal Visit in 1821, it got notions of itself as a fashionable resort. But it was a case of every man for himself in the matter of development, and as one scathing critic wrote of in the 1850s, “ no system whatever has been observed in laying out the town so that it has an irregular, republican air of dirt and independence, no man heeding his neighbour’s pleasure, and uncouth structures in absurd situations offending the eye at every turn”.
Kingstown and its harbour around 1870, with a proposed breakwater (never built) off the entrance to provide added shelter from nor’easterlies. The railway still only reached halfway along the waterfront, and the Carlisle Pier had yet to be built, with the cross-channel packet boats having to make do with a berth on the East Pier.
Could that possibly be our own dear Dun Laoghaire? That reference to a “republican air of dirt and independence” was particularly hurtful to a place which prided itself on being called Kingstown, but that’s the way it was and still is, for the fact of the matter is that while the town and harbour have developed side by side, they have never developed together.
Thus there are enormous blind spots to the interests of others. The new library may look not too bad at all from the landward side, but from the harbour it is hideous. As for the endless struggle to make George’s Street back into a successful retail shopping venue, no matter what they do it still seems to slip further down the decline, and the recent plan to sub-divide it into quarters devoted to different area of shopping interest made no reference at all to the potential of the nearby presence of the harbour, for apparently that had not been in the consultants’ brief.
As for paying for the running of the harbour, we recently got an old friend, an accountant with a maritime outlook and extensive experience in many countries, to take a look at Dun Laoghaire in its totality and how the harbour might be funded, and he concluded that trying to find out how much it actually costs to run the harbour in some sort of relationship with the town would be like being eternally condemned to peeling an onion, as one layer removed would only reveal another, and you’d ultimately be reduced to tears.
That said, he did make us sit up and take notice by suggesting that they’re wasting their time trying to revive George’s Street as a shopping venue – instead, they should think in terms of letting it become residential with some offices in a setup which would thereby encourage a few thriving local shops at strategic intervals, rather than trying to have a whole row of under-utilised shops in terminal decline with the street’s decreasing footfall.

The Carlisle Pier in its glory days, when it was possible to get into a train in Sligo and travel all the way to London without being exposed to the rain at any stage. And of course, there was no question of spending any money in Kingstown……
Today, people talk about the situation of Dun Laoghaire Harbour as if it was always the case that it was a commercial and ferry port, and that the modern administrators of the port are obliged under time-honoured traditions to show a profit. In fact, Dun Laoghaire started life as Royal Harbour serving governmental and imperial needs, and ordinary people trying to do something so vulgar as make a living and even show a modest profit had to do so under the radar.
Thus although “ferry port” is still the link which will most readily spring to public mind in relation to Dun Laoghaire, but the early ferry operators had to get by as best they could with ad hoc facilities, and even a seemingly ancient structure such as the Carlisle Pier, with its two cross-channel ferries directly serviced by the railway, was a later addition – for many years, the best the packet boats could hope for was the berth on the east pier.
So contemporary letters to the newspapers which assert that Dun Laoghaire must now develop further and pay for itself, because it would not be in being were it not for Victorian entrepreneurial flair, are actually very wide of the mark. There was nothing at all entrepreneurial and commercial about the original thinking behind the building of Dun Laoghaire Harbour. So it would be in keeping with its true character and history were it allowed to be maintained today as a sort of maritime version of the Phoenix Park.
But of course, if 250 metre cruise liners really could be slotted in without requiring drastic changes to the waterfront, then well and good. And as we came in with a discussion about the last and best ocean liner built in Belfast being 250 metres long, how’s about the most famous ocean liner ever built in Belfast? It’s said that some mysterious billionaire is having a replica of the Titanic built in China. As it happens, the original Titanic was 269 metres long. But if the new Titanic expressed an interest in berthing in Dun Laoghaire, surely those extra 19 metres could somehow be accommodated………
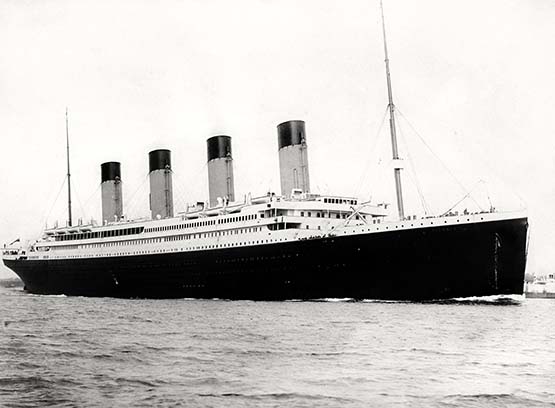

Would they allow those extra 19 metres into Dun Laoghaire? It’s rumoured that a replica of the Titanic is being built in China, but at 269 metres they’d have to stretch the regulations a little to let her into Dun Laoghaire Harbour.
Dun Laoghaire Sailing Clubs Say Future is in Leisure
Dun Laoghaire's future lies in tourism and leisure, according to a submission on the new 'master plan' for the busy harbour.
The Irish Times reports that the town's top sailing and yacht clubs, who have come together under the banner of Dun Laoghaire Combined Clubs, are putting aside their individual interests "in favour of a larger and longer-term vision for the harbour".
The clubs' submission urges a rethink on public access to both the shore and water sides of the harbour. Inprovements in linking the town with the harbour area are already a goal of the master plan.
"Properly developed with a marine tourism and leisure focus [Dun Laoghaire] can generate new and sustainable sources of income." they said.
Dun Laoghaire Combined Clubs comprises the 'big four' waterfront clubs - the National, Royal Irish, Royal St George and Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club - as well as the Dublin Bay Sailing Club and the Royal Alfred Yacht Club.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.