Displaying items by tag: Salmon
New Evidence of Migration of Young Salmon Leaving Ireland
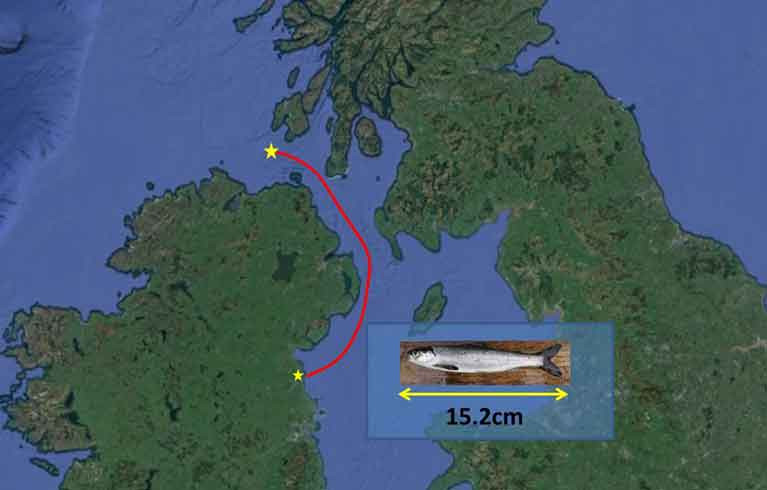
The route taken by young salmon (smolts) leaving the east coast of Ireland has been discovered for the first time. Inland Fisheries Ireland and Northern Ireland’s Agri-Food and Biosciences Institute have revealed findings which show young salmon leaving rivers on the eastern coast travelling northwards to leave the Irish Sea, rather than south and west to join salmon on the western coast. The research was carried out as part of the COMPASS project and funded by the EU European Regional Development Fund's Interreg VA programme.
The new evidence was established after researchers tagged salmon smolts with coded transmitting acoustic tags in the Castletown and Boyne rivers in County Louth during the spring of this year. Three of these tagged salmon were picked up on listening devices in the coastal seas as they travelled northwards out of the Irish Sea towards the Atlantic Ocean.
One of the smolts was recorded in Scottish waters, some 80 kilometres north of the Inishowen Peninsula. This smolt had travelled an estimated 250 kilometres in just over a month, one of the longest distances recorded for a salmon tracked at sea en route to its feeding grounds in the North Atlantic. Two more salmon smolts were tracked as far as receivers located off the Northern Ireland coast, further confirming the northward migration of the fish through the Irish Sea.
 A salmon smolt
A salmon smolt
Until now, it was unknown if juvenile salmon leaving Ireland’s east coast rivers headed around the North or South coasts to get to their oceanic feeding grounds. These first three tracked fish took a northward route from rivers on the east coast to exit the Irish Sea. These salmon also moved offshore quickly, behaving very differently from sea trout, which remained closer to their spawning rivers and swam closer to the coast and river mouths.
The tagging work was carried out by scientists from Inland Fisheries Ireland (Dr James Barry) and AFBI (Dr Richard Kennedy) who tagged and analysed the movements of 130 salmon smolts as they left their rivers of birth in the spring of 2019. This work was supported by a local angling clubs, including The Dundalk and District Brown trout and Salmon Anglers, who helped to install fish traps which enabled the tagging and release of fish. A network of acoustic receivers were moored to the seabed along the coast from Drogheda to the northeast coast by researchers from IFI and AFBI, to track the tiny acoustic transmitters in the salmon as they migrated from the rivers to the open ocean.
This research is just one element of the COMPASS (Collaborative Oceanography and Monitoring for Protected Areas and Species) project, a transnational initiative which focuses on the coastal seas between Ireland and western Scotland. The project aims to deliver improved cross border environmental monitoring programmes, including research to support highly mobile protected species such as marine mammals, salmon and sea trout. This particular research package is investigating the success of wild salmon and sea trout as they migrate from river to sea, and examining where they travel to and how many of them survive before returning to Ireland to reproduce.
Commenting on the findings, Dr William Roche, Senior Research Officer at Inland Fisheries Ireland said: “As salmon populations are in decline across the northern hemisphere, we urgently need to establish their migration journey and identify any issues which may be negatively impacting survival along that route. This research marks an exciting milestone and it will play a critical role in supporting marine conservation efforts.”
