Displaying items by tag: pollution
Seabins To Clean Up Ards Peninsula In Council Plans
#Seabin - Ards and North Down Borough Council wants to bring in the Seabin to help clean up the coastline of the Ards Peninsula, as the Belfast Telegraph reports.
The council plans to purchase 10 of the devices — which capture floating debris in harbours and marinas — in what’s being touted as a first for Northern Ireland.
Earlier this year, Dun Laoghaire Harbour in Dublin saw the installation of its first Seabin thanks to the campaigning efforts of local girl Flossie Donnelly.
It’s hoped that the move by Ards councillors will see further take up around the Northern Irish coast.
The Belfast Telegraph has more on the story HERE.
West Of Ireland Among Only Three Ocean Sites Free Of Microplastic In Volvo Ocean Race Data
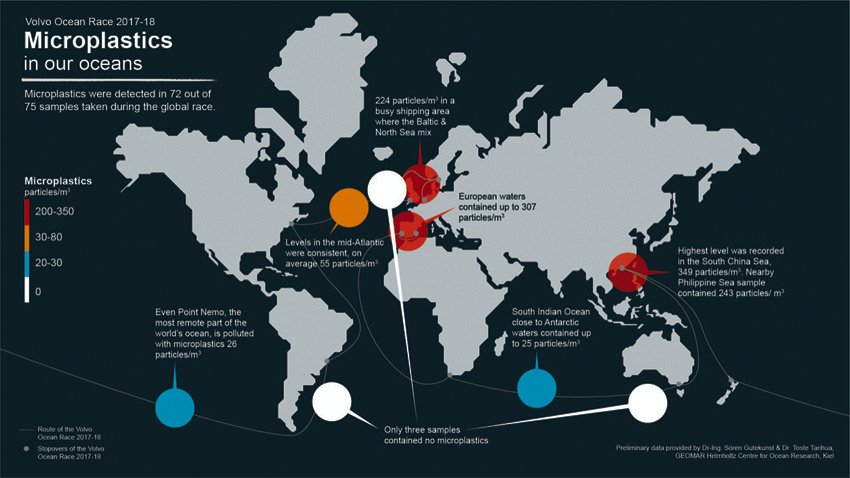
#Microplastic - The West of Ireland is one of only three sites sampled out of 75 during the Volvo Ocean Race with no trace of microplastic particles.
South of Australia and east of Argentina were the other sites found clear of microplastic in findings that give a clear mandate for positive and decisive action from national governments, international organisations, business and individuals to stop plastic polluting our seas.
The most recent data collected, before the race finale in The Hague, by scientific devices on board Team AkzoNobel and Turn the Tide on Plastic found particularly high levels of microplastics — 224 particles per cubic metre — in Skagerrak, a 150-mile strait that runs between Norway, Sweden and Denmark where the outflow from the Baltic Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean.
The highest levels of microplastic — 349 particles per cubic metre — were found in a sample taken in the South China Sea that feeds into the Kuroshio Current and the North Pacific Gyre.
The second highest, at 307 particles per cubic metre, came close from the point where the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean meet at the Strait of Gibraltar.
Even close to Point Nemo, the furthest place from land on Earth, where the nearest humans are on the International Space Station, between nine and 26 particles of microplastic per cubic metre were recorded.
The seawater samples were collected during the course of the 45,000-nautical-mile, eight-month race which passed six continents and 12 landmark host cities. The race began in Alicante last October, finishing in The Hague in June.
Anne-Cecile Turner, sustainability programme leader for the Volvo Ocean Race, said: “We have used a sporting event to collect groundbreaking scientific data to provide a global map of microplastics concentrations — even finding them in some of the remotest places on Earth.
“Our ambition is that the data will provide a new benchmark for our understanding of the spread of these ubiquitous particles and offer a template for future scientific methodology.
“With the continuation of the sustainability programme, we will continue our mission to inspire, engage and act as a pioneer, with the aim of restoring ocean health.”
