Displaying items by tag: EPA
Water Quality Research Included in Latest EPA Grants
Water quality is a research topic qualifying for grants of up to €14.5 million offered by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
The EPA says it is inviting proposals from the research community for “innovative projects to support the development and implementation of environmental policies in Ireland.
Under this year’s call, the EPA says it is delighted to be partnering with Met Éireann to co-fund projects in areas of mutual interest.
“The EPA is committed to funding excellent research to address knowledge gaps, build capacity and provide robust evidence to support the implementation of effective environmental policies in Ireland,” Dr Eimear Cotter, director of the EPA’s Office of Evidence and Assessment, said this week.
“We have recently announced an increase in the PhD stipend to €25,000 for EPA-funded students, and now invite research proposals across a range of open themes focusing on funding medium- to longer-term research,” she said.
“In 2023, 40 per cent of awardees had not previously applied to the EPA for funding and we hope to see this trend continue in 2024,”she said.
Areas of research include exploring global risks to Ireland achieving its climate and environmental goals; understanding vulnerabilities to climate change at a local level and the impact of a changing climate on our health, including water quality.
The EPA research programme is a Government of Ireland initiative funded by the Department of the Environment, Climate and Communications.
Deadline for submissions is May 30th, with decisions due in November/December of this year.
Further details are on the EPA website
“Nature-based” solutions to the impact of climate breakdown on the marine and terrestrial environments could qualify for funding from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as part of a new research call.
The EPA says up to €16 million in funding is available for new research projects, representing a significant increase over previous years.
It is inviting proposals from the research community for “innovative research projects to support the development and implementation of environmental policies in Ireland”.
“Scientific research and innovation are playing an increasingly important role in informing how governments and society can respond to the challenges posed by climate change and environmental degradation,” Dr Eimear Cotter, Director of the EPA’s Office of Evidence and Assessment says.
Areas of research include exploring how nature-based solutions can benefit the environment and society, advancing climate science in an Irish context, and identifying effective options to adapt to climate change.
Cross-cutting areas are also highlighted, such as how data and digitalisation can be utilised for environmental protection and how society can be enabled in its transition to a sustainable future, the EPA says.
The EPA research programme is funded by the Department of the Environment, Climate and Communications.
Under this year’s call, the EPA says it will be partnering with the Geological Survey Ireland, National Parks and Wildlife Service and Met Éireann to co-fund projects in areas of mutual interest.
Further details are available on the EPA website and queries can be emailed to [email protected]
EPA Report Critical of Role of Local Authorities in Tackling Water Quality
Local authorities need to take a more strategic approach to tackling the decline in water quality, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says.
A report by the EPA shows that less than half of the 620 performance assessments undertaken across 20 national environmental enforcement priorities met the required standard in 2021.
The EPA’s office of environmental enforcement director Dr Tom Ryan said that “local authorities have a fundamental role to play in protecting the environment within their counties, and their performance in that role needs to improve”.
“The local environmental challenges are great,” he said, commenting on the report analysing local authority performance.
“The water quality in our rivers, lakes, estuaries and coastal waters is in decline, and there are concerning localised issues that are impacting negatively on the air we breathe,” Dr Ryan said.
“The segregation of waste streams, which is so critical to supporting materials reuse in the development of a circular economy, is not as good as it needs to be,” he said.
“Local authorities need to have a more strategic approach to addressing these issues within their counties so as to protect people’s right to the enjoyment of a healthy environment,” he said.
“While local authorities are engaged in a great deal of enforcement activity, they need to have a better focus on priority environmental issues and increase or escalate enforcement action where required,” he said.
“Our water quality is in decline with just over half of surface waters (rivers, lakes, estuaries and coastal waters) in satisfactory condition,”Dr Ryan continued.
He said that agriculture is one sector having a negative impact, due nutrients including nitrogen and phosphorus run-off into waterways.
“ Local authorities must target farm inspections in these areas. The proper use of fertilisers and the correct management of slurry will benefit both the farmer and the environment,”he said.
The EPA report shows that the scale of environmental enforcement work carried out by local authorities is “significant”.
It documents how over 500 local authority staff handled almost 81,000 complaints and carried out over 205,000 environmental inspections in 2021.
The EPA notes that this is the first year of the revised “Local Authority Performance Framework”, which assesses the effectiveness of inspection activities in targeting key environmental issues.
The assessment is based on 20 priorities, and measures how local authority actions deliver environmental outcomes - such as better segregation of household and commercial waste, cleaner air through controls on solid fuel sales and minimising risks to water quality from farming activities, the EPA says.
