Displaying items by tag: survey
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) is relying on the knowledge and experience as a ‘citizen scientist’ anglers in a new survey about less well-known fish species.
Some migratory fish species like salmon and lesser-known species such as shad and the extremely rare sturgeon, among others, are in decline in many European countries. These species spend much of their lifecycle at sea and periods in riverine habitats.
As part of the multinational European project DiadES, IFI and other project partners are assessing the recreational fishing interest in several of these species including shad, thin-lipped mullet, smelt and flounder via an online survey which will also record the economic benefits that the species support.
Dr William Roche, senior research officer at IFI, said: “We are urging anglers who fish for these species to participate in this online survey as it will help us get a more comprehensive view of these less common species in Irish waters.
“In this way we can contribute to providing better information to inform future policy and management of these species, and the economic, social and cultural activities associated with them.”
Future predictions suggest that some of these species will see northward and southward changes in distribution under climate change scenarios, IFI says.
This may increase or decrease their availability to recreational fishing and the economic benefits they bring to businesses in local areas, as well as the enjoyment and associated health and social benefits for fishers.
The online survey consists of questions about fish-catching activities and will take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
In Ireland the DiadES case study area comprises the Suir, Nore and Barrow Rivers and the Waterford Harbour catchment but IFI is also seeking details on the named fish species generally within Ireland.
Sea Angling Survey to Document Changes in Catch Over the Years
A new online survey aims to collect changes in sea anglers’ catches in Ireland’s coastal waters over time.
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) says anglers participating in the survey will contribute towards understanding changes in angling species here.
Ireland’s sea angling resource ranges from tope in the Irish Sea to bass on the surf beaches of the Dingle Peninsula.
These fisheries attract many local anglers along with visitors from around the world. The new survey aims to track and inform possible long-term changes in the coastal fish populations targeted by anglers.
Dr William Roche, senior research officer at IFI, said: “We are looking for sea anglers of all ages and experience to take part in our new survey programme to help us to understand possible trends and changes in catch over the years.
“We know that anglers have expert localised knowledge from spending time outside observing nature and the fish they catch.
“Over a sea-angling career, this experience becomes a unique insight into the state of coastal fisheries and we want to reach out to those who have localised knowledge and care about the future of our fisheries resource to help us to understand how it has changed.”
IFI says the success of the study “relies on the knowledge, experience and observations of citizen scientist anglers. The survey has been carefully formulated to capture this knowledge and allow it to be expressed as indicators of the current state of our important fish populations.”
Each unique respondent will also be entered into a prize draw to win a voucher of up to €200 for their local angling tackle shop.
The International Maritime Rescue Federation (IMRF) to mark International Women's Day, has revealed its results of the first survey to examine the representation of women across the maritime search and rescue (SAR) sector.
The #WomenInSAR survey, which was supported by Trinity House, attracted more than 1600 participants from women and men in 48 different countries. The research sought to explore the challenges and barriers faced by women in maritime SAR, along with their personal aims, any experiences of discrimination, and factors affecting recruitment and retention.
Theresa Crossley, CEO, IMRF said: “The theme for International Women’s Day this year is ‘choose to challenge’. It’s remarkably appropriate, as most of the women and men who completed the survey felt that one of the biggest barriers to more women entering maritime SAR, was the perception that it’s a man’s world.
“Male dominance remains a fact in the maritime sector in general and maritime SAR is no different. This can have an indirect discriminatory effect, for example in terms of the facilities and equipment provided. Many of the respondents said that ‘you need to see it to be it’ - there are still not enough women in senior roles, or not enough pictures of women in SAR recruitment, training and promotional materials – perpetuating the myth that SAR is just for men. As one respondent said: ‘We don’t need men or women - we just need crew.’”
Captain Ian McNaught, Deputy Master of Trinity House added: “Trinity House is a charity dedicated to safeguarding shipping and seafarers and we have been providing education, support and welfare to the seafaring community for more than 500 years. Women and men working in maritime search and rescue save the lives of those in trouble at sea, providing a vital service. In today’s world, it is only right that women should be equally represented across all roles and we are proud to support this initiative.”
For the majority of women who responded to the survey, the reasons for becoming involved in SAR were generally the same as for male respondents and a significant majority of women questioned did not report any experience of direct gender discrimination. However, a significant minority of women respondents reported that issues related to both direct, or indirect, gender discrimination were among the most challenging aspects of their SAR work. Quite a few women still felt the need to outperform men to be taken seriously.
