Displaying items by tag: sustainability
New Guide to Responsible Boating Is a ‘Call to Action’ Against Plastic Pollution in Oceans and Waterways
EBI, which represents the European boating industry, has teamed up with NGO The SeaCleaners to publish a new Guide to Responsible Boating.
Released on Friday (22 March) to coincide with World Water Day, the comprehensive guide is being touted as “a call to action for boaters worldwide to be involved combatting plastic pollution in our oceans and waterways”.
The guide provides practical recommendations for anyone who enjoys boating or watersports to minimise their environmental impact while enjoying their passion for water.
From reducing plastic consumption to participating in waste collection efforts, they are encouraged to take an active
role in preserving the oceans for future generations.
Stéphanie Poey of The SeaCleaners, an NGO tackling the scourge of plastic pollution, said: “We are proud to partner with EBI, a key player in the boating industry, to get this message across: recreational boating has an environmental impact that is often underestimated.
“Every trip out to sea has consequences for the marine ecosystem and the planet. By adopting the actions set out in this guide, boaters can help preserve the ocean and sail in a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way.”
A Guide to Responsible Boating can be downloaded in both English and French from the EBI website HERE.
The Ocean Race has taken the top prize in the sustainability category of the 2023 International Sports Awards, hosted by the International Sports Convention.
The award recognises the efforts of the race’s Racing with Purpose initiative, which was created with premier partner 11th Hour Racing to put ocean protection at the heart of the round-the-world sailing competition.
11th Hour Racing has a number of Irish connections. Two Kerry women are working on the Racing with Purpose programme: senior advisor is marine biologist Lucy Hunt, founder of the Sea Synergy marine awareness research and activity centre based in Waterville and Cahersiveen, while Rebecca White of Portmagee is an advisor on the learning programme, which is shortlisted for its own sustainability prize next week at the Reimagine Education Awards. And Kerry offshore racing veteran Damian Foxall is sustainability programme manager of 11th Hour Racing Team, the winning IMOCA in the latest edition of The Ocean Race.
Hosting an event that was as sustainable as possible was imperative in the race’s goals for its 2022-23 edition. Through a series of measures, the race reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by 75% compared with the previous edition.
It was also powered entirely by renewable energy, and the race’s plastic footprint was measured in a first for any major sporting event.
Inspiring the next generation is also a key element of Racing with Purpose, with learning programmes in host cities via on-the-ground workshops.
Richard Brisius, race chairman at The Ocean Race said: “Sport has the potential to unify, educate and inspire in ways that can make a meaningful difference. For The Ocean Race, we’ve used our platform and created new opportunities to reach as many audiences as possible, from fans and children to business leaders and heads of state, in order to accelerate action to protect the planet.
“We’re delighted that our efforts have been recognised by the International Sports Awards. It is thanks to the unprecedented spirit of collaboration with our fantastic network of sailing teams, host cities, partners, stakeholders and many other ocean advocates during this edition of the Race that our Racing with Purpose sustainability programme has been able to create such impact.
“And last, but definitely not least, it is thanks to the relentless dedication, expertise and hard work by The Ocean Race team.”
The International Sports Awards take place each year to celebrate “the finest sports work in the world”. The Sustainability Award trophy will be presented at the International Sports Convention which takes place in London from 20-21 March 2024.
This article was updated on Friday 8 December to clarify that Damian Foxall is sustainability manager of 11th Hour Racing Team, not the title sponsor 11th Hour Racing, and to add other Irish connections.
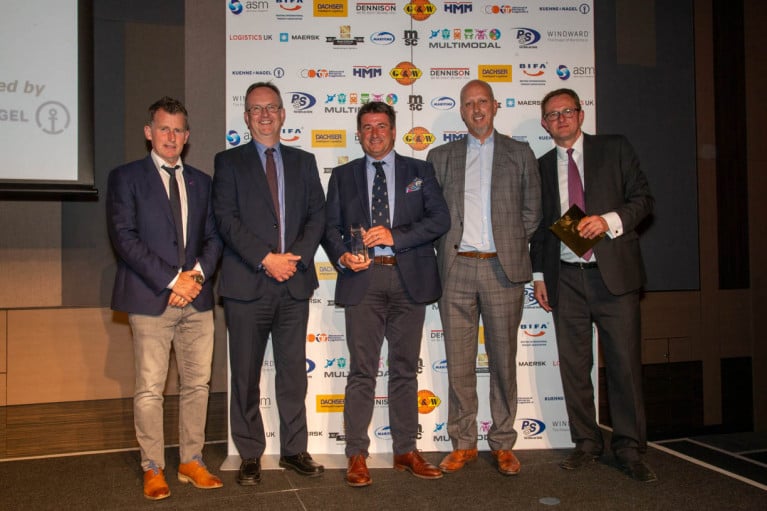
Operator of Liverpool Port, Peel Ports Group Achieves New Sustainability Accolade at Multimodal Awards
In the UK, the Peel Ports Group has been recognised as the winner of the ‘Sustainability’ category at the 2022 Multimodal Awards in acknowledgement of its impressive environmental efforts.
