Displaying items by tag: Sailing Club
Irish Sailing Say Support Your Sailing Club
Since the outbreak of Coronavirus (COVID-19) the situation has quickly evolved, and now we are realising the global perspective of the pandemic. Over the last few weeks, there has been a lot of communication and information shared within the Irish sailing community, and I would like to thank all Irish Sailing members for your positive response to restrictions as they were imposed with ever-increasing severity week by week. It is critical however that our clubs are ready to open their doors for sailing as soon as restrictions start to be lifted, and in order for them to be able to do that they need your support.
The strength of a club is its members, and your support is more important now than ever. Our clubs are where we play, compete and have fun. Clubs aren’t just a place to launch a boat – right now they’re a support network – we hear of amazing stories from up and down the country of clubs organising meals on wheels for more vulnerable members, making sure those cocooning are looked after and raising spirits with online quiz nights. They play a vital role in our society, and they need your help.
Irish Sailing is keen that when the restrictions imposed by the COVID 19 virus are lifted, we will all be in a position to get back out on the water quickly. Even though there’s a lockdown in place, and clubs have had to stop all external operations, a lot of work continues behind the scenes to plan for the summer so that our sports can resume as quickly and efficiently as possible. There are still bills to pay – and that’s where members play their part. Clubs need the subscription income from their membership now if they are going to be fully operational when the time comes.
We understand that these are difficult and uncertain times, but we urge you to support your club. Please pay your membership fees and help your club in these difficult times, so that we have many happy sailing days ahead.
Harry Hermon, CEO
Inter-Club Sailing Competition for Ireland?
Is a new inter-club regatta the boost to dwindling interest in sailing club membership? Has it's time come, particularly now that there are clubs with one design fleets that can cater for fleet racing?
“Real Madrid captain, Sergio Ramos has reaffirmed his loyalty to his club after the Spanish player broke his nose in Saturday's goalless La Liga draw with Atletico Madrid.
"I would bleed a thousand times for this badge and this shirt. Thanks for your support. I'll be back in no time," he wrote.
There are many examples in the sporting world of athletes putting their physical health on the line in competition, whether it be for club, county, province or country. The privilege of representative honours in many cases results in outstanding on-field performance. While physical danger may not be as present in many sports, there is no doubt that loyalty to the jersey can inspire above average performance levels and team togetherness.
Sailing is a sport structured on clubs. They are fundamental to all aspects of sailing, and in this, sailing is no different from most other sports. Clubs provide the introduction to sailing, access to and storage for equipment, race organisation and social occasions for members. Why then is there no national sailing club competition that seeks to combine the competitive and representative urges? Its not that it doesn’t exist in sailing clubs, - there are interclub competitions in snooker, quizzes and even cookery! And yes, there are some prizes for club entries in some events, but these are largely individual entries grouped conveniently by home club. Team Racing partially fills the void, but this genre does not represent the mainstream activities in club sailing. There were some attempts to get interclub match racing off the ground, but other than these exceptions, are there any club team events, where a team selected by a selection committee, coach or team manager of a club earns club representative honours?
Is this a void that needs to be filled in Irish Sailing? Would it bring a boost to dwindling interest in club membership? Has it's time come, particularly now that there are clubs with one design fleets that can cater for fleet racing?
Afloat would like to suggest the parameters for such an event and recommend its consideration as a new national club event.
- Fleet Racing in one-design keelboats that can accommodate five people.
- Crew to include one under 18, one over 50, and to have a 3:2 gender split.
- Teams to be selected by clubs, no individual entries.
- Clubs to open up selection to all members and to provide evidence of an open, transparent selection process.
- No Cat 3 sailors
With the basis for an event established, the possibility of developing an exciting, inclusive national event becomes feasible. Some outcomes could be
- Regional qualifying
- Club qualifying
- National Representation
- Grand Prize
A well-managed national annual event would have the ability to create a new direction for Irish Sailing, giving clubs an offering to their members that can re-invigorate the club sailing scene.
Is there merit in this suggestion? Reader comments appreciated below
Irish Sailing Encourages Yacht Clubs To Spend Sports Capital Grant At Home
Irish Sailing is encouraging yacht and boat clubs who won over €1.1m in Sports Capital grants in November to try to spend the money in Ireland.
In the interests of 'supporting the Irish Boating industry', Irish Sailing has appealed to clubs to 'seek quotes from local suppliers and help to support the Irish Marine industry'.
Of the €1.1 million, awarded to clubs, Irish Sailing estimate approximately €750k will be spent on boats and equipment.
See the full list of clubs and awards as previously reported by Afloat.ie here
'The Sports Capital support for Irish Sailing clubs is brilliant for club development and creating new opportunities. If every club then bought from an Irish broker the knock on effect to the Irish marine industry would be tremendous' Irish Sailing CEO, Harry Hermon, told Afloat.ie.