The IMRF launched its #WomenInSAR initiative in June 2019, to increase the representation of women in maritime SAR and provide support for women and girls involved in the sector. The results of this survey, the first of its kind, will help the IMRF to focus its efforts on improving awareness of, and access to, the opportunities available to women in maritime SAR.
The IMRF is now planning a #WomenInSAR STEM event to highlight the opportunities open to women, showcasing international female trailblazers and intends to introduce a mentoring scheme for women in SAR. The organisation is also calling for nominations to be submitted for the IMRF Awards, specifically the #WomenInSAR Award which is presented to someone who has made a major contribution to improving opportunities for women in the sector.
Theresa Crossley concludes: “Over and over again, it’s been proved that organisations with an equal balance of men and women are more successful. Maritime SAR has been traditionally a male preserve. Although much has changed over recent years, we’ve still got a way to go. Gender diversity makes sense on every level – we need to make it happen. We’re ‘choosing to challenge’ the perceptions and aiming for equality.”
The report was launched via an online webinar open to anyone in the industry, and is free to download from the IMRF website here.
The IMRF as the only maritime SAR organisation with consultative status at the International Maritime Organization (IMO), will be sharing the results with the IMO in support of its Women in Maritime initiative.
Subsea Cable Survey Operations Off South-East Coast
Mariners off the South-East Coast of Ireland are advised of subsea cable survey operations currently under way, subject to weather conditions.
The survey was scheduled to begin this past Thursday 26 November and continue for at least eight days and up to two weeks.
It follows a route south-west from the 2m contour at Ballyteige Bay before veering south to the 12-nautical-mile limit.
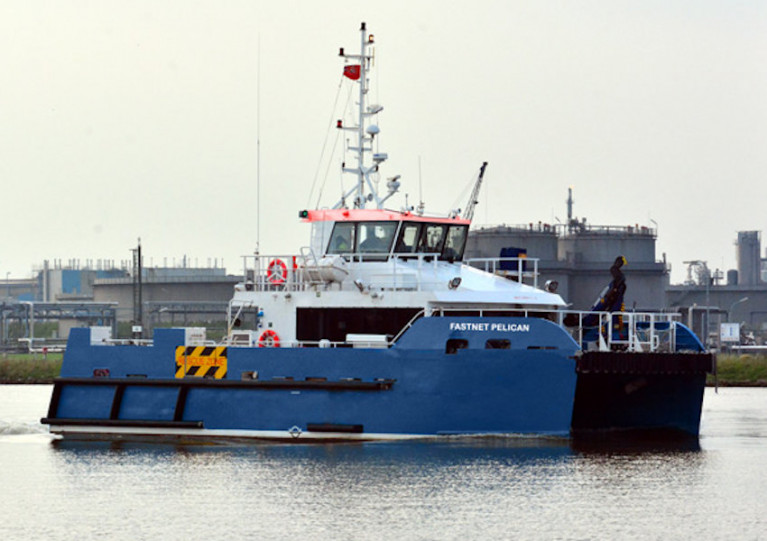
The DNV-classed wind farm service and survey support vessel Fastnet Pelican (Callsign 2FNX7) is conducting this survey using a multibeam echo sounder and sub bottom profiler as well as a towed array with a sidescan sonar and magnetometer.
The vessel will have active AIS and will display all relevant lights and shapes.
Due to restricted manoeuvrability, other vessels are asked to maintain a distance of at least one nautical mile from the Fastnet Pelican.
Full details of this survey, including all relevant coordinates, are included in Marine Notice No 54 of 2020, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
New Survey Asks Public To Share Views On Irish Seascapes
The people of Ireland are being invited to share their views on Irish coastal seascapes.
And the feedback gathered will inform Ireland’s Seascape Character Assessment Report, a key technical study for the National Marine Planning Framework.
The new survey follows an online poll this past summer to help classify and describe the essential character of Ireland’s coastal areas and communities.
The responses gathered have informed a draft assessment on which the Marine Institute is now seeking public input — from today, Wednesday 7 October, to Friday 30 October.
“Seascapes are very much about the relationship between people and place and how humans have settled and interacted in and along our coastline — from the earliest inhabitants on this island right up to today,” said Caitríona Nic Aonghusa, manager of marine spatial planning at the Marine Institute.