Dr Toste Tanhua of the GEOMAR Institute for Ocean Research Kiel, funded by the Cluster of Excellence Future Ocean, analysed the preliminary microplastics data at their laboratory in Kiel, Germany.
The data has since been uploaded to a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) database where scientists are able to access it open source.
Dr Tanhua said the Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme “has contributed enormously to the understanding of microplastic contribution around the world, and has contributed to a global map of CO2 uptake by the oceans. The race has showed that the race yachts and sailors can be excellent science supporters.”
The boats also collect other oceanographic data measurements including temperature, dissolved CO2, salinity and algae content (as chlorophyll a) that gives an indication of levels of ocean health and acidification and supports quantification of the ocean’s uptake of carbon dioxide.
In parallel, 30 scientific drifter buoys deployed during the race are transmitting data that is essential for forecasting of weather and climate changes, in both the short and long term. This is being utilised by the World Meteorological Organisation and UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission.
The Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme is funded by Volvo Cars, which is donating €100 from the first 3,000 sales of the new Volvo V90 Cross Country Volvo Ocean Race edition to support the initiative.
Microplastics are often invisible to the naked eye and can take thousands of years to degrade. By collecting information on their levels, the science programme is helping scientists gain insight into the scale of plastic pollution and its impact on marine life.
To build upon the programme’s sustainability achievements, it will be embedded at the heart of the race going forward. And in the run up to the next edition, the programme will continue to organise a range of international Ocean Summits, further expand the education programme and continue to pioneer a scientific programme focussing on ocean plastic.
It will also collaborate with a range of innovative partners, including 11th Hour Racing and UN Environment, to help deliver a lasting legacy and drive real change for a healthy planet.
Since the end of the latest race, the sustainability programme convened a workshop with key global stakeholders from science, academia, the private sector and other institutions, including UN Environment and Mirpuri Foundation, to identify the gaps to fill in order to advance our understanding of these issues and to align our missions.
Fiona Ball, head of responsible business at Sky Ocean Rescue, said: “The data that Turn the Tide on Plastic collected throughout Volvo Ocean Race highlights the critical state of our oceans. By supporting the Turn the Tide on Plastic yacht, Sky Ocean Rescue aims to raise awareness and inspire everyone to make simple, everyday changes to stop our oceans from drowning in plastic. We can all play our part and turn off the plastic tap, now is the time for fundamental change to protect our planet.”
Survey Says Just 8% Of Irish Waterside Spots Are Litter-Free
#Litter - Only 8% of beaches, harbours and rivers in Ireland can be considered clean, according to the first national survey on littering at waterside spots.
An Taisce investigated 50 sites nationwide on behalf of the Irish Business Against Litter (IBAL) group and found that just four – Salthill in Galway, Kinsale Harbour in Co Cork, Lanesborough and Carrick-on-Shannon – were clean when measured against EU standards.
Outsider.ie has the full survey results, which point at Cork Harbour and the Wild Atlantic Way as among the biggest offenders for litter blight around the coast.
“We know the success of the Wild Atlantic Way is placing strains on infrastructure of various kinds,” said IBAL spokesperson Conor Horgan. “Litter is a likely consequence of this and one local authorities need to manage to ensure the appeal of the way is sustained.”
Among inland waterways, the Boyne in Drogheda, the Shannon at Portumna, the Suir in Waterford city and the Tolka at Annesley Bridge were considered “heavily littered” — mostly by plastic bottles and drinks cans, cigarette butts and plastic sweet wrappers.
In an editorial earlier this week, The Irish Times warned over “the permanent damage being caused to the marine environment in the form of plastic pollution”.
The issue is one that many campaigners around the country are attempting to tackle – including young Flossie Donnelly and her clean-up efforts in Dun Laoghaire Harbour.
It’s also considered a threat to Ireland’s angling resource. “Our waterways and the fish which they sustain are one of our great natural assets,” said Suzanne Campion, head of business development at Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI).
“Ireland has a reputation as an outstanding angling destination however this is reliant on our ‘green’ image. We are disappointed to learn that angling destinations such as the Boyne, Shannon, Suir and Tolka feature on the ‘heavily littered’ list.”
