Displaying items by tag: Corinthian
Sailing the Enduring Dragon Keelboat on Irish Waters
#dragonsailing –After a weekend of intense Dragon keelboat action on Dublin Bay, Class Captain Conor Grimley writes that after eight decades in the making, the Dragon class is breathing new fire into the Irish sailing scene – and it’s much more accessible than it appears
The Dragon class has never been so strong in international waters as it is today. At over 80 years old, the classic design has endured – and its popularity has ensured that build quality is second to none.
True enough, the class has been somewhat elusive on the domestic scene, with international competitions tending to take precedence over regional events and club racing.
Still, the Irish Dragon fleet has a strong core spread between Dublin Bay, Kinsale and Glandore, where Corinthian sailors mix it with professionals, providing for exciting racing.
Into the bargain is the fact that newer boats don't have it all their own way, such is the quality of older models. And now momentum is coming back to the domestic scene as well.
Take the eighth and final race of the 2014 season at Kinsale, where Lawrie Smith, the Whitbread Round the World legend and current Irish champion, pipped the all-amateur Dublin Bay crew of Phantom – a 10-year-old boat – in a virtual photo-finish. You can't get better than that for club sport.
Sleek design
There are few better sights in yacht racing than the sleek lines of a fleet of Dragons, with their beautiful hull shape and timeless sail plan.
To sail one is just as great a pleasure. Surprisingly responsive at the helm, the Dragon moves beautifully upwind and downwind in all conditions. If a little over-canvassed in heavier conditions, simply drop the main sheet down the track, crank on more running backstay, and you'll find its performance is very reassuring indeed.
Crew weight is a consideration, but it's not the whole story – and over time Dragon sailors develop a strong body core. Sail trim is aided by fine-tuning on the main and genoa sheets.
Contemporary designs are brilliantly thought-out overall, with modern-specification rigging systems that are second to none.
Running costs
Appropriately enough, the basic running cost of the Dragon sits midway between that of dinghy keelboats and cruiser-class yachts.
At eight metres, it is bigger than the average six-meter dinghy keelboat but a tad smaller than the nine-meter cruisers. The Dragon is dry-sailed, and club parking, like marina berths, tends to be priced on a per-metre basis, so size really counts here.
A new suit of sails for the average Dragon costs up to €5,500 for genoa, spinnaker and main. The difference? That’s about 30 per cent up from the keelboat dinghy, but 30 per cent less than what you’d pay for cruiser racer sails. Again, there’s nothing unfair in any of that. In fact, these figures may come as something of a surprise. Dragon sailors, however, bemoan the common observation that it’s a beautiful boat but unduly expensive.
Outlay
So where’s the catch? Well, a new Dragon, complete with its wonderful German-made trailer, will set the buyer back a cool £82,500 but like any boat there is great value to be had in the second–hand market where a race ready competitive boat could be found for as little €18000.
So yes, a brand new Dragon is not a giveaway, but endure they most certainly do. The level of build quality is truly a testament to the strong professional interest globally that’s driven innovation in the class, particularly over the past 10 to 15 years.
The future
Corinthian sailor Tim Pearson of the Royal St George Yacht Club takes over as international class secretary in 2015, a measure of the esteem in which the Irish fleet is held.
He takes up his role at a time when the class is having much debate about the balance between the amateur side and the professional, where there is no shortage of worldwide participation.
Both sides are expected to mix it up in the busy 2015 season that awaits. Moreover, the endorsement of Kinsale for the 2019 Gold Cup raises the incentive for one of the international fleet's great events to return to Irish waters.
“Another challenge everywhere,” says Pearson, “is to encourage more owners in the 37-year-old age bracket.”
Undoubtedly, changing lifestyles and a proliferation of yacht designs are challenges in themselves to all yacht racing, the Dragon included. But the issue of cost may be particularly misrepresented for this class.
Peter Bowring, co-owner of Phantom, concurs. “The Dragon fleet has possibilities for all comers,” he says. “We just have to fly the ‘D’.”

Close competition during the 2015 Dragon East Coasts – Photo: Michael Keogh
Irish Dragon fleets
Dublin Bay: The Dublin Bay Dragon fleet had 15 active boats in 2014. Not all boats opt to register for club sailing, although the National Championships in Dublin and the Dun Laoghaire Regatta looks set to change that in 2015.
Kinsale: The Kinsale Dragon fleet has a long-standing tradition of competition, and the popularity of the Cork town saw an influx of Abersoch-based Dragons for the 2014 Irish Nationals. In 2012, Kinsale hosted the prestigious Dragon Gold Cup, and the success of that event looks set to win the endorsement of the International Dragon Association for the 2019 event.
Glandore: The Dragon and Glandore are a long-standing family tradition. The fleet celebrates its Corinthian legacy, and the annual Rose Bowl Trophy is often an all-Cork affair between the Kinsale and Glandore fleets. Before the establishment of the Glandore Harbour Yacht Club, the South Coast Championships, which moves by rotation with Kinsale, was hosted by the local hotel.
DRAGON KEELBOAT SPECIFICATIONS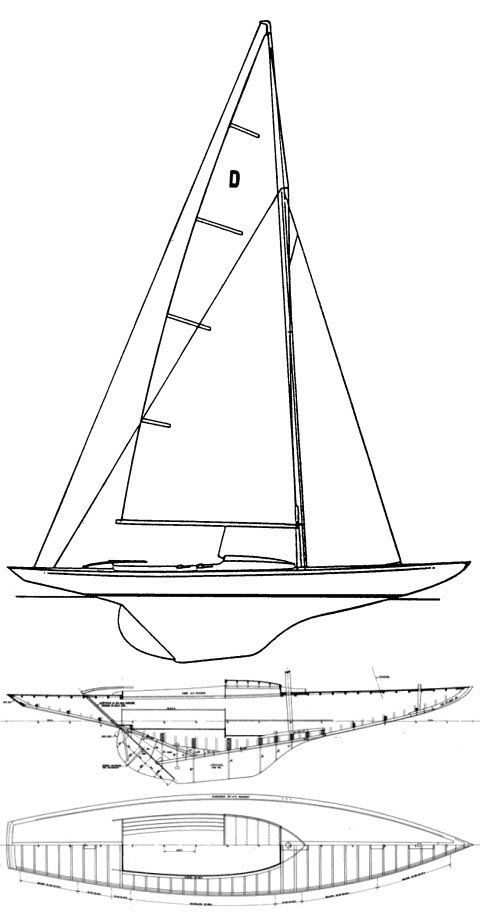
Hull Type: Fin Keel
Rig Type: Fractional Sloop
LOA: 29.17' / 8.89m
LWL:19.00' / 5.79m
Beam: 6.42' / 1.96m
Listed Sail Area: 286 ft2 / 26.57 m2
Draft (max.) 3.92' / 1.19m
Disp. 3740 lbs./ 1696 kgs.
Ballast: 2200 lbs. / 998 kgs.
Designer: Johann Anker
Construction: Wood or FG
First Built: 1928
This article also appears in Summer Afloat magazine 2015
Racing Round Up: Lasers, E Boats, Puppeteers,DBSC, VDLR, Royal Cork, Cove and Sailor of the Month
In Cork Harbour 'Mid-Summer Madness' regatta attracted 40 Boats. We have the photos. There was a Fun Time for Cruisers at Cove Sailing Club's 'At Home' Regatta.
Galway's Martin Breen is June's Sailor of the Month and the Waterford Tall Ships Parade of Sail Photos are here.
Reasons to be cheerful? You bet. Click here to read how Dublin Bay sailors celebrate these wins.





























































