Displaying items by tag: Maynooth University
A new Master’s course specialising in remote sensing and the principles of seabed mapping has been successfully delivered by a joint partnership between the Department of Geography at the Maynooth University and Ireland’s marine mapping programme INFOMAR.
The level 9 post-graduate module teaches students about the science of seabed mapping by providing a combination of class-based learning and practical offshore survey experience.
The course outlines the importance and impact of seabed mapping, and features a range of topics including how seabed data are collected and processed to produce high resolution maps of seafloor depth, type and habitat.
Lectures illustrate how scientists measure and describe the seafloor in incredible detail, using state of the art acoustic sonar, positioning, and optical instrumentation.
The use of satellite imagery analysis is explained in studying coastal seabed depth and shape, with practical examples utilising images of Dublin Bay acquired on the Sentinel-2 satellite’s sensor almost 800km above the Earth’s surface.
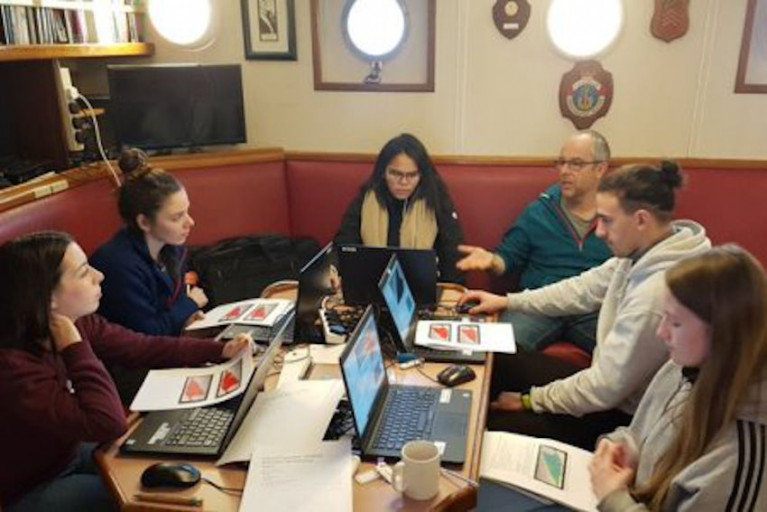
The module includes a two-day offshore practical where students are given an opportunity to apply the theoretical learning aboard the RV Celtic Voyager.
This is one of six survey platforms deployed by INFOMAR during seabed mapping operations, tasked with operating along the continental shelf and coastal waters.
Students get exposure to the dry and wet/chemical laboratories, as well as to operating an array of scientific equipment including the multibeam sonars and associated oceanographic instrumentation.
Participants boarded the RV Celtic Voyager in the Port of Cork and departed to the outer reaches of Cork Harbour where the offshore element of the module was conducted successfully on 15 and 16 February.
Training activities undertaken onboard included a marine mammal observation deck watch, survey computers and software use, benthic ecology, sedimentology classification, sound velocity probe deployment, multibeam echosounder, and sub-bottom profiler data gathering.
‘This module … demonstrates the welcome influence of Irish seabed mapping expertise on new sectors of society’
After exposure to the scientific equipment, workflows and data processing onboard, the students were tasked with the design, planning and implementation of a real-life survey scenario. This enabled them to apply their newly acquired seabed mapping knowledge as a team of scientists would in real-world conditions.
Overall the INFOMAR MSc module gave Maynooth students an overview of remote sensing techniques, helping them to understand bathymetric data products, to recognise data limitations, and to identify key systems and practices used in the field of seafloor surveying.
Students also developed a technical grounding in mapping at different resolutions, and the importance of instrumentation calibration, quality control and processing of bathymetry datasets, before product delivery to end users.
In addition, students learned how to source marine data online from INFOMAR’s Interactive Web Data Delivery System and online Webviewers, and via web-based portals operated by the European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet) and the Copernicus Marine Environment Service.
Importantly, says the Marine Institute, the module was taught within the context of end users, stakeholders and the policy framework underpinning ocean science and ocean literacy, highlighting both the relevance and importance of mapping the Earth’s seafloor.
Participants benefited from the fact that the course was delivered directly by the INFOMAR team, who have extensive experience of offshore surveying, and were able to share their own experiences and varied employment backgrounds with the students.
Sean Cullen, of the Geological Survey Ireland and INFOMAR joint programme manager, said: “I’m pleased to see the very positive feedback on the course overall both from the students and the tutors.
“This module, newly developed by the INFOMAR team, with steering from the Department of Geography at Maynooth, demonstrates the welcome influence of Irish seabed mapping expertise on new sectors of society and is timely addition to the INFOMAR education initiative as we face into the United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development.
“The collaboration is an encouraging sign that seabed science belongs in the space of third level education, and sets to further promote Ireland as leaders in marine science and of ocean literacy on an international stage.”
Thomas Furey, INFOMAR joint programme manager from the Marine Institute, added: “It is critical that we create a legacy to build on Ireland’s world leading role in seabed mapping, and through launching our third level delivery of INFOMAR specific training, we are contributing to capacity build, marine economy growth, and Ireland’s marine plan, Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth.”
Geophysical Research Survey Off North West Coast In May
#MarineNotice - Maynooth University will carry out a geophysical research survey off the North West Coast of Ireland from next weekend.
Work is expected to commence on Sunday 6 May and last for approximately nine days, subject to weather conditions.
The Marine Institute’s research vessel RV Celtic Voyager (Callsign EIQN) is scheduled to carry out the works for the Mara survey, undertaken by researchers in Maynooth University to collect geophysical acoustic survey data as well as sediment grab and core samples.
The survey will use relatively low amplitude sound sources to image into the seabed including an echosounder and a sparker system, which will allow for the characterisation of seabed type to inform the deglacial dynamics of the climatically driven British Irish Ice Sheet.
The vessel will, on occasion, be towing a hydrophone cable and other equipment, up to a maximum of 50 metres behind the vessel. The vessel will be restricted in its movements when towing a cable astern.
All other vessels are requested to give the operation a wide berth. The vessel will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
Details of the survey area, relevant co-ordinates and contact information are included in Marine Notice No 19 of 2018, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.