“By identifying, classifying and describing our seascape character in a holistic way, we can provide a baseline to better inform the planning and management of our seascapes.”
In addition to the public survey, a series of online workshops will be held for those interested in further discussion of the draft assessment.
These will take place next week, on Monday 12 October from 2pm–3pm and Tuesday 13 and Wednesday 14 October from 8pm–9pm. To attend any of these online workshops, email [email protected]
And to celebrate and raise awareness of International Landscape Day on Tuesday 20 October, the Marine Institute is also encouraging people across the island of Ireland to share photographs of seascapes on social media.
Post your photos of Ireland’s seascapes on that date on social media with #IrishSeascapes and tag the Marine Institute on Twitter or Facebook.
Galway Seabed Survey for Submarine Fibre Cable Between Iceland & Ireland
Iceland has selected Galway as the European landing location for international telecommunications cables.
Farice, a company fully owned by the Icelandic Government, currently owns and operates two submarine cables linking Iceland to Northern Europe.
It has been undertaking preparatory work for a new submarine fibre cable from Iceland to Europe since early 2019.
A survey ship named Ridley is now exploring suitable seabed approaches from Galway out to the boundary of the Irish exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
 The 58-metre Ridley Thomas (IMO: 8112744) is a Research/Survey Vessel built in 1981
The 58-metre Ridley Thomas (IMO: 8112744) is a Research/Survey Vessel built in 1981
Farice chief executive officer Thorvardur Sveinsson said that “after careful consideration of many factors, Galway was selected by Farice as the European cable landing location”.
“The Icelandic landing site will be on the Reykjanes peninsula with the final location to be decided during the winter 2020/2021,” he said.
“ This coupled with Galway’s reputation for business, education and hospitality will lead to a win-win situation. The enhanced global activity provided by the system will be a catalyst for attracting high tech business to the city and the regions,” he said.
The company said the project could result in a new submarine fibre cable between Iceland and Ireland becoming operational within two years from financing being secured.
“Ireland has many important attributes that make it attractive as a destination for this new cable from Iceland, over and above the relatively short distance between the two countries,” Mr Sveinsson explained.
 Ireland is at the nexus of new trans-Atlantic connections - A map showing the new cable route between Iceland and Ireland that could be operational within two years
Ireland is at the nexus of new trans-Atlantic connections - A map showing the new cable route between Iceland and Ireland that could be operational within two years
“Ireland is at the nexus of new trans-Atlantic connections, is a centre of choice for European operations for many international businesses and has a rich and diverse pool of skilled labour in its workforce. Ireland has thus firmly established itself at the forefront of the development of Europe’s digital infrastructure and as such is an important connection point for a new submarine cable between Iceland and Europe,” he said.
“It is often perceived that international telecommunications are carried out by satellite. This is a common misconception and in reality, the vast majority of global communications is carried on fibre optic cables and particularly sub-sea cables,” he explained.
“The capacity of such cables is quite incredible and a single pair of fibre strands could satisfy the demands of most of Galway city,” he said.
“Due to the very high capacity of modern systems, subsea fibre cables are incredibly small in size (approx. 25mm diameter) and are very fast and non-intrusive to install. The overall benefits greatly outweigh the short-term inconvenience during the installation,” he said.
“The presence of the Farice system landing in Galway will provide direct high capacity links to Iceland but also to Northern Europe via Denmark and the UK and will greatly increase capacity and connectivity in Galway city and the regions,” he added.
The company currently operates the FARICE-1 cable between Iceland and Scotland with a branch connection to the Faroe Islands and the DANICE submarine cable between Iceland and Denmark.
A third submarine cable Greenland-Connect links Iceland to Canada and US. The Icelandic government said the fourth cable would “increase further the security and resiliency of Iceland’s international telecommunications.”
The new cable could cost up to €2 million during the research phase, with the actual laying estimated last year at around 32 million US dollars.
Irish Maritime Administration Launches Engagement Survey
A new survey from the Irish Maritime Administration (IMA) of the Department of Transport encourages feedback regarding its communication with stakeholders and service users.
Marine Notices are one method used to communicate important information by the IMA and its divisions, which include the Marine Survey Office, Maritime Transport Division, Maritime Safety Policy Division, Marine Mercantile Office, Maritime Service Division and the Irish Coast Guard.