As one of the country's largest port groups, Peel Ports manages several key regional trading hubs, including major facilities in Liverpool and Manchester, Heysham, London Medway, Great Yarmouth and Glasgow. In addition across the Irish Sea at Dublin Port,it also operates a container terminal (MTL) and owns BG Freight Line, which provides short sea container services between the UK, Ireland and mainland Europe.
The leading port operator emerged victorious amongst a credible line-up of finalists, including Maersk, ONE and Howard Tenens Logistics, thanks to its commitment to drive a more sustainable future via the pledge to be a carbon neutral business by 2040.
The award acknowledges steps taken by the group to become the first port operator to make such a commitment towards a Net-Zero status, and recognises its ongoing work to lower emissions.
Recent adoptions include switching the vast majority of its fleet to electric vehicles and transitioning machinery and plant equipment to the environmentally-friendly diesel fuel alternative, Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO).
This transition to HVO recently saw the group hit the million-litre milestone as the first port operator to make the change, representing a third of the Port of Liverpool’s entire annual fuel consumption and in partnership with local Merseyside supplier County Oil Group Ltd.
More than £1.2bn has also been invested across the last decade on sustainable infrastructure and technology to futureproof operations, including the delivery of energy-efficient cranes, LED lighting and working with sustainable suppliers and equipment.
Claudio Veritiero, CEO of Peel Ports Group commented: “Peel Ports has taken industry leading steps to decarbonise our future and it’s fantastic to see this publicly recognised. Winning the Multimodal Sustainability award and being acknowledged for our efforts amongst our peers reinforces our continued drive towards becoming the leading sustainable port operator in the UK”
“Our goal is to be a sustainable business that can enable a positive future for the UK’s supply chain, driving change for the better whilst achieving commercial goals and business growth. The collective efforts of our employees and the strategic drive of the teams behind much of this change have been key to this success, so this award is a testament to their hard work”
At a meeting between the European Sea Ports Organisation (ESPO) and global trade association Interferry, a common work programme was agreed to promote an environmentally sustainable future for the European ferry business through the provision and use of onshore power supply (OPS).
Underlining the shared challenges and priorities of their Europe-wide memberships, ESPO and Interferry confirmed the following joint approach:
1. Ferries must be recognised as a sustainable passenger transport mode that link Europe’s cities and regions, as well as providing a green mode of urban transport. This should be better reflected in Europe’s transport policy, in particular in Flagship 3 of the European Commission (EC) Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy (available here).
2. Ferry ports should act as soon as possible to deploy OPS, and ferry lines should commit to using OPS whenever it is available. The agreement notes that, increasingly, many ferries will use OPS not only for their energy consumption at berth, but also to recharge batteries for propulsion – prompting significantly higher power demand that will require corresponding upscaling of the grid network.
3. To optimise the effective deployment and use of OPS for the ferry industry, investments should initially be made where it makes most sense in terms of maximising emissions reductions per installation. Accordingly, first priority for OPS development should be given to ferry terminals with high frequency of operation, as opposed to those with only occasional ferry calls. The OPS obligations set out in the EC proposals for Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR), which refer to a specified minimum number of calls per port, should therefore be adapted to foresee a minimum number of calls per terminal.
4. The exemptions to the OPS requirements under FuelEU Maritime and AFIR should be aligned to ensure the effective deployment and use of OPS. Both ports and ferries call for a coherent and predictable framework that provides legal certainty for stakeholders.
5. Since greening the shipping sector and deploying OPS in ports will require huge investments, revenues from a maritime European Union (EU) Emissions Trading System, or any similar market-based measure, should go towards funding OPS deployment through a dedicated fund benefitting both the ports and shipping sectors.
6. New fuels and technologies for greening the shipping industry should be encouraged and promoted, alongside development of the relevant safety and operational standards. The accompanying financial and regulatory framework should be technology-agnostic to ensure due consideration for all viable options. With the exception of OPS, at this early stage it does not seem desirable to impose a requirement to deploy infrastructure for certain other technologies or fuels. Developments and investments should be based on bottom-up projects and bilateral commitments among different stakeholders.