'Our industry is a close knit community that offers an incredible support to the boating community – lets help keep the cogs oiled', he added.
30 sailing clubs throughout the country will share over a million in funding.
Dun Laoghaire's National Yacht Club on Dublin Bay is one of the biggest sailing club recipients with a grant of €142,375 for Increasing women and teenagers participation in the sport. The east pier club is the home of Rio Olympic silver medalist Annalise Murphy.
Also in Dun Laoghaire, the country's bggest sailing centre, the Irish National Sailing Club (Locaste) got €40,058 for the renewal of sailing equipment and the purchase of new boats.
The Royal St. George Yacht Club (RSGYC) got €31,228 for a Firefly dinghy renewal programme, Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club got €18,515 for the purchase of a 5m RIB and capstan winch. The Royal Irish Yacht Club got €25,000 for its safety and support fleet. Dublin Bay Sailing Club got €11,236
Who Is To Blame For The Decline in Sailing?
#sailing – Sailing is a sport, not the qualification of a superior social standing.
Is that fully understood by everyone involved in the sport or is there still an element of elitism which needs to be eradicated?
The term 'yachting' was dropped a few years from the title of the national representative organisation which became the Irish Sailing Association, amidst an apparent belief that 'sailing' would be less elitist as a descriptive term and more acceptable to the public.
Most 'yacht' clubs did not become 'sailing' clubs, though there are more 'sailing clubs' it would seem than 'yacht' clubs around the country. Boats did not generally become described in the American term of 'sailboats' but remained yachts.
I see no major problem with the term 'yachting' though I understand the sensitivities which surround the different terminology. I have no qualms about admitting that I own a yacht and feel fortunate to do so.
What is of more concern to me is that the sport becomes truly a 'sport for all' and is not riddled with different levels of social strata.
There remains a degree of public perception that sailing is an elitist sport. This has dogged it gaining more general acceptance and bedevilled its reputation.
Sailing, or yachting, should be a 'sport for all' in an island nation where it is based on access to the magnificent resource of waters surrounding us.
The perception of wealthy people with big boats, sitting in clubs behind signs of 'strictly private', is not conducive to creating a widely popular sport. There is a dichotomy here because the growth of interest amongst young sailors, with more involvement in dinghy sailing such as through Optimists, has been encouraging. So has the advent of more interest in schools in adopting sailing onto their sports curricula.
The movement for change within the ISA came initially from the dinghy fraternity, where many of us who now sail cruisers, began their love affair with the sport.
The breakthrough which sailing needs, to gain more general popular public acceptance, has not been made.
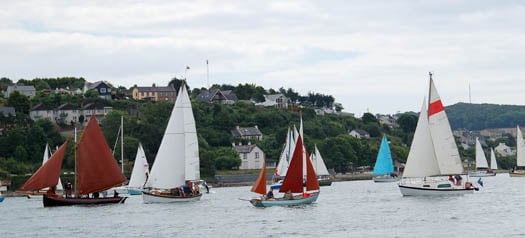
People sail boats of all types
Why is this?
Throughout my years of being a marine journalist and when marine correspondent within RTE, it was difficult to get coverage for sailing. I did achieve it, but there was always a bit of a battle to establish acceptance that the sport was not just for the wealthier part of the population, but that it permeated across all social milieu. I did get that message across by quoting figures of how many are actively involved in a day's racing organised by major clubs, compared with the attendance for example at some Irish soccer matches which got plenty of media coverage. I also stressed that it was a participative sport more than a spectator one. More people within the broadcast service have become involved in the sport. But generally in the media, there is still an impression that sailing is a sport for which you need a lot of money and this is perpetuated by the oft-quoted unfortunate analogy of standing under a cold shower and tearing up money.
But sailing – and yacht – clubs are also contributors to this failure to get the message of sailing as a sport for all across. In my experience as a journalist, most clubs are poor at their public relations and the issuing of information to the press, but yet complain that the sport does not get enough coverage, even if they do not provide the information. There are honourable exceptions, who provide good circulation of information and websites, but there are many other clubs who are pretty bad at sending information and whose websites are dismal failures, not updated for long periods of time.
At the annual meeting of the South Coast Offshore Racing Association in Kinsale Yacht Club in the Spring one participant told the audience that "yacht clubs to most people would be the scariest places to walk into."
Another said: "It is no wonder that we struggle as a sport to keep people as lifelong participants, even though we can and do attract younger people into the sport at an early age."
The warning signs have been there for years, for those who wanted to note them. Sailing needed to widen its appeal, to get more people into the sport for lifelong participation.
To survive a sport needs an organised structure and clubs are needed to provide this, they must have members who pay to join and support them. They cannot exist if people use them without joining and therefore not giving on-going financial and volunteer support.