“The survey is an opportunity for you to provide helpful feedback and will assist the IMA to improve how communicate sand engages with its many and varied stakeholders and service users,” the administration says.
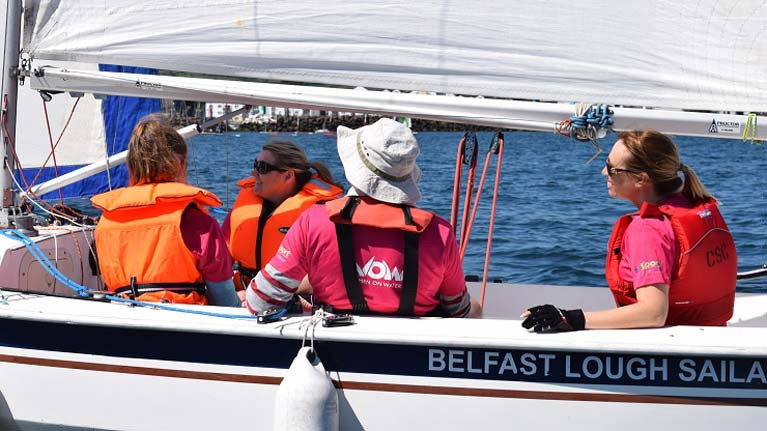
RYANI Wants Feedback On ‘Women On Water’ Programme
RYA Northern Ireland is calling for women across Northern Ireland to give feedback on its Women on Water programme.
The governing body hopes to find out what boaters want through a development survey, which will help to shape future programmes.
The Women on Water initiative began in 2016, allowing over 500 female participants to get on the water and 12 clubs supporting the programme.
RYA Northern Ireland’s active clubs co-ordinator Lisa McCaffrey said: “To expand the Women on Water programme we want to find out about our boaters aspirations.
“We are calling on as many female boaters as possible to complete the 10-minute survey so that we can find out exactly what will work best.
“The programme has been extremely successful over the last three years and we are now working on progressing Women on Water with the aim of developing our female workforce. We hope to provide a programme that helps support the development of RYA coaches/officials and instructors.
“This is an exciting opportunity to assist our boating community with increasing their skills and qualifications.”
Over the last three years, participants of the Women on Water programme have had many achievements, including:
- A Women on Water Leader Group who organise and run a Women on Water Festival and help to support the development of the programme at clubs across Northern Ireland.
- At Strangford Lough Yacht Club, six women completed the Women on Water programme in June 2018 and went on to win the regatta series at their club in the same year.
- Two Women on Water graduates were due to take part in their first GP14 class World Championship in 2020.
- One participant is going on to become an Advanced Powerboat Instructor.
- Many of the graduates regularly volunteer at their clubs on committees, as well as being race officials and providing event support.
McCaffrey added: “RYA Northern Ireland is asking for any female that is involved in boating in Northern Ireland to take part in the survey, whether you have been a lifelong boater, completed a Women on Water programme since 2016 or a sailing course, we want to hear from you.”
Online Survey To Help Classify Ireland’s Seascapes
A new online survey aims to deepen our understanding of Ireland’s ‘seascapes’.
Commissioned by the Marine Institute, the survey seeks responses from the public that will help identify classify and describe Ireland’s the essential character of Ireland’s coastal areas and communities.
The end results, including a final report and maps, will support the implementation of the National Marine Planning Framework.
“Seascapes are an important part of our sense of identity and culture,” the Marine Institute says. “Our experience of the character of seascapes includes coastal and marine history, folklore, art, nature and recreational and commercial activities that take place on and close to the sea.
“Seascapes can also include views from land to sea, from sea to land and along the coastline. When we describe seascape character, we are essentially talking about a sense of place — what makes one part of our sea and coast distinctive and different from another?
“Often this relates to natural influences such as the rock type, depth of sea and coastline, the force of the sea and how humans have settled and interacted in and along our seascapes – from the earliest inhabitants on this island right up to today.”
Minogue and Associates have been commissioned to carry out the study and get a better understanding of how Irish people value the coast and seas.
The short online survey aims to capture thoughts and comments about the seascapes that you are familiar with, and asks you to indicate on a map where these are. The survey is completely anonymous and the information will be used only to identify draft Seascape Character Areas.
