Displaying items by tag: New Terminal
On Merseyside, the new Isle of Man Steam Packet Co. ferry terminal in Liverpool won’t be open in time for this year’s TT.
The £70 million facility at the Princes Half-Tide Dock, where work began in 2019 has been plagued with delays coupled with soaring costs to develop the infrastructure ever since.
According to the Manx Government, which now says it wants to ensure a 'smooth transition' to the new facility and avoid the busiest time of year for the tourism industry.
As Afloat reported fast-craft Manannan which began berthing trials in March, are continuing to take place at the single-berth linkspan facility of the riverside terminal.
Commenting on the new terminal, Infrastructure Minister Tim Crookall said: ‘Ensuring the safety of passengers by enabling the captains to become familiar with the demands of the new berth is of the utmost importance, and it’s therefore vital that the operational requirements of the Steam Packet and its staff are taken into full consideration.
More ManxRadio has a report on this development.
Preparations By Isle of Man Steam Packet to Start Ferry Trials at New Liverpool Terminal
Preparations by the Isle of Man Packet Company reports 3FM are to see the ferry operator start trials and safety training at their new terminal in Liverpool.
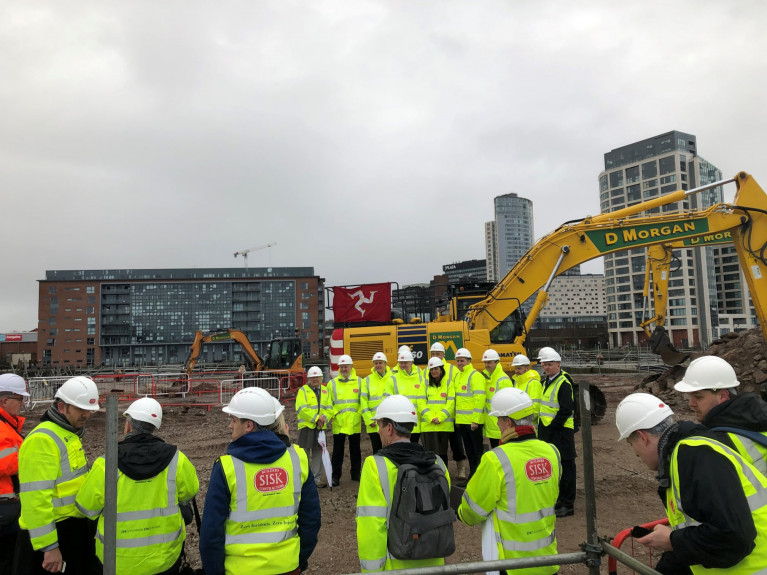
The infrastructure built by a UK arm of the Irish contractor, John Sisk & Co as Afloat previously reported is located at Princes Half Tide Dock. The Department of Infrastructure is also working to ensure the berth will be ready for sea-trials to take place in early March.
This is to see the Steam Packet’s fast-craft, Manannan become the first vessel to berth at the new link-span which is less than a 1 km downriver of The Pier Head, the existing ferry terminal on Merseyside.
As long as such works can be put in place, the company expects the new terminal will be enabled to undertake Manannan’s mooring trials and familiarisation to be concluded towards the end of March.
According to the Steam Packet, the main priority is for Manannan to be in operation from Liverpool also at the end of the same month on the route to Douglas. Should it arise, a contingency plan will be put into effect for its first sailing to take place using the Pier Head terminal.
A fleetmate, flagship Manxman is also to make a debut at the new ferry facility for berthing trials in April, providing that everything goes according to plan. The flagship’s inaugural commercial call, however will be later in the year, when the terminal is scheduled for such sailings in November.
More here on the new Irish Sea terminal.
Stena Line Open New Passenger Terminal in Belfast Harbour following £3m Extension and Upgrade
The largest ferry operator in Northern Ireland Stena Line has opened the doors of its new passenger terminal in Belfast Harbour at Victoria Terminal 2 (VT2).
The new-look passenger terminal has been expanded and refurbished to provide new facilities to cater for the increased passenger levels on the busy Birkenhead (Liverpool) route, with a further £3m investment by Belfast Harbour.
Facilities have seen a significant upgrade with the transformation extended to the original terminal building with new check-in booths for passenger vehicles and includes a full refurbishment of the interior of the terminal.
The development includes a new departure lounge with an increased capacity for approximately 200 people, as well as a new Barista café area and passenger waiting area. Externally, there are three new vehicle check in booths and an extended queueing area for passengers in vehicles and coaches.
Paul Grant, Stena Line’s Irish Sea Trade Director said: “It is great to see the next stage of the investment in our Belfast operations come to fruition. In partnership with Belfast Harbour, we have taken our old and dated building, with limited space, and totally modernised the design with a great new range of improved facilities. Customers using our new modern vessels needed a new modern terminal to serve them and now they have that, to ensure they get the best travel experience from departure to arrival. Over the past 26 years we have grown our Belfast hub into the biggest within the Stena group across all of our European routes, and we will continue to invest and improve our services in Belfast and Northern Ireland.”
