Displaying items by tag: Cruising Association
‘VAT Trap’ & Visa Rules Brew Up a ‘Perfect Storm’ for British Boaters, Says Cruising Body
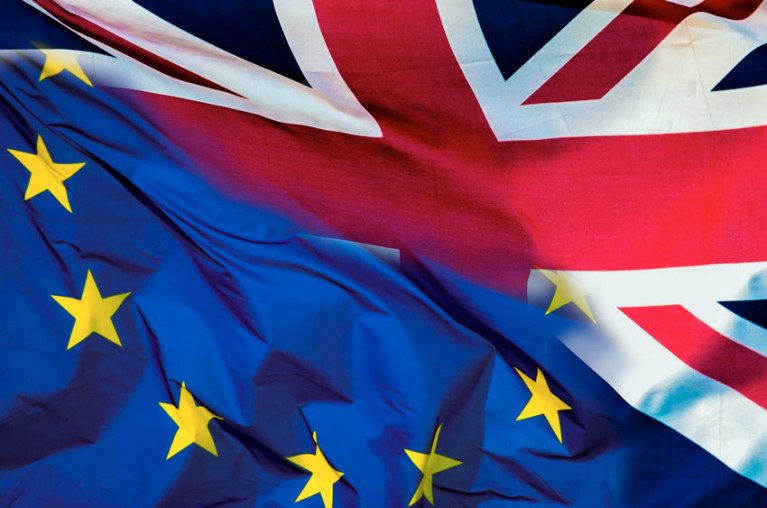
British cruising boaters are in the middle of a “perfect storm”, with visa issues just the latest ill wind to blow, according to a leading voice in the Cruising Association.
As Marine Industry News reports, the CA’s Regulations and Technical Services (RATS) committee chair Robin Barron says the new post-Brexit visa regime for Britons entering the EU — which allow for a 90-day stay in any 180-day period — “simply doesn’t work for cruising yachts”.
He elaborates: “My worry is that second-home owners — who find themselves in the same position — will lobby successfully to have an extension, but the Cruising Association needs to make sure that any development includes people in boats and that a visa status change isn’t dependent on having a second address.”
Baron adds that he is looking at ways to make reciprocal arrangements happen within the Schengen Area.
“We’re trying to raise localised support, from marinas and other marine trades in target countries like Spain, Portugal and Greece,” he says. “We’re hoping they’ll help pressure their MPs to grant extended visas.”
Meanwhile, the so-called ‘VAT trap’ threatens to tie up countless numbers of British-owned boats in foreign marinas as the costs to bring them home run into the thousands.
Marine Industry News has much more on the story HERE.
UK Boaters Sailing EU Waters In for Strange Year, RYA Warns
“All sorts of strange things” will emerge this year for UK sailors in EU waters as post-Brexit issues remain to be ironed out.
As Sailing Today reports, RYA cruising manager Stuart Carruthers has outlined some harsh truths for British boat owners who had been used to easy cruising excursions beyond home shores.
“As an example, the whole idea of taking a sabbatical in the Mediterranean, living on your boat, which you’ve bought with your pension, has just disappeared out of the window now that we are subject to Schengen Area visitor visa rules. That is just one post-Brexit reality,” he said.
Meanwhile, EU member states appear to be taking a less than harmonious approach to recognition of British boats’ VAT paid status, as the Cruising Association’s Brexit spokesperson Roger Bickerstaff has warned.
“We’re going to be seeing different countries taking different views,” he said.
Carruthers also noted: “The status of boats in Northern Ireland is also unclear — are they classed as UK goods, Union goods, will they be able to enter Great Britain VAT-free?”
Sailing Today has much more on the story HERE.
‘Istanbul Convention’ Should Apply for UK Boats With Red Diesel Cruising in EU Waters, CA Says
Marine red diesel is still on sale to leisure vessels in the UK despite Westminster’s pre-Brexit plans to phase it out, the Cruising Association says.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the British Government made clear its intention to legislate for a ban on the use of subsidised dyed or ‘red’ diesel except for agriculture, railway and non-commercial heating.
It follows a judgment from the European Court of Justice that also necessitated Ireland’s own ban on green-dyed diesel use for cruising and leisure boating which came into force at the start of 2020.
Now that Britain has left the EU, red diesel will continue to be legal for the propulsion of vessels in the UK until April 2022, says the body that represents Britain’s small-boat cruising community.