Additionally, the research team hopes to facilitate small, online group-based discussions on the draft areas over the month of July, using online resources. Register your interest (name/interest/organisation) by emailing [email protected]
Irish Anglerfish & Megrim Survey 2020 Set To Begin Next Weekend
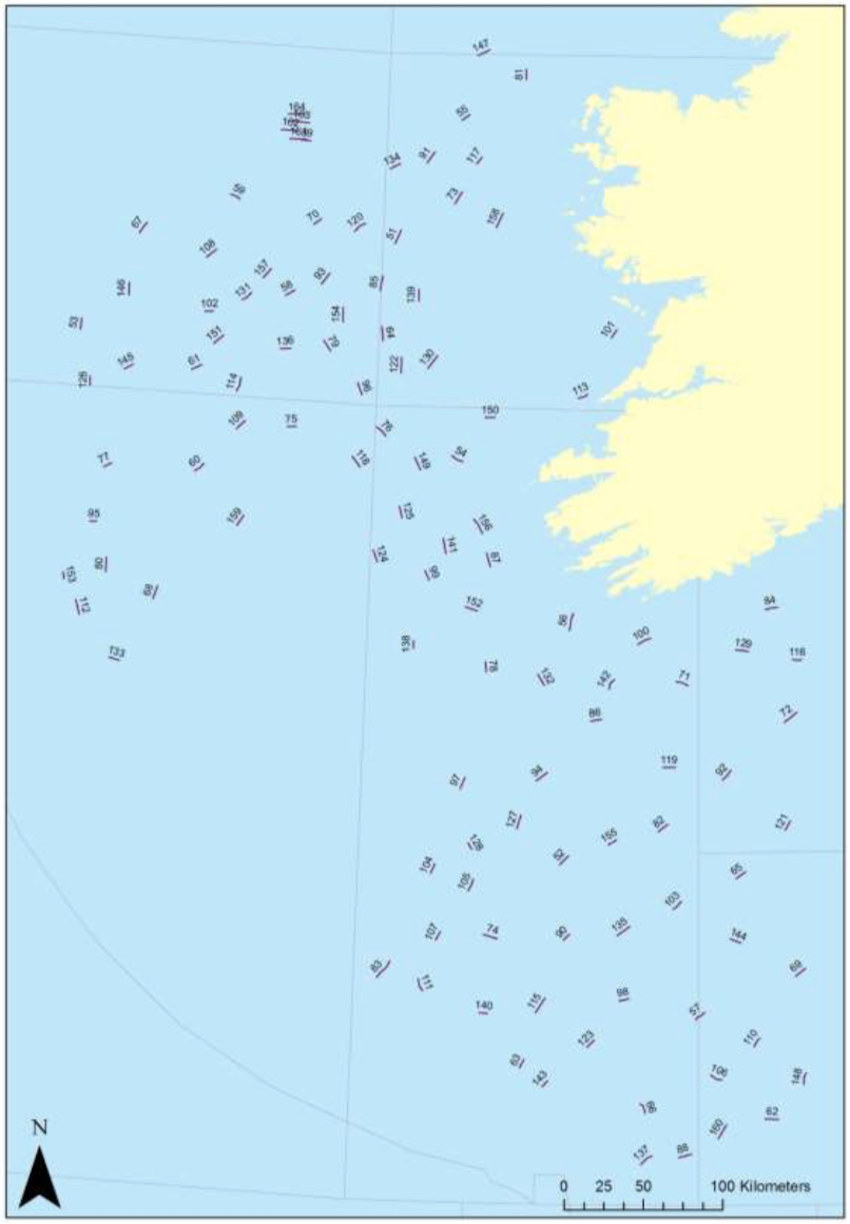
The first and second leg of 2020’s Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey will be carried out from next weekend off the West, South West and South Coasts of Ireland by the Marine Institute, in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy obligations.
As with previous years, IAMS 2020 — which will run from Sunday 23 February to Wednesday 18 March — is a demersal trawl survey consisting of approximately 110 otter trawls (60 minutes) in ICES areas 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign: EIGB) which will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl during fishing operations and will display appropriate lights and signals.
Commercial fishing and other marine operators are requested to keep a three-nautical-mile radius area around the tow points (indicated below) clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
Further details of the survey, including co-ordinates of the survey stations, are included in Marine Notice No 07 of 2020, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.