This also requires a follow-up and “closure of issues detected so that real environmental improvements are achieved”, the EPA says.
EPA office of environmental enforcement programme manager David Pollard said that air and noise enforcement “continues to have the lowest level of dedicated resources within local authorities”.
Pollard said there is a “need for increased enforcement efforts to improve segregation of domestic, commercial, construction and demolition waste to improve reuse and recycling of materials”.
He also said it is “crucial that local authorities tackle air pollution issues by making sure that only approved solid fuels are sold”.
“The Focus on Local Authority Environmental Enforcement – Performance Report 2021” report is available on the EPA website.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says as much as 500 million litres of potentially untreated wastewater is being released into Ireland’s rivers and coastal waters every day.
As the Irish Independent reports, the agency warns that it will take decades, and billions of euro, to correct the problem — but as yet Irish Water has “no clear action plan or time frame” for remedial works at many of what the EPA identifies as priority areas.
As of the middle of 2022, as many as 32 small towns and villages were discharging raw sewage as they have no wastewater treatment infrastructure.
Overall, the EPA claims that 49% of Ireland’s sewage — far above the EU average of 10% — is “still not treated to the standards set to protect the environment”, according to the agency’s programme manager Noel Byrne.
The Irish Independent has more on the story HERE.
Bathing Waters: Quality Continues to Improve - EPA
Beaches and the quality of bathing waters in Ireland is continuing to improve, according to the Environmental Protection Agency.
EPA director Dr Micheál Lehane said local authorities must remain vigilant to ensure public health was protected and continue to identify and fix sources of water pollution.
The EPA's Bathing Water in Ireland 2019 report found that 95% - 140 out of 147 - of bathing waters assessed met or exceeded the minimum required, slightly up on 2018.
Three new bathing waters were classified as excellent or good, while the water at five beaches was classified as poor.
Merrion Strand in Dublin Bay has been declassified after five years at poor status.
Three bathing waters, all in Dublin, were classified for the first time; Forty Foot Bathing Place and White Rock Beach, which were both classified as excellent and Sandycove Beach, which was classified as good.
RTE News has more and reported that under Phase One of the lifting of Covid19 restrictions, beaches along with other outdoor amenities are open.
Historic Low In Fish Kills Welcomed - But Water Quality Concerns Remain
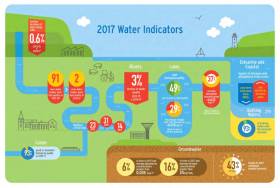
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has noted with caution the findings from the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) report on water quality in 2017.
While it welcomes the fact that the number of fish kills in Irish waters were at a historic low last year, IFI is calling for continued awareness of water quality issues in light of the EPA’s conclusion that water quality is once again in decline.
According to this latest report, there was 14 fish kills in 2017, affecting 7.8km of river with 2,123 dead fish recovered. This is significantly lower than the worst years of 1987 and 1989 when there were more than 100 fish kills reported.
IFI’s Environmental Officers carried out 26,000 environmental inspections last year across agricultural sites, habitats, industrial sites, wastewater and water treatment plants, civil engineering sites and forestry sites.
Despite the positive drop in serious pollution events causing fish mortalities, IFI remains concerned about the reduction of water quality, with the EPA reporting a 3% drop in river water quality since 2016 and a 0.6% loss in high-quality river sites.
The inland fisheries and sea angling resource contributes €836 million to the Irish economy every year and supports 11,000 jobs in rural communities.
“Ireland has some of the best wild fisheries in Europe and while water quality in Ireland still compares favourably with our European neighbours. The current decline is a source of concern as any impact on the quality of our waters can have a negative impact on the freshwater fisheries resource,” said IFI chief executive Dr Ciaran Byrne.
“Not only is the quality of our natural environment and aquatic habitat inextricably linked to the appeal of Ireland as an angling and holiday destination, it is also a very important source of wellbeing for our people.
“It is essential that we protect and conserve our freshwater assets, meaning our rivers and lakes. The long-term conservation of the resource requires maintenance of healthy and ecologically viable ecosystems.
“That means that we need to prioritise monitoring and protecting water quality as well as dealing with other issues such as removing fish migration barriers, improving practices which cause physical changes to fisheries habitat, dealing with changes in water quantity and controlling the spread of invasive species,” Dr Byrne added.
#CoastalNotes - Seven beaches in Dublin and Galway have failed to meet the EU’s minimum standards for bathing water quality.