Dr Cathal Gallagher, Head of Research and Development at Inland Fisheries Ireland said: “Salmon hatch in their native river, spend their juvenile life feeding in freshwater and prepare for their long sea migration before returning as adults, usually one year later to mate in their native river. Genetic analysis has shown this loyalty to their native river which can be traced back to the Ice Age.
The COMPASS project has for the first time identified the northward migration route of young salmon from some of Ireland’s east coast rivers, as they start their epic and dangerous journey to their feeding grounds in the North Atlantic Sea. Research results like these offer insights which will enable policymakers and managers to focus actions aimed at the protection and conservation of Ireland’s iconic salmon stocks, which have suffered considerable decline over the past decades. Inland Fisheries Ireland will continue in its research efforts, nationally and internationally, to support the conservation of our salmon stocks which are threatened by current and increasing threats posed by a changing environment.”
Dr Robert Rosell, Principal Scientific Officer for freshwater fish at AFBI said: These observations are an exciting first for long-distance tracking of individual young salmon at sea. We are now in a position to carry out follow up studies to find out much more. These results will optimise the placement of further detection equipment and add information, for instance on survival rates, for further releases of tagged fish. Now that we know where to look, advancing technology and longer battery life tags may soon give us not just the outward journey, but also detail of the routes taken by adult fish coming back to spawn.
Salmon & Sea Trout Angling Licences For 2020 Are Now Available Online
Licences for salmon and sea trout angling for the 2020 season can now be purchased online along with log books and gill tags, Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has announced.
Licence fees remain the same across all classes including those for juvenile anglers. An annual licence covering all districts costs €100 (€10 for juveniles under 18 years), while licences for single districts are €56 for the year, €40 for 21 days and €20 for a single day. Licences for the Foyle Area Extension are €80.
Anglers are legally required to be in possession of a licence when fishing for salmon or sea trout.
Licences should be purchased online by next Wednesday 18 of December to allow time for delivery before Christmas and the New Year. IFI cannot guarantee dispatch in advance of the holidays due to postage deadlines.
Online licences can also be acquired directly from your local IFI office or approved online licence sales distributors.
Angling licences other than online sales will be available to purchase in approved licence sales distributors from the end of December or early January.
IFI also reminds all salmon and sea trout anglers to return their 2019 angling logbook and unused gill tags as soon as possible, even if there is no catch recorded.
These returns will provide vital information regarding the status and management of our wild Atlantic salmon and sea trout stocks for the future.
Anglers are asked to use the business return envelope which was supplied at the time of license purchase. In the absence of the prepaid return envelope, anglers can return their completed logbook and unused tags to the IFI office address on their licence/logbook.
Concerns Over Mass Use Of ‘Cleaner Fish’ In Irish Salmon Farms
Campaigners against salmon farms have raised concerns over the state of Irish wrasse stocks after it was confirmed the fish have been taken en masse to help clean lice from farmed salmon.
As Donegal News reports, a number of salmon farms in Donegal, Galway and other areas owned by Mowi — the former Marine Harvest — have between them moved in tonnes of wild wrasse, a known ‘cleaner fish’ that feeds on sea lice, over the past four years.
Responding to a Dáil debate question from Catherine Connolly TD this past summer, Marine Minister Michael Creed confirmed that “several special of cleaner fish are used in Ireland as a method of controlling sea lice”.
But there are fears that the mass withdrawal of wrasse and other such species from the wild could tip the balance of Ireland’s delicate marine ecosystem.
“The absence of wild wrasse in bays may result in stress and disease in other large species of fish which rely on wrasse to keep them clean of parasites,” said Billy Smyth, chair of Galway Bay Against Salmon Cages.
Donegal News has much more on the story HERE.
Collective Work Needed To Arrest Decline Of Salmon In Foyle & Carlingford, Conference Hears
Collective work between scientists and the angling community for the survival of salmon in the cross-border catchments of Foyle and Carlingford was to the fore at the recent conference in Omagh hosted by the Loughs Agency.
Stark warnings over the decline of the species were heard along with presentations from the likes of Dr Diego Del Villar, who discussed the new SeaMonitor project that is currently studying the seas around Ireland, Northern Ireland and western Scotland, and will in time help produce a salmon management plan for the River Foyle.
The Loughs Agency says it will soon launch a public consultation to gauge the views of the public in managing the salmon fishery.
John McCartney, Loughs Agency director of conservation and protection, said: “We value the input and opinion of the public when reviewing our salmon management programme. I would encourage everyone take time to consider and respond to the questions.”