Michael Robinson, Port Director at Belfast Harbour, said: “We are really pleased to see the newly refurbished VT2 open to passengers after a significant investment from both Stena Line and Belfast Harbour. We believe that providing modern facilities for our customers and investing in the Port’s core infrastructure is essential to supporting our partners’ ambitions, and to achieving our goal of becoming one of the world’s leading regional ports. As passenger traffic levels on Stena Line’s services continues to grow, we are committed to supporting our partners at Stena Line, as they meet increasing customer demand.”
The VT2 upgrade project took more than a year to complete and was undertaken while maintaining current ferry services. It follows significant investment in recent years by Stena Line in its Belfast operations, with the recent the launches of two brand new ferries on the route, Stena Edda and Stena Embla, which increased passenger and freight capacity by over a third and has now led to record traffic volumes being carried on the Belfast-Birkenhead route.
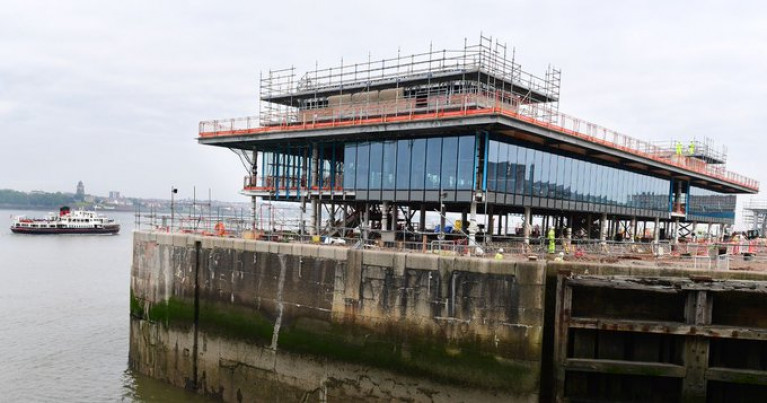
Construction on the brand new Isle of Man ferry terminal in Liverpool is continuing to press ahead with new images showing the latest progress achieved on the project.
Plans for the new terminal were approved by Liverpool City Council ’s planning committee in April 2019. The project, which would see the Isle of Man Steam Packet company continuing to operate ferries from the city, is expected to be completed by June 2023.
Work initially began in November 2019 and was expected to have been completed by August 2021, but delays have seen the completion date moved back.
Once open, the Manx Government will have invested over £70m into the project, having initially estimated it could cost in the region of £38m.
The Manx Government told the ECHO last month that the Covid-19 pandemic was one of the main causes for the delays - with the impacts on the construction industry affecting the development. However significant progress is now being made on the terminal structure.
LiverpoolEcho has more on the new Irish Sea ferry terminal that is to serve the Merseyside-Manx link.
Irish Minister Opens New Dunkirk Terminal As Connections on Ireland-France Routes Reach 44
Minister for European Affairs, Thomas Byrne, is today inaugurating a new Irish terminal at the French ferry port of Dunkirk, with Ireland-France shipping routes rising from 12 before Brexit to 44 now.
It has already handled nearly 50,000 freight units (trucks and un-accompanied containers) moving from Rosslare Europort and back, as exporters side step the UK landbridge since Brexit took effect on 1 January.
"It's basically sold out now with freight lorries," said Minister Byrne.
"The whole port, the [Nord Pas de Calais] region, the [Dunkirk] chamber of commerce, is behind this, to get even more connections to Ireland.
"We only had 12 direct routes to France before Brexit, now it’s 44," he added.
"We are looking as well next summer towards tourism to get Irish tourists into this region, but also of course, tourists from Northern France, Belgium, Holland and Germany. They have more direct routes into Ireland too."
Further reading RTE News reports including the Minister's response to the Northern Ireland protocal.
In addition Afloat's coverage of the latest development of DFDS's Rosslare-Dunkirk route. The direct route to the EU which started the day after Brexit was officialy implemented.
Newly appointed Isle of Man Steam Packet MD says securing the Liverpool ferry route is vital.
As Manx Radio reports, the excessive cost of the new ferry terminal in Liverpool is worrying but will be worth it to secure the future of the Merseyside route.
That's the view of the Steam Packet Company's new managing director after it was announced an additional £13.8m is needed for the project.
It takes the spend to more than £52m - the construction is being overseen by the Department of Infrastructure rather than the ferry operator.
But Brian Thomson says all Manx residents have a right to be concerned.
Click this link to listen to a podcast from the MD including news of the finally reopened Irish route to Dublin Port.
New Ferry Terminal Hub in Liverpool Faces Further Delays
A new ferry terminal along with a promenade both multi-million pound projects funded by the Isle of Man government are facing further delays, reports BBC News.
The terminal in Liverpool, which was originally scheduled to be completed in December, is now set to be finished in January 2022.
The development had been held up due to the impact of Covid-19 on the UK construction industry, Infrastructure Minister Tim Baker said.
The Douglas Promenade revamp is also set to be delayed a further two months.