7. An EU-wide permanent and total tax exemption for electricity provided to ships at berth should be introduced in the Energy Taxation Directive in order to provide stronger and clearer incentives that promote the uptake and use of OPS.
Interferry CEO Mike Corrigan comments: “Electrification of ship propulsion is key to meeting massive regulatory challenges for reducing maritime greenhouse gas emissions - interim cuts of some 50% are due by 2030, leading to ‘net zero’ status by 2050. Ferries are already leading the shipping industry’s transition to hybrid and fully electric systems, but major expansion of the electricity grid network is absolutely crucial to supporting the ultimate objectives. To this end, Interferry has embarked on a schedule of meetings with senior decision makers from governments, ports and energy companies to urge investment in OPS infrastructure. I very much value our collaboration with ESPO to work on mutual sustainability ambitions".
ESPO Secretary-General Isabelle Ryckbost concludes: “Ports in Europe are very eager to move forward in achieving the decarbonisation goals and progressing their green priorities. The greening of shipping is a priority for ports. The best way to go forward is to engage in dialogue with the different stakeholders. Each segment has its own priorities and solutions. I am very happy we started this dialogue a few months ago with Interferry and can now engage together on an efficient way to reduce emissions at berth. Moreover, the role ferry transport can play in greening passenger transport in Europe is severely underestimated. Ferries are connecting people, regions and economies. I’m happy to continue the discussions with Interferry”.
Save Our Seafront Holding Public Meeting on Ireland’s Sustainable Future
Dun Laoghaire campaign group Save Our Seafront is holding a public meeting at the Royal Marine Hotel on Monday 1 November on the topic of Ireland’s sustainable future.
From 7.30pm all are welcome to join the discussion on how Ireland can best protect its marine resources while simultaneously developing renewable resources in a sustainable and responsible way.
Speakers will include Richard Boyd Barrett TD, Fergal McLoughlin of An Taisce and Valerie Freeman of the Coastal Concern Alliance.
Attendees are also welcome to join remotely via Zoom; register for the access details HERE.
 A Save Our Seafront poster advertising the public meeting at 7.30pm on November 1st at the Royal Marine Hotel
A Save Our Seafront poster advertising the public meeting at 7.30pm on November 1st at the Royal Marine Hotel
Boat Builders Want More Sustainable Industry, Says Ocean Race Survey
An overwhelming number of people working in the sailing and boat building industry say they want the field to become more sustainable.
And nine out of 10 respondents to the survey by The Ocean Race feel that not enough is being done to reduce the environmental impact in their area.
The survey results were shared today (Tuesday 14 September) at The Ocean Race’s Innovation Workshop on Sustainable Boat Building in Lorient.
This third in the series of workshops on the subject brought together 100 participants — including boat builders and designers, sailors, NGOs, universities, sponsors and federations, both in situ and remotely — to tackle the main challenges that need to be met for the boat-building industry to become more sustainable.
Anne-Cécile Turner, sustainability director at The Ocean Race, said: “Competitive sailing has been focused on speed and performance for years, but building the boats remains material, energy and waste intensive. This urgently needs to change.
“The world has just nine years to halve greenhouse gas emissions to be on track with the global ambition to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2030 and prevent even more catastrophic climate change.
“Currently, the boat-building industry is not on target to achieve this, but it isn’t too late. By collaborating and committing to change we can slash emissions and show real leadership as an industry.”
Damian Foxall — Co Kerry round-the-world sailor and sustainability programme manager for 11th Hour Racing Team — also spoke at the event, following the launch of the team’s new IMOCA 60 last month, which has been built in preparation for the next edition of The Ocean Race in 2022-23.
Aiming to set a benchmark for sustainable boat building, a range of techniques have been used to reduce the impact of the new vessel, including substituting highly-polluting materials with new alternatives, reducing single-use elements and refining the boat’s shape to make it more energy-efficient.
 11th Hour Racing Team’s new boat is hoisted at the boatyard of MerConcept in Concarneau | Credit: Amory Ross
11th Hour Racing Team’s new boat is hoisted at the boatyard of MerConcept in Concarneau | Credit: Amory Ross
Ahead of the workshop, Foxall said: “Our approach to the build of our new IMOCA 60 has been to measure everything — from the energy used in the design, computations and construction, to the material usage and the waste.
“By measuring our footprint, we can manage our approach to reducing it through introducing alternative materials, processes and innovations. We now have a benchmark for our IMOCA 60 build which can be used for future builds within the class.”