IFI promotes a ‘leave no trace’ ethos with anglers and all water users, and Campion appealed to the public “to refrain from littering in or around our waterways”.
Campion added: “If we are to ensure the sustainability of the resource in the long term and to safeguard Ireland’s enduring appeal within the world of angling then we each need to quickly remedy this litter issue.”
As previously noted on Afloat.ie, Doolin ferry operator Eugene Garrihy hit out at the IBAL’s claims that the Clare town is a “litter blackspot”.
Toxic ‘Algae’ Threatens Wildlife In Killarney Lake
#Toxic - Pet owners have been advised to be vigilant over an outbreak of toxic blue-green ‘algae’ in a Killarney lake, as The Irish Times reports.
Lough Leane has been signposted by Kerry County Council over the presence of Cyanobacteria that has turned the waters a soupy pea-green colour.
A number of dogs died after exposure to the bacteria during a previous bloom on the lake shore in 2016.
Suspected similar cases have also been reported at Lough Mask as well as waterways further east, including Ballymore Eustace on the River Liffey.
Meanwhile, scientists at the Galway-Mayo Institute of Technology are preparing to use drones to test the water quality of lakes on the West Coast.
GMIT’s Marine and Freshwater Research Centre has secured €132,000 in funding from the EPA for the scheme that will allow for real-time feedback of camera images and data.
Licensed drone pilots will work with lake biologists and water scientists on the two-year project, part of Ireland’s mandate under the EU’s Water Framework Directive.
The Irish Times has more on this story HERE.
Plastic Problem For Gannets On Little Skellig
#MarineWildlife - Concerns have been raised over the levels of plastic pollution at an important gannet colony on the smallest of the Skellig Islands.
As The Irish Times reports, discarded plastic waste – including parts of old fishing gear in the Atlantic for more than a decade – now comprises a large proportion of the material used by some 70,000 gannets to build their nests on Little Skellig.
And conservationists fear the problem is being ignored by authorities focused on marketing nearby Skellig Michael to tourists based on it appearance in recent Star Wars films.
“I film marine life underwater [and] it’s very difficult to get a frame without plastic in it, and that wasn’t an issue 15 years ago,” said local filmmaker Vincent Hyland, who added that plastic pollution levels had reached “frightening proportions” in the last year.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Preventing Plastic Pollution on Waterways: Infographic
You don’t have to look far to see a scary story involving plastic, whether that story involves a whale washing up to shore as a result of ingesting too much plastic or a video that shows a turtle having a straw pulled out of its nostril, the truth is that plastic pollution has become an epidemic that needs to be taken seriously.
Although plastic waste is everywhere, its detrimental effect on our waterways and marine life have made people take notice of the problem at hand. It is estimated that plastic makes up 60-90% of marine debris, and some of that debris, such as fishing lines can take up to 650 years to break down. 650 years is the equivalent of the whole of the series of Friends playing continuously 4693 times.
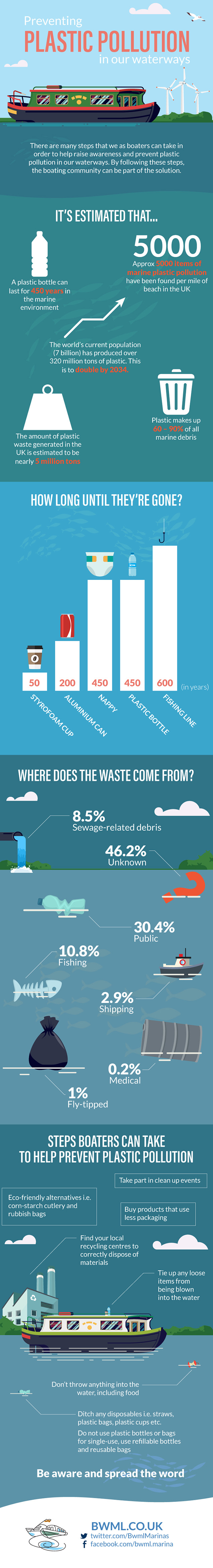
Boaters will be noticing first-hand the problem plastic pollution is causing, with it washing up on riverbanks, blocking weirs and floating next to their marina boat moorings. Luckily not all hope is lost in this cause, there are several steps that boaters can take to ensure the issue doesn’t get any worse and starts to head in the right direction.
