Displaying items by tag: Gulf Stream
Winters in Ireland could be as cold as Toronto in Canada if a potential collapse in the Gulf Stream happens, an Irish climate scientist has said.
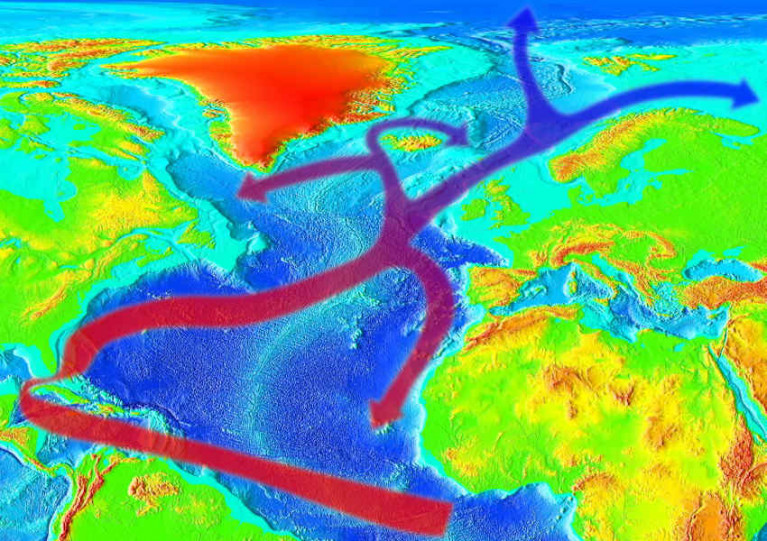
New German research has found “an almost complete loss of stability over the last century” in the series of currents that researchers call the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC).
The currents are already at their slowest point in at least 1,600 years, but the new analysis shows they may be nearing a shutdown.
The study by Dr Niklas Boers, of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, published in the journal Nature Climate Change, indicates that AMOC may have been losing stability over the course of the last century and that the process has accelerated.
AMOC transports warm water from the tropics northward at the ocean surface and cold water southward driving the Gulf Stream.
Climate scientist Dr Brian Kelleher, of DCU said the Gulf Stream is the principal reason why Ireland has such mild winters given its relative high latitude.
Without the Gulf Stream, he said, Ireland would have winters similar to Toronto where, despite being at a lower latitude, temperatures are below zero for much of the winter.
More from the Irish Times and today's coverage on a stark UN report on climate change.
The findings of the IPCC report provide a stark backdrop to the forthcoming UN climate summit, COP26, to be held in Glasgow next November.
Ireland is represented in an international team of researchers who have identified a possible link between human-caused climate change and a weakening of the Gulf Stream.
And as The Irish Times reports, a continued weakening of the Atlantic Ocean current system could mean more extreme weather for Ireland — and an end to our typically mild climate.
The researchers’ study, published in journal Nature Geoscience, used a variety of sources to plot the history of the flow of the Gulf Stream: the Atlantic Ocean current that pulls warm water from the equator north while pushing colder water south and, via its extension as the North Atlantic Drift, gives Ireland and the UK our mild, wet weather.
Maynooth University’s Dr Levke Caesar, lead author on the study, said the team combined three different types of data — including deep-sea sediment samples dating back many centuries — to reveal “a robust picture of the overturning circulation” in the Atlantic.
It’s this picture that’s a worrying one for climate scientists, as it shows a distinct weakening of the Gulf Stream’s flow since the mid 20th century, and a trend that suggests it could reach a tipping point by the end of this century.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
US Schools Send Mini Sailboats Across The Pond
Mini sailboats could soon be spotted in Irish waters if a US school project goes according to plan.
The Bangor Daily News in Maine reports on the Educational Passages programme, through which middle school students will equip miniature sailboats with GPS trackers and set them out to sea to follow their progress across the Atlantic.
In previous years the programme - which is designed to give youngsters hands-on experience in maritime professions and skills such as oceanography and chart reading - has sent its self-steering boats as far as Portugal.
This year's students are hoping to catch the Gulf Stream to send their boats to Europe. The boats will be launched by trainees on the Maine Maritime Academy's training vessel State of Maine, which will also be retrieving a boat from a previous project that was recovered in Ireland.