However, red diesel in craft engine tanks is not permitted in the EU27 and other countries — including Ireland.
The CA’s Regulations and Technical Services group (RATS) says it has received information from HM Revenue and Customs that they agree the Istanbul Convention of 1990 allows vessels to make visits to the EU27 and elsewhere without import prohibitions or restrictions on propulsion fuel.
This includes visiting craft with UK red marine diesel — or red dye traces — in their engine tanks, it adds. But it is unclear whether EU27 countries will implement their own laws in accordance with the Convention as expected.
The situation is also different in Northern Ireland, where the Northern Ireland Protocol means relevant EU directives will continue to apply.
“If this affects what fuel private pleasure craft (PPC) in Northern Ireland can use, HMRC will provide an update at the appropriate time,” the CA says.
The UK’s Cruising Association’s Regulations and Technical Services group (RATS) has welcomed the move by the Scottish government to update its rules for marking lobster pots in Scottish waters.
The best practice guidance, which came into force on 20 June, makes unlawful the marking of a string of creels (lobster or crab pots) with anything other than a buoy made for that purpose.
RATS said it has been “vociferously campaigning” for clearer marking of static fishing gear and lobster pot markers since 2017, and will be pressing for England, Wales and Northern Ireland to follow suit.
More details on guidance for marking fishing creels in Scottish waters can be found on the Scottish government website HERE.
Permission for overnight stays in England from this Saturday 4 July means a “cautious” return to cruising for those who see their boats in the country, according to the UK’s Cruising Association (CA).
The move follows similar changes already introduced in Northern Ireland in line with the lifting of coronavirus restrictions in the Republic of Ireland.
Wales and Scotland are expected to follow suit by mid July, while Schengen countries throughout the European Union are now working to “get back in sync” with open borders and random testing.
England-resident owners with boats in other countries will be looking to announcements on ‘air bridges’ to allow travel to their vessels — which for now excludes popular cruising destinations like Portugal and Sweden.
The CA reminds that rules for those who travel abroad from England on their own boat are “not yet clear” as permissions and restrictions are on a frequency changing, country-by-country basis.
However, based on requirements in Spain, it’s expected that all on board cruising vessels must social distance at a minimum of 1.5 metres from anyone not a family member; use face coverings in close quarters, such as in shops or on busy streets; and continue hygiene measures such as regular hand washing. Fines of €100 are being levied in Spain for breaking these rules.
CA president Julian Dussek said: “Of course, I’m delighted that many of our members will be able to do some sailing this summer.
“But there are still many challenges in getting to and equipping your boat, sailing safely, and identifying destinations where facilities are open and you can enjoy your stay.
“That’s where the CA comes in. If our members keep posting their experiences on our forums, it could make all the difference for another member following in your tracks.”
The CA website has a section regularly updated with the latest information for cruising in Europe and the Mediterranean.
UK’s Cruising Association Confirms Proposals For Dyed Diesel Ban On Private Pleasure Craft
The UK’s Cruising Association (CA) says it has confirmed with HM Revenue & Customs that it is their intention to legislate that dyed or ‘red’ diesel can only be used for agriculture, railways and non-commercial heating from April 2022.
This move would be in line with EU regulations and follows Ireland’s own ban on green diesel use for leisure boating that came into force at the start of this year.
The CA’s Regulations and Technical Services group (RATS) also confirms that the duty on standard white diesel for boats will be the same as the full rate paid on white road diesel in the UK.
This means that the present so called '60/40' fuel duty split will disappear — but commercial vessels, such as fishing boats, will still be able to claim a rebate on the full rate through their Marine Voyages Relief scheme.
But the HMRC says it is exploring the possibility of introducing a scheme that allows private pleasure craft to pay only the current lower rate for red diesel non-propulsion uses.
The CA says it “welcomes the clarification on the use of white diesel which should make it more conveniently available throughout the United Kingdom from marinas and ports as they will have to supply all marine vessels with one colour of diesel”.
The “bonus” of such a situation would be that boaters fulfil the SOLAS V regulations for sea voyages and “no longer have the concern of the presence of red diesel in their tanks when visiting EU maritime states”.
A public consultation will deal all issues involved in the proposed legislative change but there is no timetable for this amid the current Covid-19 pandemic.
A spokesperson for the CA’s RATS group says private pleasure craft from the UK should continue to legally use red diesel as they currently do, since it is still the only easily available diesel fuel at home marinas. The CA’s current advice on using dyed diesel wen visiting the EU is available HERE.