That project, which was due to be completed by 31 March next year, has faced several hold-ups due to the "complexity" of work underneath the carriageway and would now not be completed until "more towards June", Mr Baker said.
The reopening of Broadway, a major junction onto the promenade that had been due to reopen in September, would now take place on Thursday, he said.
The cost of the refurbishment is still set to remain within the £26m currently allocated for the scheme, he added.
More details on the delays by clicking here.
A new cruise berthing and visitor centre at Greenock Ocean Terminal on the Forth of Clyde, Scotland has been confirmed, it was revealed today.
At its June meeting, the Glasgow City Region City Deal Cabinet approved a contribution of £9.693m from its overall £1bn pot, which is funded equally by the Scottish and UK governments.
The balance of the Marine and Landside Works will be paid for by Greenock Ocean Terminal operator Peel Ports (£8m) and the George Wyllie Foundation via arts funder the Dunard Trust (£1.5m).
The news comes as early stages of site work begins on the overall project, which is led by Peel Ports and Inverclyde Council.
The development, which is scheduled for completion in summer 2020, will boost the number of cruise ship passengers welcomed to Scotland through the successful Greenock facility.
It will allow up to 150,000 passengers per annum to pass through Greenock Ocean Terminal, delivering £26 million in annual visitor and crew spend to the Scottish economy.
In addition to the cruise berthing and the visitor centre designed by Richard Murphy Architects, the plans also include a purpose-built gallery celebrating the work of legendary Inverclyde artist George Wyllie and a restaurant with panoramic views across the Clyde.
Peel Ports Clydeport Port Director Andrew Hemphill said: “The confirmation of City Deal funding comes as the Terminal celebrates its 50th birthday. This overall investment is crucial to the remarkable growth of cruise traffic to Greenock, allowing us to create a welcoming and comfortable environment for passengers.
“Year on year, we are building a major cruise business on the Clyde and, thanks to the success of Greenock Ocean Terminal, more people than ever are taking a cruise to Scotland.
“Who 50 years ago would have anticipated the level of success we’ve had in bringing the world’s biggest container and cruise ships to Greenock? Now we are about to expand our capability further to attract thousands more visitors every year with the new development, up to 150,000 cruise passengers annually. It’s fantastic news for Inverclyde and for Scotland.”
Inverclyde Council Leader Councillor Stephen McCabe said: “The project is part of the Glasgow City Region City Deal and aims to boost the capacity at Greenock Ocean Terminal for cruise ships. The addition of a restaurant and Wyllie Gallery will help to provide a year-round attraction for visitors to Greenock and Inverclyde.
“As a key City Deal project, the new visitor centre at Greenock Ocean Terminal aims to make a significant contribution to economic growth and international tourism across the wider city region area.”
Greenock was named the top UK cruise destination, and placed in Western Europe’s top five, in the second Cruise Critic Cruisers’ Choice Destination Awards by Cruise Critic, a leading cruise review site. It has also been named as the most welcoming cruise terminal.
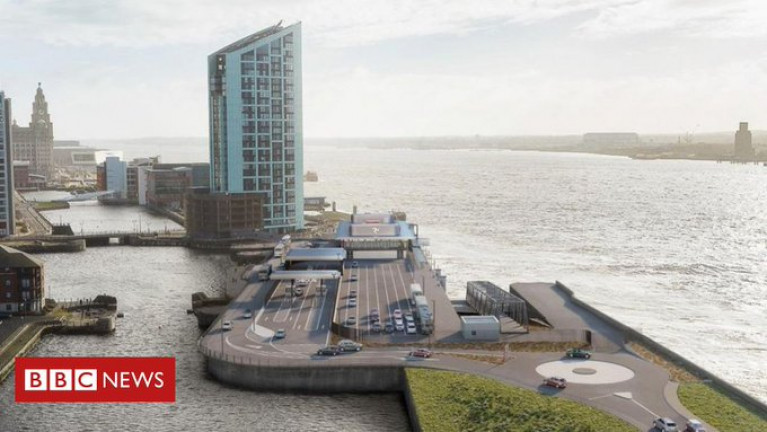
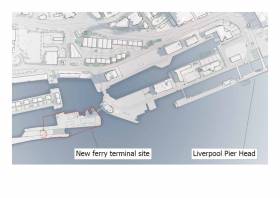
New Ferry Terminal Deal for Isle fo Man Agreed for in Port of Liverpool
#FerryNews - A new ferry terminal for Isle of Man services, BBC News reports could cost up to £30m and open in Liverpool in 2021, the Manx government said.
It will be built half a mile (800m) from the current Pier Head facility at Princes Half-Tide Dock.
Subject to Tynwald approval, the Manx government will sign a long-term leasehold agreement with Peel Land and Property Limited for the site.
Liverpool Mayor Joe Anderson said: "It will cement our strong links with the Isle of Man. I'm delighted."
The existing Pier Head facility is set for a major redevelopment as a cruise liner berth as part of the £5bn Liverpool's Waterfront scheme.
More on the story click here.