Displaying items by tag: Seabed Mapping
First Of Six INFOMAR Seabed Surveys In 2017 Completed
#MarineScience - The Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Voyager returned to Cork Harbour last week after the first of six INFOMAR seabed mapping surveys planned for 2017.
The two-week seabed survey carried out its operations in the Celtic Sea south of the Waterford and Wexford coastlines.
The research team — involving geophysicists, geologists, marine biologists and data processors Kevin Sheehan, David O'Sullivan, Oisin McManus, Nicola O'Brien and Michael Arrigan — were tasked to accurately map the physical, chemical and biological features of the seabed area.
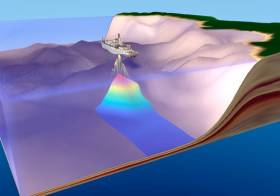
INFOMAR survey operations are conducted by a fleet of research vessels — including the RV Celtic Voyager, which is used for mapping seabed terrain in water depths between 20m and 100m.
The vessels are equipped with advanced mapping technologies including state-of-the-art acoustic sonars, geophysical instrumentation and ground-truthing capabilities, as well as geophysical equipment and precise satellite positioning.
“This helps to ensure data collection is of the highest possible quality across a wide range of water depths, conditions and environments, providing us with full coverage mapping of the shape and type of the seabed below,” says David O'Sullivan.
The INFOMAR survey around Ireland is one of the largest civilian seabed mapping projects in the world and aims to gather high resolution seabed data that contributes to the sustainable development of Ireland's marine resource.
As an island nation, Ireland is responsible for the sustainable management of its marine resources and it is important that accurate seabed maps are created to enable effective governance.
“Gathering up-to-date information about our ocean is cognisant of ensuring we have the best available science and knowledge to inform decisions affecting our ocean, particularly in relation to fisheries management and the development of ocean energy,” added O’Sullivan.
The INtegrated Mapping FOr the Sustainable Development of Ireland's MArine Resource (INFOMAR) programme is a joint venture between the Geological Survey of Ireland and the Marine Institute, funded by the Department of Communications, Climate Action and Environment.
Seabed Mapping Seminar In Galway Next Week
#INFOMAR - Galway’s Marine Institute hosts the 2016 Seminar for INFOMAR – Integrated Mapping for the Sustainable Development of Ireland’s Marine Resource – next Wednesday 19 October.
With a focus on ‘collectively creating an INFOMAR legacy’, the free day-long event will look back on the development and impact of seabed mapping in Ireland, as well as plans for completion of the coastal and shelf-mapping project, and optimising the use and value of knowledge gained from mapping data.
The morning’s two main sessions include a ‘birds eye view’ of mapping the seas of Ireland’s Exclusive Economic Zone, and exploring the latest mapping technology for coastal development and management.
Afternoon presentations will also look at INFOMAR’s role the in energy, infrastructure, environment and education sectors.
The full seminar agenda is online, and free registration is available HERE.
Marine Notice: Seabed Mapping Off East Coast
#MarineNotice - All vessels on the East Coast, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give a wide berth to a survey vessel carrying out seabed mapping operations on behalf of Clinton Marine Survey AB.
M/V Northern Wind (Callsign 2IOX2) began its survey on Thursday 22 September for a 15-day period, weather permitting. The vessel is displaying appropriate lights and markers, and is listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
The vessel may also be towing equipment including a sonar scanner, prompting the call for all other boats to keep a sharp lookout in relevant areas, the co-ordinates for which are detailed in Marine Notice No 40 of 2016, available to read or download HERE.
Transatlantic Seabed Mapping Survey Now Under Way
#SeabedMapping - The Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance's fifth transatlantic seabed mapping survey launched last Friday 22 July from eastern Canada.
Sailing on the Canadian Coast Guard Ship Louis S St-Laurent, the team will map the seafloor across the North Atlantic between Halifax in Nova Scotia and Tromso in Norway till next Tuesday 2 August.
The marine science team led by Paola Travaglini of Fisheries and Oceans Canada's Hydrographic Service are using state-of-the-art deep-water multibeam sonar technology to survey the seabed and study the physical characteristics of the seafloor, as well as other oceanographic data such as temperature and salinity, to better understand little-known areas of the North Atlantic and build on the work done last summer.
These surveys support the Galway Statement on Atlantic Ocean Co-operation, the goals of which are to join resources of its three signatories to better understand the North Atlantic, to promote sustainable management of its resources, and to promote citizens' understanding of the Atlantic through ocean literacy.
Participants in the survey include Fisheries and Oceans Canada's Hydrographic Service, the University of New Hampshire's Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Joint Hydrographic Center, and the Fisheries and Marine Institute of Memorial University of Newfoundland.