‘Our Foyle Salmon’ Conference In Omagh Next Month
The Loughs Agency is teaming up with the Foyle Association of Salmon and Trout Anglers (FASTA) to host an evening salmon conference in Omagh, Co Tyrone next month.
Our Foyle Salmon – The Upstream Battle at the Mellon Country Inn from 7pm on Wednesday 25 September will hear from speakers on a range of issues including the status of salmon in the River Foyle, current research, threats and steps that can be taken to sustain and protect the species.
This is a fully ticketed event; tickets are free and available through Eventbrite with a maximum of two tickets per transaction.
When registering for tickets you can also submit a question to the panel for the Q&A session at the conference.
A small number of salmon are returning to Irish rivers with signs of bleeding and skin ulceration, according to Inland Fisheries Ireland. This follows reports of salmon also returning to Norway and Scotland with a red rash skin disease in recent months. Anglers and fishery owners are asked to report incidences of salmon with rash like symptom to Inland Fisheries Ireland to help determine the scale of the problem nationally.
Salmon first began appearing in Irish rivers with these symptoms in early June and by mid-June, there were reports of fish with ulceration in at least six rivers, both on the east and west coast of Ireland. The salmon who are affected show signs of bleeding, ulceration and haemorrhaging mainly along the area on the belly of the fish and on the head and the tail. Secondary fungal infection normally sets in and may result in death of the salmon.
"Inland Fisheries Ireland appeals to anglers and fishery owners to report incidences of affected salmon"
Inland Fisheries Ireland is working with the Fish Health Unit in the Marine Institute to sample live salmon in affected rivers to determine the cause of the skin disease. Until the cause of the disease has been determined and the risk of spreading the disease established, affected salmon should not be removed from the water. Any anglers who capture salmon with these symptoms are advised to follow normal biosecurity procedures and disinfect tackle, waders and equipment.
Dr Paddy Gargan, Senior Research Officer at Inland Fisheries Ireland said: “It is unclear at this time what is causing these symptoms. There is some evidence that the disease may become less frequent with rising water temperatures and the problem has been worst in multi-sea-winter fish entering rivers early in the year in Norway and Sweden. There is also a suggestion that the disease is related to a change in salmon diet but this has not yet been established. We are asking anglers and fishery owners to report any catches of salmon with these symptoms to us as soon as possible”.
Research Vital As International Year Of The Salmon Highlights Challenges To Iconic Species, Says Canney
Sean Canney, Minister of State with responsibility for the inland fisheries resource, visited the River Erriff in Co Mayo recently to understand more about the current issues facing Ireland’s salmon.
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has designated the River Erriff, one of Ireland's premier salmon and sea trout fisheries, as the National Salmonid Index Catchment.
Salmon and sea trout migrating upstream in the Erriff must pass through fish counting and trapping facilities located at Aasleagh Falls, where the Erriff flows into Killary Harbour.
Since 1985, salmon and sea trout smolts and kelts migrating downstream pass through a trap located below Tawnyard Lough.
The facilities at this research station are used for a wide range of scientific research and monitoring activities on the salmonid populations and their migratory behaviour.
Minister Canney met with Dr Ciaran Byrne, CEO of Inland Fisheries Ireland, who outlined that fisheries managers and scientists have been concerned for a number of years about the declining numbers of salmon returning to the Irish coast — a key concern in this International Year of the Salmon.
In the mid-1970s, almost 1.7 million salmon were estimated to have returned to Ireland, compared to only some 250,000 today.
Salmon are a key indicator species and they tell us so much about the health of our aquatic environment, IFI says.
And the issue is not unique to Ireland, as populations over the entire southern part of the North East Atlantic — which includes France, Spain, England, Scotland and southern Iceland — have declined significantly in the past number of decades.
Following the visit, Minister Canney commented: “Salmon are an iconic fish species in Ireland. They have always had a special place in Irish culture, heritage and mythology with stories such as the ‘Salmon of Knowledge’ familiar to generations of our school children.
“While they are widely distributed throughout Irish river systems, with over 140 designated salmon rivers, the numbers of salmon returning to Irish rivers, in common with salmon rivers internationally, have shown a worrying decline in recent decades.
“Today they remain an important resource to many people, playing an invaluable ecological, social and cultural role in Ireland and across the Northern Hemisphere.
“International Year of the Salmon offers us an opportunity to start an important conversation around how we can protect, conserve and restore salmon populations in Irish and international waters and how we can inspire action.