The survey identified three main barriers to change: a lack of technical knowledge of alternative materials; lack of funding for research and development; and concern that sustainable developments could affect boat speed.
When asked what would motivate them to create more sustainable boats, increased demand from clients comes out top among those surveyed. Six out of 10 feel that this will drive change, followed by a better selection of sustainable products and changes to the racing rules, with half of respondents stating that these factors would make a difference. More industry collaboration is also cited by four in 10.
The Ocean Race has introduced specific rules to help drive teams to be more sustainable. For the 2022-23 edition of the race, teams will be required to generate at least 30% of the energy they use on board through renewable energy sources (hydro, wind, solar) and may be asked to carry scientific equipment onboard to gather data about the state of the ocean.
It’s hoped that these rule changes will help inspire solutions for 100% renewable energy to manage life on board, as well as new construction materials and technologies that have minimal environmental impacts.
The survey, which was conducted by The Ocean Race in August and September 2021, was sent to 100 people in the sailing and boat building industry and supported by 40 stakeholder consultation calls to deep dive into industry barriers and enablers.
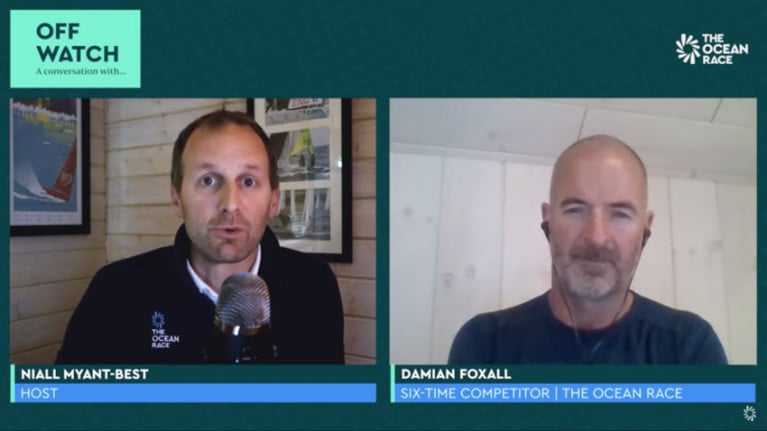
In Conversation With Damian Foxall: ‘You Can Take A Sailor Off The Water But Not For Very Long’
The latest edition of The Ocean Race’s Off Watch video interview series sits down with Damian Foxall, Irish veteran of the yachting challenge formerly known as the Volvo Ocean Race.
Kerryman Damian Foxall has competed in the round-the-world race six times, including a winning campaign in the 2011-12 edition.
In more recent years, he’s charted a new course as an advocate for sustainability both in the sport of sailing and the world in general.
But in his own words: “You can take a sailor off the water but not for very long.”
Here he tells Niall Myant-Best how how listening to glaciers shearing off Antarctica during an expedition last year gave him a new respect for sea ice, and about his pride in sailing into Galway as part of the winning Groupama team and helping to raise the profile of sailing in his homeland.
He also steers into choppier waters, such as how winning does come with costs — to family, to the environment — that he’s hoping to change through his work in sustainability for 11th Hour Racing and with Irish Sailing.
Watch the full interview below:
Sustainability To The Fore At This Weekend’s RYANI Youth Championships
Youth sailors from all over Northern Ireland are getting ready for RYANI’s Youth Championships weekend at Strangford Lough Yacht Club from today, Saturday 21 September, with over 160 sailors competing for the coveted Northern Ireland Schools Cup and Club Trophy.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, this is the 30th year of the popular competition — and this year there is a focus on reducing plastic and ensuring the event is more environmentally sustainable in line with The Green Blue Charter.
In 2018, The Green Blue and RYANI delivered a series of workshops to educate clubs and instructors in Strangford Lough on the importance of protecting marine habitats and species in this area of natural beauty.
A new-look website has also recently been launched which provides useful resources as well as educational activities for young boaters that can be delivered on the water and onshore.
The most popular of these is Marine CSI, which gives young people the chance to become marine ‘special agents’ by analysing fingerprints, unscrambling puzzles and testing water samples.
By working towards an environmentally self-regulating boating community, The Green Blue aims to help boaters minimise the impact they have on the environment and protect wildlife and its habitats so they can enjoy the marine environment far into the future.
#ferries - Artificial Intelligence (AI) assisted vessels to save fuel, battery power propulsion, huge reduction of single use plastic on board, continued low level of crew and passenger accidents and an increased rate of female leaders. These are some of the highlights in leading ferry company Stena Lines sustainability review for 2018.