Cruising Association’s New Guides For Inland Waterways Of France, Belgium, Netherlands & Germany
Newly updated 2020 editions of the UK Cruising Association’s three main inland waterways cruising guides for France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany have been published by the CA’s European Inland Waterways Section (EIWS) in time for the Christmas season.
All three editions — Cruising the Inland Waterways of France and Belgium, Through the Netherlands via the Standing Mast Routes, and The German Rhine — reflect the more than 200 updates posted by EIWS members up to October 2019 on the CA’s unique CAptain’s Mate app.
The publications also include a 25% discount offer on the first year’s CA membership when paid by direct debit to anyone purchasing one of the guides up to 31 December 2020.
Members have access to the online editions of the guides, which contain hyperlinks to the CAptain's Mate app, enabling users to access the most up-to-date information on mooring locations.
All three guides are available via the Cruising Association online shop at or from the print-on-demand publisher Lulu.
In addition to these three guides, the CA’s European Inland Waterways Section also produces full-colour photo guides to moorings and other facilities on 12 French inland waterways. Members and non-members can find further information from the EIWS section online.
UK Campaign To Make Static Fishing Gear Safer For Small Boats
#LobsterPots - Are lobster pots a danger to yachts? That’s the question posed by Yachting Monthly as the UK’s Cruising Association relaunches its campaign to make static-gear fishing safer for small vessels.
The CA has already received nearly 4,000 signatures on its online petition to the Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA) to seek “views regarding forceable regulation among other options” for improving the way static fishing gear is marked.
Before its original petition was shut down until after this summer’s UK general election, nearly 6,000 people had signalled their support for the initiative which also has the backing of CA patron and yachting legend Sir Robin Knox-Johnston.
The RYA has additionally launched an online reporting form for boaters to identify incidents of entanglement with poorly marked static fishing gear.
“We think it is time for everybody with an interest to work together to find a solution, particularly one that is cheap and practical for our fishermen,” said a CA spokesperson.
Yachting Monthly has more on the story HERE.
#Cruising - The Cruising Association is set to launch a new section to cover activity in Ireland's busy cruising waters.
The London-headquartered organisation has set 19 October as the launch date for the new 'Celtic Seas' section, which will comprise the whole of Ireland plus the west coast of Scotland, the Isle of Man and the west coasts of England and Wales.
As Sail World reports, the proposed new section would complete the CA's coverage of the British Isles, along with the North Sea and Channel sections. Events and cruises-in-company would be arranged, not to mention the creation of a 'CelticNet' online forum for section members.
It's hoped that the Celtic Seas section would work together with existing cruising clubs and associations using the waters around Ireland - the Atlantic, North Channel, Irish Sea and Celtic Sea - to organise joint events, expanding on the CA's current presence in Ireland via honorary local representatives.
The first meeting of the Celtic Seas section will take place on Saturday 19 October at CA House in Limehouse, East London, where members of existing Irish and British west coast associations - and non-members with an interest in cruising - will be invited to discuss motor cruising and sailing in the region.
Greystones Harbour & Marina Hosts its First Gathering Cruise
Less than four weeks after opening its initial batch of pontoon berths, Greystones Marina has hosted its first gathering of cruisers with the Cruising Association of Ireland mustering at the new harbour over the weekend of April 27/28 writes WM Nixon.
The severe weather of the Spring of 2013 has delayed many fitting-out programmes, but so keen were CAI members to celebrate the new facility that those whose boats weren't ready joined their Commodore John Leahy at the venue by road.
He was among those who'd sailed down from Dublin Bay with his Moody 33 Eblana to enjoy glorious if cold sunshine on the Saturday, and a fine fair wind off the land to speed them home on Sunday.
The Beach House was the natural venue for the shoreside conviviality, and numbers using Greystones – both as marina residents, and as visitors – will steadily increase as the season gets going.
The Gathering Cruise will call by in July, while the Irish Cruising Club Eastern Region are planning their first major fleet movement to the re-born North Wicklow harbour in late August.
But historically speaking, they'll all be following the Eblana, which is now indisputably in the records as the first leader of the first cruising group to visit Greystones.

The new marina in Greystones is starting to attract an eclectic fleet of resident boats. Photo: Aidan Coughlan

The flagship of the first fleet to Greystones – John Leahy's Moody 33DS Eblana brings the sunshine to North Wicklow. Photo: Aidan Coughlan