“I am delighted to see the excellent research facility here in the Erriff. I am assured that the ongoing scientific research by IFI adds to our understanding of the issues facing salmon and will inform Ireland’s position as part of the EU delegation in discussions which will shortly take place at Nasco — the North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organisation — on this important topic.”
Appeal For Anglers To Become Citizen Scientists As Part Of National Salmon Scale Project
Anglers are needed as citizen scientists for a new National Salmon Scale Project, says Sean Canney TD, Minister of State with responsibility for the inland fisheries sector.
Minister Canney said: “As we celebrate International Year of the Salmon, this project will help researchers understand the challenges which salmon are facing today.
“The project, which has been initiated by Inland Fisheries Ireland, aims to collect vital information through scales taken from salmon and sea trout which are caught in Irish rivers and lakes and will contribute to international efforts to conserve wild salmon.”
Fish scales record the life history of a salmon, and one scale can reveal a lot about the lifestyle and behaviour of the fish.
Scales can tell scientists what age the fish is, how many winters it spent at sea, how many times it spawned, how slow or fast it grew, what it ate and how long it spent in the river before it went out to sea.
Scales can also reveal the general feeding area where the salmon travelled to in the ocean, whether it went to the Faroe Islands, the Norwegian Sea or all the way to West Greenland. Scales help scientists to understand the biology and ecology of Irish salmon and sea trout.
As part of the project, anglers are asked to take a scale sample from a salmon or sea trout by gently scraping and removing approximately 20 fish scales using a clean knife, then post their samples to Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) using the sample envelopes which will be made available to them.
Scales can be removed from both harvested and catch-and-release fish. Sampling of fish for release should be handled carefully and fish should be only briefly removed from the water with every effort made to avoid injury or stress while weight should be estimated.
Information from salmon scales is used in setting conservation limits for Irish rivers. Conservation limits for each river are set based on the proportion of salmon who have spent one winter at sea and those that have spent multiple winters at sea.
The conservation limit for a river represents the number of spawning salmon required to produce the next generation of salmon and this information helps inform angling regulations and management. Information from scales on multi-sea winter salmon entering rivers in spring is also important for managing individual river stocks.
Dr Paddy Gargan, senior research officer at IFI, said: “It is important to have anglers collecting scales as they can provide broad coverage across Ireland and collect scales throughout the fishing season.
“A scale resource which includes many different river systems in Ireland over several years is a great asset from a research perspective as it allows us to examine the factors affecting salmon survival at sea. We can compare how factors, such as climate change, are impacting survival by analysing today’s salmon scales alongside those from many decades ago.”
All scales collected through the National Salmon Scale Project will be added to the National Salmon Scale Archive which is managed by IFI.
The archive, which consists of a dedicated storage facility and associated database, currently holds 19,300 scale samples from a total of 38 rivers representing 152 sampling years. The National Salmon Scale Project aims to increase the scale resource available to scientists for ongoing and future research.
IFI’s head of research and development Dr Cathal Gallagher said: “Ultimately the National Salmon Scale Project will help inform future salmon management policies and activities.
“It is fitting therefore that we are launching this campaign during International Year of the Salmon which aims to raise awareness of what humans can do to ensure salmon and their habitats are conserved and restored against a backdrop of several environmental pressures. This project offers anglers a very tangible and practical way of playing an active role in salmon conservation.”
For more information on the National Salmon Scale Project, including how to take a sample safely and to request sample envelopes, visit the project webpage. To find out more about International Year of the Salmon visit YearOfTheSalmon.org.
Young Salmon Survival is 'Surprisingly Low' When Migrating to Sea - Report
A new study shows low salmon survival leaving freshwater is an important factor in declining European salmon populations, according to early results from a project examining the early migration phase of salmon smolts (young salmon) from rivers across Europe. Leading salmon scientists from Denmark, Spain, Sweden, UK and Ireland are today attending an important meeting in Dublin, hosted by Inland Fisheries Ireland, to mark International Year of the Salmon. The scientists will discuss some of their new findings from the international SMOLTRACK project, the results of which reveal factors in the known decline of salmon stocks.
The SMOLTRACK Project, which is funded by the North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organisation (NASCO) / EU, aims to help determine the survival rates of young salmon as they move from rivers into the marine environment. Work commenced in 2017 and early results show that survival during movement from rivers to the sea is lower than expected. While it was already accepted that salmon are impacted by a number of factors when they migrate at sea including the effects of climate change, limited feeding opportunities and sea lice-induced by fish farms, the low survival rate in river systems which is presenting in this research is a new development.