Students and early-career scientists representing Canada and the United States sailing on board the CCGS Louis S St-Laurent are writing daily blog posts to chronicle the mission. The team comprises:
- David Thornhill, Hydrographer, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Hydrographer Service
- Danielle Roche, Marine Institute of Memorial University of Newfoundland
- Darren Hiltz, Hydrographer, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Hydrographer Service
- Elizabeth Weindren, University of New Hampshire's Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Joint Hydrographic Center Fisheries
- Chris Hemmingway, National Director of UNCLOS, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Hydrographer Service
- David Levy, Electrical Technician, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Hydrographer Service
- Paola Travaglini, Hydrographer–In–Charge, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Hydrographer Service
Seabed mapping was one of the ocean research priorities and challenged discussed by the Marine Institute's CEO Dr Peter Heffernan with other heads of European marine science institutes in Ostend earlier this month, which followed a previous consultation that identified such mapping as crucial for managing human activities in our seas.
#MarineScience - Marine Institute chief executive Dr Peter Heffernan was among the heads of European marine science institutes meeting with Karmenu Vella, EU Commissioner for Environment, Maritime Affairs and Fisheries, at the European Marine Board offices in Ostend, Belgium yesterday (Friday 8 July) to discuss ocean research priorities and challenges.
The meeting with Commissioner Vella follows a previous consultation attended by Dr Heffernan in March, which identified ocean observation and seabed mapping as crucial for managing human activities in European seas and across the global ocean.
The European Marine Board said the latest meeting will advance the discussion on ocean observing and seabed mapping in Europe, set within a global context, by identifying critical gaps in our capability, investment needs and potential funding sources for the future.
“Ocean observation and seabed mapping are essential for managing human activities in the ocean," said Dr Heffernan. "With better observation and prediction capability, we can de-risk investment; we can have well informed licensing and regulation for sustainable economic developments; and we can protect ocean ecosystems and the essential services they provide, like food, medicine, and providing half of the oxygen we breathe.”
The Marine Institute CEO added: “Ireland has much to contribute to these consultations as we have significant seabed mapping expertise through INFOMAR, the national seabed mapping programme led by the Geological Survey of Ireland and the Marine Institute.
"And we are developing key ocean observation and marine research infrastructure in Ireland to advance our understanding of the ocean and to underpin innovation in the ocean."
Mapping, observing and predicting changes in the ocean were the focus of discussion at the Our Ocean Wealth conference in Galway last week, at which Ireland’s first ocean observatory was officially launched.
The meeting with Commissioner Vella in Ostend marks the second in a series and is an important platform for the ocean research community to communicate directly with the commissioner on ocean research issues.
Marine Notice: Seabed Mapping Operations Off West Coast
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises that V.Ships Ltd will be carrying out seabed mapping operations off the West Coast of Ireland.
The work started today (Saturday 2 April) and will last for approximately 14 days, weather permitting, carried out by the Survey Vessel John Lethbridge (Callsign H8PY).
The vessel, towing equipment including a sonar scanner, will display appropriate lights and markers and will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
Details of co-ordinates of the work area are included in Marine Notice No 13 of 2016, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Transition Year Students Learn About Mapping Ireland’s Seabed
#MarineScience - Three Transition Year students recently completed placements hosted by INFOMAR at the Marine Institute.
Jack Lillis, Aoife Muldoon and Emily Egan learned how seabed mapping can improve safety at sea, how it relates to the fishing industry, and how it can help the development of sectors like ocean energy.
Each student spent a week visiting the various Marine Institute facilities and learning about the different activities of the institute.
At the end of their experience, each created a 'story map' and PowerPoint presentation to show what they achieved during their placements.
"We really enjoyed our week at the Marine Institute and we now know a lot more about what a career in marine science really means," said Muldoon and Egan, from St Brigid's Vocational School in Loughrea. "It's a hugely interesting area of science that we don't learn about in school.
"We especially enjoyed our visit to the Celtic Explorer, seeing the multibeam system, learning about seabed mapping and how this information improves the admiralty charts so that vessels like the Celtic Explorer can safely visit ports. We also learnt about how seabed mapping relates to the fishing industry and helps sectors like ccean energy, this was of particular interest to us.
"We would like to thank Vera and all the Advanced Mapping Services and Marine Institute staff for teaching us so much about seabed mapping, fisheries, the laboratories and how all the different areas interlink. We now have a much better idea of what subjects to pick for the Leaving Cert."
Lillis, of Gort Community School, also had "a fantastic week, all the areas I worked in were really enjoyable. I was particularly interested with the laboratory work. Everybody knew what they were talking about and nobody shied away from any questions in fact they encouraged them. Everybody had something lined up for me to do so I was kept really busy, which was great.
"Overall I really enjoyed my week in the Marine Institute and I'm a glad I chose it for my first week of work experience. It was both a good way to see a working environment but also has encouraged me to pursue a career in marine related chemistry. Thanks so much to Tommy, Vera, the Advanced Mapping Services team and staff at the Marine Institute for taking time out of their busy day to facilitate me."
The Marine Institute will run its Transition Year course placements on a pilot basis at the end of April for up to 20 students.