The ferry operator has now released its third sustainability review “A Sustainable Journey” describing initiatives, improvements and challenges in the operations from the sustainability perspective as well as results on their ambitious sustainability targets. The review also highlights the main initiatives the company has worked on during the past year.
Stena Line CEO Niclas Mårtensson said: “With size comes responsibility and our ambition is to improve our operations every year to become a leader in sustainable shipping. The past year we have had exiting developments pairing artificial intelligence with the know-how of our experienced employees on-board as well as increased focus on electrification. We have continued our efforts within crew and passenger safety as well as launching a new initiative for more diversity in our operations. This is a very exciting time for our company and I’m proud that Stena Line continues help shape the industry for European short-sea transportation.”
A sustainability strategy for Stena is divided into five focus areas tied to the UN Global Goals for sustainable development with ambitious targets set in each focus area. They are Equality & Inclusion, Good Health & Wellbeing, Clean Energy, Responsible Consumption, Life Below Water.
“We have more than 5,500 employees who all make big and small contributions towards our sustainability targets and it’s great to see that we are making good progress in many areas while maintaining a safe and efficient operation. Our industry has a big challenge with our fossil dependence and our total carbon emissions increased in line with freight volumes so we have more to do in this area. The initiatives started within electrification are relatively new to our industry but extremely important going forward as we gradually move to low-carbon operations,”said Erik Lewenhaupt, Head of Sustainability.
The full review can be found through this link which leads to a download pdf file.
On Earth Day (Monday 22 April) The Ocean Race and 11th Hour Racing have forged a partnership that aims to bring sustainability initiatives to the heart of the race.
The Ocean Race says it is building on its position as the sustainability leader in global sport by announcing a visionary partnership with 11th Hour Racing — the largest of its kind in sport.
The legendary round-the-world sailing event and its premier partner will focus on a broad range of initiatives to promote the restoration of ocean health, embedding sustainability in all event operations.
As part of this ‘Racing with Purpose’ initiative, the partners have committed to a comprehensive action plan to initially:
- Convene 11 Ocean Race Summits and Innovation Workshops, focused on ocean health, with the first being held in Europe in September 2019.
- Work with experts and sailing teams to explore the use of state-of-the-art renewable energy systems onboard the IMOCA 60 and VO65 classes during the next edition of The Ocean Race in 2021.
- Inspire school children around the world to take action for the ocean through a multi-lingual, curriculum-based, education programme, to be released in May 2019.
- Continue the powerful science program developed in the last Ocean Race, which gathered critical oceanographic and microplastics data, and examine ways that all teams are able to participate in this groundbreaking research.
- Inspire millions of Race Village visitors with the possibility of a sustainable world through interactive experiences at each stopover.
Johan Salen, managing director of The Ocean Race, said: “Through this partnership with 11th Hour Racing, and by harnessing the power of sport, we are using our collective global influence and extensive networks to reach millions of people to affect meaningful, long-term change for ocean health.
“The sailing community has a deep connection with the sea so it’s natural that we would work together to safeguard its future. The integration of our collective vision within every area of our operations will engage and inspire the wider sailing community, teams, our stakeholders and suppliers, future host cities, schoolchildren and, of course, the race fans to take decisive action on this urgent issue.”
11th Hour Racing says it works with the sailing community and maritime industries to advance solutions that protect and restore the health of our oceans.
The renewed and expanded partnership is intended to build on the momentum of the multi-award winning Sustainability Programme, featured in the past edition of the race, of which 11th Hour Racing was the founding principal partner.
“11th Hour Racing has developed an impact-driven model with sustainability at the core of all of its programs,” said Wendy Schmidt, co-founder of 11th Hour Racing and president of The Schmidt Family Foundation.
“During the last edition of this iconic race around the planet, we raised visibility with the race crews, fans and students all over the world about the breadth of issues threatening the oceans and innovative solutions to address them, some that we already can put into practice. These efforts were a powerful catalyst for positive action.
‘This is a unique opportunity to create a coalition between sport, business, and policymakers.’
"Together, we have the power to deliver science and sustainability through the platform of sport. 11th Hour Racing is excited to continue its collaboration with The Ocean Race to create one of the most forward thinking and unique sport sponsorships of our time.”
The Ocean Race Summits aim to provide a platform that uses a mix of storytelling and groundbreaking announcements to help advance solutions to environmental issues. Industry-led Innovation Workshops will explore ways to evolve business models and reduce impact on the environment.
Growing the Learning Programme, used during the previous race by more than 110,000 children in 41 countries, a new science and sailing module will be launched this spring. This will provide the next generation with the tools to become future ocean advocates.