Displaying items by tag: Liffey ferry
It's back the Old Liffey Ferry service in Dublin's 'Docklands' has returned following easing of Covid-19 restrictions but running in a more subdued environment of the financial and cultural quarter since the outbreak broke, writes Jehan Ashmore.
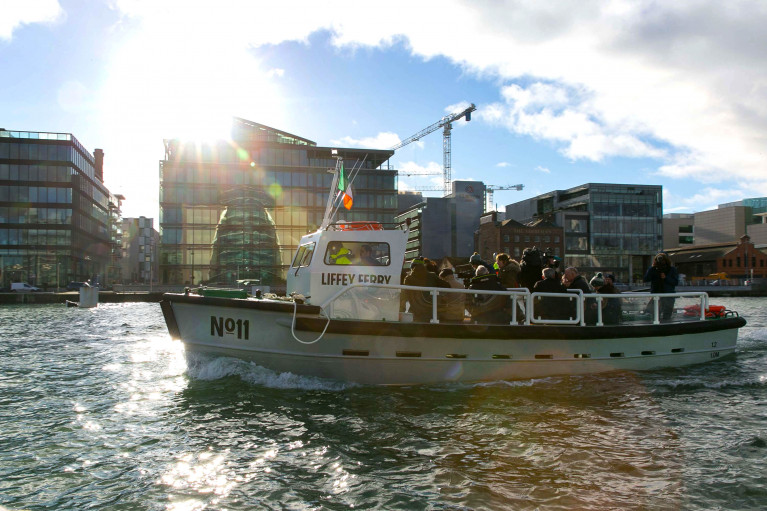
Operators of the historic river-crossing granted a Royal Charter of 1665 but with origins stretching further back to the 1400's, has in the present day seen ferry No.11 operating to a strict social distancing measure regime. In addition capacity has been considerably reduced from 18 passengers down to just 9 onboard any given crossing. This is to ensue passenger and crew safety during the brief crossing along the capital's under-used water thoroughfare compared to other European capitals, notably in Scandinavia.
The No.11 ferry was due to resume the seasonal service in March but is now available running to a routine Mondays to Fridays schedule. This involves serving three pontoon-based stops lining the Liffey quays. They are on the North Wall next to static-berthed Cill Airne and opposite on the south bank at Sir John Rogerson's Quay before returning across the Liffey to The Point Depot (3Arena) near the East-Link (Tom Clarke) Bridge.
Operating time are as follows:
Mornings: 8am - 10am
Lunchtime: 12pm - 2pm
Evenings: 4pm - 6:30pm
Last year the restored Liffey No.11, an original ferry from the service that closed in 1984 following the opening of the East-Link toll lift-bridge, was re-launched by The Irish Nautical Trust along with the Dublin Port Company and Dublin City Council.
The venture brings back and highlights the proud tradition of the Liffey ferry where dockers commuted across the river before the service ceased due to the new East-Link bridge which remains a vital part of the port's infrastructure and also for commuters.
The bridge was never officially named until recent years as the Tom Clarke Bridge with its lift-bridge section can be raised to permit vessels to reach the capital's older former port quays. These days there is no commercial shipping traffic since regular 'stout' tankers The Lady Patricia and Miranda Guinness ceased trading to Merseyside in the early 1990's. The only callers now are Irish Naval Service patrol ships, visiting naval vessels, motoryachts and tallships notably during festivals that have become infrequent in the last decade.
Currently the only 'Liffey' based activity, albeit domestic is the summer excursion operator, Dublin Bay Cruises which in June resumed service following a delay of an original debut planned for St. Patrick's Day.
Likewise of No.11, DBC's 100 passenger capacity vessel has reduced capacity by 60% leaving 40 passengers to take excursions on a network of cruises involving calls to both harbours of Dun Laoghaire and Howth. In addition a cruise off Dalkey Island incorporating a visit into Killiney Bay.
Further south along the eastern seaboard, Arklow Marine Services carried out further work earlier this year as Afloat noted No.11 was hoisted out of the water, albeit not in Co. Wicklow port. The activity actually took place downriver of the 'Docklands' at the nearby Poolbeg Y&BC in Ringsend which forms part of the modern Dublin Port.
The works saw the installation of a new propellor manufactured by Jimmy Walsh Propellers & Marine Engineering based in Rosslare Harbour Co. Wexford. This is where AMS assisted and also carried out standard maintenance while the UK built ferry was out of the water.
Dublin's Liffey Ferry Service Starts for First Time Since 1984
#ferries - Dublin city had for the first time in 35 years, a new ferry service writes The Irish Times.
It was a cold, bright pre-dawn morning when the Dublin No 11 Liffey Ferry left its berth beside the MV Cill Airne at 7am for its maiden voyage as a passenger ferry.