So there is a dichotomy here. Why are clubs not getting enough members, a situation which appears widespread?
The economy over the past few years has undoubtedly been a contributory factor. People have lacked disposable income and, amongst families in particular, expenditure on non-essential matters has had to be cutback. Some clubs have responded with different arrangements for membership, but as I wrote in this blog last week, I still think that new, flexible approaches are needed, particularly to encourage crews, of which most active racing boats are short.
There are also people who sail and who do not join clubs, either they don't want to, or can't or there are not clubs close to them or for whatever reason. But they do sail, are they outside of the system and should they be considered. How can they be appealed to because they are involved in the sport. There are the traditional boats and the huge support they get. Some are members of the ISA, some of clubs, but many not so perhaps. There is a huge level of support for sailing in this sphere and many organised events which draw big support. Should the ISA reach out to these sailors, to this area of sailing activity?
This and many other aspects merit consideration to band together all interested in sailing, in all its facets. United in approach there would be a strong force which official authorities could not ignore when improved facilities and recognition are sought or when government and officialdom has to be challenged, such as in the imposition of new regulations.
On this month's edition of my radio programme, THIS ISLAND NATION, (click to play podcast above) I talked to the President of the Irish Sailing Association about his plan for a Strategic Review of the sport to deal with a decline and he accepted my suggestion that the impression of elitism is not good for the sport and has not helped its expansion and development. We also discussed whether there was too much concentration on racing and whether more support should be given to other forms of sailing, encouraging cruising.
David Lovegrove wants to get across the message that sailing is open to everyone. He would be particularly happy, he told me, if he could get that understood and accepted widely in public. We discussed how sailing can be a sport for all ages and for all people, with the uniqueness of enabling families to participate together if they wished. He recalled the time when he first got involved in sailing and the enjoyment and sense of friendship that abounded. Perhaps too, we agreed, there was less concentration then on being winners in racing and in high performance levels.

Ocean racer Damian Foxall of County Kerry
I think there is a need for Ireland to have a good presence on the international scene and that it is good for the country. It is also good for sailors to aspire to the highest levels of achievement, but have we got over-committed to competition to the detriment of the enjoyment of participation, of being on the water. Had the ISA also been too focussed on its own high performance programme and those who qualify for it and not given enough support to other sailors who may not have made it through the ISA system, but want to try on the international scene and should there be arrangements to support that. Also, for example, has the ISA been close enough to the top international sailors who have come from Ireland and sought to include them and utilise their services in promoting Irish sailing, such as Damian Foxall and Justin Slattery and where is the ISA in regard to the efforts of such as young David Kenefick making his own way onto the international scene through the Figaro Race.
All of these are interesting points to debate.
I take part in club racing, but I always try to make it clear to the crew that we are going out to enjoy ourselves and winning is not the overall aim, though it would be nice and we have been fortunate enough to do so from time-to-time. I don't like shouting on a boat, though sometimes getting something done quickly when needed can raise the vocal level. But if the enjoyment is taken out of the sport, that is not for the best.

All forms of sailing need to be engaged
Again, here we have a dichotomy, other sports are hugely competitive-oriented, why should sailing not be?
There are issues to be addressed and I wish David Lovegrove and his team every success as they try to come up with answers. He told me in our interview, that this would not be a short-term solution, but would take a lot of work and commitment by the clubs themselves. Indeed. As I wrote in this blog last week, encouraging participation is essential to arrest decline. That will mean more innovative ways of involving people, a point which Denis Kiely, who has given tremendous national service to sailing made at that SCORA meeting in Kinsale and which impressed me.
He said that often crews did not get enough of a proper introduction to the sport, didn't have enough knowledge of it and weren't given such, didn't get training, could therefore feel unwelcome and then leave the sport.
Club marinas are pretty full of boats around the country, so it is at times hard to accept that there is a decline in participation, but the meetings which have led to the new approach by the ISA have shown problems, including dissatisfaction with the national association itself. David Lovegrove has accepted this and the need for change.
He spoke to me of his enthusiasm about the work ahead to re-define the sport and his confidence in the team he has appointed to oversee different aspects of the sport and to suggested changes. These are outlined in detail in the current/Summer edition of AFLOAT magazine.
His determination to create a strong, vibrant sport, is welcome. I wish him success with his efforts. Listen to his interview in my programme here on the Afloat website (above). Everyone interested in the future of our sport should respond positively. That commitment is what the sport needs.
So – who is to blame for the decline in sailing – all of us are, if we do not make changes to encourage more people into the sport and to stay in it and if we do not adapt existing systems to ensure they feel welcome. That means all of us who want to see sailing being a sport for all accepting that sailing is just that - a sport - not a badge of social approval.
































