That’s according to the latest Bathing Water Quality in Ireland report from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which identifies Sandymount and Merrion Strands, Loughshinny, Portrane and Rush South in Co Dublin, as well as Ballyloughane in Galway city and Clifden in the west of the county, as problem areas.
Three of the Dublin beaches are repeat offenders, with Merrion and Loughshinny marked as ‘poor’ in the previous two reports, while Portrane was listed among 2016’s worst bathing spots.
Galway fares a little better in 2017’s report, with Trá na bhForbacha upgraded to ‘vulnerable’ — though it, along with Clifden and Ballyloughane, remains at the mercy of pollution from runoff, septic discharges and the like.
Pollution events were also up in 2017, with 163 incident notices issues by local authorities — almost double the total recorded the previous year. Twelve of these notices resulted in bathing restrictions at Merrion and Sandymount Strands alone.
On a more positive note, 93% or 132 of the 142 bathing areas surveyed for the 2017 report meet the EU minimum for swimming water quality.
Nationally, bathing water standards are on par with last year’s report, which found almost three-quarters of Irish swimming spots met the EU’s strict bar for ‘excellent’ water quality.
The full EPA report is available to read or download HERE.
#CoastalNotes - Three beaches in Dublin and three in Galway have failed to meet the minimum standards for bathing water quality, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
The Irish Times covers the latest EPA Report on Bathing Water Quality, which listed repeat offenders Ballyloughane in Co Galway and Dublin’s Merrion Strand and Loughshinny, along with Portrane in North Co Dublin and Galway’s Clifden and Trá na bhForbacha as beaches especially vulnerable to pollution.
Youghal’s front strand, Duncannon in Wexford and the south beach at Rush in Co Dublin, which were listed as ‘poor’ in last year’s report, showed enough improvement in their bathing water quality to be classified as ‘sufficient’.
Overall, almost three-quarters of Ireland’s bathing spots — both coastal and inland — were classified as having ‘excellent’ water quality.
The Irish Times has more on the story, while the full EPA report on Ireland’s bathing water quality can be found HERE.
Raw Sewage Discharged In Over 40 Spots Nationwide Says EPA
#Pollution - Cork Harbour, Ringsend in Dublin and more than 40 other Irish riverside or coastal towns and cities in still fail to meet EU sewage standards, according to a damning new EPA report.
RTÉ News has details of the environmental agency’s 2015 Urban Waste Water Treatment Report, which identifies 43 urban areas — 29 of them classed as large towns or cities – that continue to release raw sewage into the sea and rivers across Ireland.
A number of these locations have seen their timetable for tackling such discharges slip by almost two years due to lack of sufficient capital investment, which the EPA decries as “unacceptable”.
In locations such as Youghal and Merrion Strand, the release of untreated waste has been linked to a significant lowering of bathing water quality.
The news is little different from almost three years ago, when the EPA identified the likes of Killybegs in Co Donegal and Cork Harbour as black spots for untreated wastewater.
More recently, Housing Minister Simon Coveney promised that the problem of discharges from a number of communities around Cork Harbour would be solved within the next 18 months, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
#BathingQuality - Six Irish coastal beaches – half of them in the Greater Dublin Area – fall short of the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) minimum required standard for water quality.
Rush's south beach and Loughshinny in north Co Dublin joined Merrion Strand in south Dublin, Youghal's front strand in Co Cork, Duncannon in Wexford and Ballyloughane in Co Galway in the list of bathing areas classed as being of 'Poor' quality in the EPA's Bathing Water Quality in Ireland report for 2015.
The EPA explains that the 'Poor' class, which averages data collected between 2012 and 2015, reflects bathing areas that "may be subject to more frequent, or more significant, pollution events" often impacted by "nearby sewage discharges, most commonly as a result of heavy rainfall".
All six beaches on the current 'Poor' list showed improvement in the last year, recording a number of 'Excellent' scores in 2015, but pollution concerns remain.
And in the case of Merrion Strand, bird droppings from seagulls congregating in the area are a serious issue, as they carry as much as 10 times the bacteria of human waste.
Overall, bathing quality in Irish waters remains "very high", according to the report, with just over 93% of sites meeting the minimum EU standards.
Three-quarters of these – 101 of the 137 areas monitored - were classed as being 'Excellent', with the counties of Clare, Kerry, Leitrim and Louth standing apart with unblemished records for their bathing quality.
The complete EPA bathing water quality report is available to read or download HERE.