The Liffey was like glass and as the boat turned east in the direction of the Tom Clarke (East-Link) Bridge, a beautiful red sunrise framed the Poolbeg Towers.
It was a perfect start. The only thing that was missing was passengers. There were none.
“It’s a bit early,” confessed Charles Sheridan, one of the three members crew on the No 11 for its first three minute trip across the Liffey to Sir John Rogerson’s Quay. “From a commuter point of view, the 7am start will take some time to generate traction.”
He was not fazed by the no-shows saying that the service will take some time to establish itself and they already have a group booked in from one of the many companies headquartered in Dublin’s Docklands.
For more on the relaunch of the ferry service and the related role of the East-Link bridge, click here.
“Cross the Liffey in a Jiffy” in Dublin Docklands As Historic Ferry to Return After 35 Years
#dublinport - In Dublin’s Docklands, the historic No.11 Liffey Ferry otherwise known as the 'Dockers' ferry will today officially return to the capital’s waters after a 35-year absence.
The much-loved service that linked the north and south docks is to return following a complete restoration of the ferry in a joint project by Dublin Port Company and Dublin City Council.
The ferry was a vital link for the Liffey side communities at a time when the nearest river crossing was Butt Bridge but was decommissioned in 1984 following the completion of the East Link Bridge.
But now the No. 11 will be a familiar sight again in the heart of Dublin as she taxis passengers between three points - the 3Arena to Sir John Rogerson’s Quay to MV Cill Airne at North Wall Quay and back starting Monday 11th February, running Monday to Friday between 7am and 7pm.
On board today's relaunch will be the Lord Mayor of Dublin, Nial Ring, as a guest of honour at a ceremony held by Dublin Port Company to mark the No. 11 Liffey Ferry’s return to service.
Also coming on board for her first official trip across the river again will be Mr Richie Saunders from Ringsend, who worked on the No.11 originally as a coxswain, who was instrumental in preserving the boat in recent years, and who will be back at the helm again to ferry a new generation of passengers north and south of the river.
The service to cross the Liffey dates back to 1665 when it was given a Royal Charter by King Charles II and went on to last more than 300 years.
A capacity of 18 passengers will be taken on each crossing and the ferry service will also enable commuters across the Docklands. Fares for the trip will be €2 for each of the three-minute journey point to point – with the vessel equipped to accept both Leap Card and cash fares.
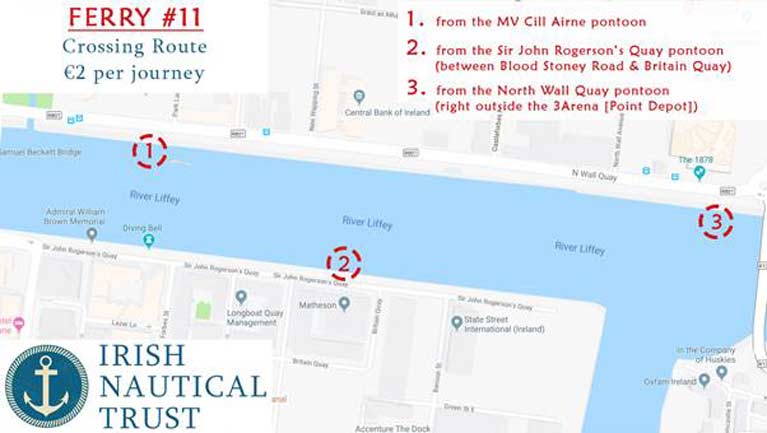 A map of the No.11 Liffey Ferry crossing route
A map of the No.11 Liffey Ferry crossing route
The No. 11 was essential transport for workers at the docks and became affectionately known by Dubliners as ‘the dockers’ taxi’. The boat was bought by Dublin Port Company in 2016, having been preserved by Richie Saunders with the aim of bringing her back to service. Operated by the Irish Nautical Trust, all proceeds from passengers’ fares will be used to help fund the return of a new maritime training programme.
The Irish Nautical Trust’s original maritime training programme, which has been dormant for the past 12 years, is now set to resume next month, and will offer young adults from the inner city and docklands areas the opportunity to gain practical marine experience and a formal qualification accredited by the Irish Sailing Association.
Each course will provide 8-10 people at a time with six months’ hands-on experience of the port, the wider maritime industry, driving, skippering, essential boat maintenance and repairs under the tutelage of experienced and retired seamen.
The objective of the programme is to give young people a skill set and future in Ireland’s maritime industry through learning by doing, with the No. 11 Liffey Ferry the new mascot of the programme. In this way, essential maritime skills now in short supply are less at risk of being forgotten or lost if they can be passed on to a new generation through formal training and mentoring.































