The low survival of smolts in some river systems could be attributed to changes in temperature and flow while predators have also been shown to impact on the numbers entering the sea. The survival of smolts varies by catchment and in a bad year, survival of smolts can be three times lower than in a good year. These results will be published in international journals on completion of the research.
The international project sees scientists from each participating country tag salmon smolts with miniaturised acoustic and radio transmitter tags in rivers in their own country, and track their migration journey through the lower parts of rivers, estuaries and coastal areas. This study includes populations in Southern Europe which are most vulnerable to climate change. In Ireland, this work is being carried out in the River Erriff, Inland Fisheries Ireland’s National Salmonid Index Catchment (NSIC).
In addition to the activity in Ireland, tagging is being carried out on the River Bush (Northern Ireland), River Tamar (England), River Ulla and River Minho (Spain), River Göta and River Högvadsån (Sweden), River Skjern and River Storaa (Denmark). This information will help scientists to understand the survival rates of salmon smolts during their migrations under varying conditions ranging from cooler climates in Sweden to warmer climate in Spain. Already SMOLTRACK is providing new data on the initial migration of salmon smolts which will inform future management and conservation measures for this iconic species.
Dr William Roche, Senior Research Officer at Inland Fisheries Ireland said: “Understanding and comparing early marine survival of salmon in EU waters is a key output of this project in addition to providing data on smolt run timing and migration behaviour. The project has established a European-wide counting, tagging and tracking system to monitor smolts and will also contribute to understanding of the possible impacts of climate change.”
Dr Cathal Gallagher, Head of Research and Development at Inland Fisheries Ireland said: “We have seen a substantial reduction in the numbers of salmon returning to Irish shores in recent decades. This project is examining what is happening to our young salmon as they migrate to sea and what the international community needs to do to help salmon populations. While this research identifies issues in early mortality of salmon, this part of a salmon’s life cycle is where management actions can be targeted to support the future of these salmon stocks. International Year of the Salmon offers an opportunity to share knowledge across the Northern Hemisphere with a view to inspiring action and collaboration with a positive effect on salmon survival.”
International Year of the Salmon is a joint worldwide initiative of the North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organisation (NASCO) and the North Pacific Anadromous Fish Commission (NPAFC) alongside other partners across the globe, creating an international framework for collaborative outreach and research. It is hoped that IYS will raise awareness of what humans can do to ensure salmon and their habitats are conserved and restored against a backdrop of several environmental factors.
For more information about the SMOLTRACK project, visit here
New Project To Improve Angling Access On River Easkey
#Angling - A new project on the River Easkey in Co Sligo which has improved and developed angling access to the wild salmon river between Sligo and Ballina has now been completed.
The project, which was delivered by River Easkey Angling Association, received support from Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) via the National Strategy for Angling Development.
Structures such as footbridges, stiles, and ladders were installed along the river, which is located on the Wild Atlantic Way, while walkway routes on the banks of the salmon and trout fishery were also improved.
The work took place upstream of the famous Workhouse Bridge as part of the second phase of this project which initially involved similar works downstream of the bridge last year.
In total, the project has delivered eight new access points to angling, 13 footbridges ranging from three to four metres in length, and five kilometres of improved trail access.
Sean Canney, Minister of State for responsibility for inland fisheries, said on Wednesday (23 January): “I welcome the continuing efforts of Inland Fisheries Ireland in delivering under the National Strategy for Angling Development in partnership and collaboration with local angling clubs and community groups nationwide.
“Inland Fisheries Ireland committed €23,500 in total to support the Easkey project with €10,000 awarded in 2017 and a further €13,500 granted in 2018.
“I also want to congratulate the River Easkey Angling Association on its excellent development ethos. They are a progressive group that helpfully operates an open policy for holders of a State Salmon License with season and day tickets available for access,” he added.
Suzanne Campion, head of business development at IFI, said: “The River Easkey Angling Association has done fantastic work in developing this area as an angling destination. While completing this project and working closely with our project officers, they have given due diligence to everything from financial and environmental governance to biosecurity considerations ensuring the conservation and protection of this wonderful resource.”
Alan Spencer, assistant secretary of the River Easkey Angling Association, expressed the club’s thanks to Inland Fisheries Ireland’s staff for all their help and support during the project, as well as gratitude to landowners who permitted the club and its contractor access to the river through their property.