For example, use reusable bags instead of opting for single use carrier bags. You could also replace plastic cutlery with bamboo or corn starch cutlery. These are just small changes that could make a big difference.
#Angling - At a sitting of Ardee District Court on Monday 12 March, Irish Water pleaded guilty to the discharge of deleterious matter to the River Dee on 15 May 2017.
The offence related to a poor quality discharge from a wastewater treatment plant at Ardee, Co Louth.
The River Dee rises near Bailieboro in Co Cavan and flows through Co Meath and Co Louth, where it enters the Irish Sea at the village of Annagassan.
Michaela Kirrane, senior fisheries environmental officer with Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI), told Judge Coughlan that during a routine inspection of the river on the 25 May last year, it was noted that the river appeared to be in a poor condition downstream of the discharge point from Ardee Wastewater Treatment Plant.
A series of water samples were taken and analysis confirmed that the discharge from the treatment plant was having a deleterious impact on the quality of the River Dee, an important brown trout fishery.
Irish Water co-operated fully with IFI’s investigation and remediation works were carried out. Upgrade works are currently underway to increase capacity at the wastewater treatment plant.
Irish Water was fined €4,500 with costs and expenses awarded to IFI amounting to €4,381.61.
Plastic & Nitrates Concerns For Irish Shores In Latest Coastwatch Survey
#CoastalNotes - Plastic continues to litter Ireland’s coastline, with over 8,800 drinks bottles recorded around the island’s shores in the 2017 Coastwatch survey.
Preliminary results from the volunteer survey conducted in September and October show that more than four-fifths of shoreline sites had plastic bottles, according to RTÉ News.
While the rate of 3.6 per 100m of shore indicates a downward trend, it is still far higher than those in Scandinavia.
And it comes with a rising rate of bottle tops, especially “complex caps” that come with sports drinks, as The Irish Times reports.
In other summary results ahead of the final report due in the sprint, plastic bags were found at 40% of sites, though their numbers have fallen from a peak of 18 per site before the bag tax to an average of two this year.
While nearly half of locations surveyed were rated as “reliably free” of pollution by sewage, there are concerns over “worrying” nitrate levels in freshwater streams entering the sea.
That’s particularly so on the South and East Coasts, and in Northern Ireland where 13% of sites had levels exceeding EU directives.
The Irish Times has much more on the story HERE.
#Pollution - RTÉ News reports that a swimming ban was lifted yesterday on bathing spots at Seapoint and Killiney on Dublin Bay’s southern shore after high levels of E.coli were detected last Friday (30 June).
The bathing ban remains at Blackrock Baths pending the results of samples expected later today (Wednesday 5 July). Blackrock and Seapoint were subject to a similar ban for high E.coli levels back in January, according to TheJournal.ie.
More recently, the beaches at Dollymount and Sandymount were closed to swimming after heavy rains caused by a sewage spill in the River Liffey.
Dublin Beaches Closed To Swimmers After Liffey Sewage Spill
#Pollution - The beaches at Dollymount and Sandymount on Dublin Bay have been closed to swimmers after a sewage spill in the Liffey caused by heavy rain on Thursday (8 June).
According to BreakingNews.ie, swimming is banned at both of the popular city bathing spots pending the results from water samples expected tomorrow (Monday 12 June).
It comes just weeks after two Dublin region coastal beaches lost their Blue Flag status in the latest list of EU beach quality awards.
That announcement followed days from the news that three other Dublin beaches — including Merrion Strand, adjacent to Sandymount — had failed to meet the minimum standards for bathing water quality.

































































