Displaying items by tag: Dredging
Another Sighting of Dredger ‘Charnock’ as Warrenpoint Port Maintenance Works Continue
Afloat reader Lee Maginnis has shared a new image of the suction dredger Charnock returning to Warrenpoint in Co Down after emptying its load in the open sea on Sunday (24 March).
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the vessel has been carrying out dregding operations in the approaches and deep-water berths of the inner harbour of Warrenpoint Port since the end of February.
These operations are expected to continue until mid April.
Annual maintenance dredging at Warrenpoint Harbour in County Down will continue until the end of March and possibly into April.
According to Afloat reader Lee Maginnis, residents and visitors to Warrenpoint and, indeed, Omeath have been treated to the sight of the trailing suction dredger "Charlock" hard at work over recent weeks.
The dredging, say the harbour authorities, will 'secure the safety and accessibility of the shipping channel for commercial and recreational purposes'.
Since the end of February Charlock has been carrying out operations in the approaches and deep-water berths of the inner harbour of Warrenpoint Port, an operation that will take approximately 48 days.
The sleek, grey ship, with a bulbous bow transports dredged material to the WARRENPOINT B licenced sea disposal site outside the lough.
The Charlock is supported by the "Forth Trojan" workboat vessel, which will undertake bed levelling operations.
Dredging Campaign at Port of Waterford Set for Late October
Dredging work is about to begin at the Port of Waterford with a maintenance dredging campaign to be carried out by a Dutch company.
Baggerbedrijf De Boer B.V.'s trailing suction hopper dredger Amazone is next week to conduct activities in the vicinity of Belview, Cheekpoint and further down in the estuary at the Duncannon Bar.
The campaign's main objective is the removal of accumulated sediment from the channels, turning areas and berths at (Belview) the main terminal at the Port of Waterford. This work will mostly involve work at the Cheekpoint lower bar and also at the Duncannon Bar.
The removed material will then be disposed by the 2771m3 hopper capacity dredger at an approved site beyond the estuary at a location south west of Hook Head.
It is expected that the campaign will take approximately 28 days and be followed by a bed levelling works by the Fastnet Sound which Afloat adds is a 21m MulitCat operated by a local firm Fastnet Shipping.
The marine plant and services company is based on the River Suir at Bilberry which is just westward of Waterford city's Rice lift-bridge.
One of the country’s leading marinas will become unusable for keelboats unless urgent action is taken to address increasing silting in the harbour area writes David Forsythe in West Cork
Kinsale-based Fine Gael councillor Kevin Murphy told the recent meeting of Cork County Council’s Western Division that the issue was among the most serious he had ever had to bring to the attention of the council.
“The story is that Kinsale Harbour itself has severe silting at the yacht marina and around pier head itself. A substantial number of the keelboats are bottoming out now. This is a very serious issue and a very expensive one to sort out because there is a substantial dredging to be done,” he said.
Matthias Hellstern, Commodore of the Kinsale Yacht Club said that the issue had become much more serious in the last few years and the rate of silting in Kinsale Harbour seemed to be increasing.
“During Covid there was obviously a lot less activity at the marina and in the harbour in general because of the restrictions. It has been happening over a number of years but seems to be getting much worse now. It is something that we really need to address urgently,” he said.
 Matthias Hellstern, Commodore of the Kinsale Yacht Club Photo: Bob Bateman
Matthias Hellstern, Commodore of the Kinsale Yacht Club Photo: Bob Bateman
The 200 berth marina brings in some 3,500 visiting boat nights to the town every year contributing an estimated €525,000 to the local economy according to the yacht club’s own estimates. A non-profit organisation run by volunteers, it is one of only three yacht clubs in the country that owns its own marina, the others being Howth Yacht Club and the Royal Cork Yacht Club in Crosshaven.
“We have visitors coming from France, the UK, Spain, Germany, the USA and all around Ireland,” said Matthias Hellstern, “and we run also run national and international sailing championships which we could not do without the marina facility.”
The KYC is due to host the upcoming Squib UK National Championships, Dragon Gold Cup and also hosts the biennial Sovereign’s Cup, but silting is already causing problems for events in Kinsale.
“We hosted the April Spring series recently and we were having yachts running aground at low tide,” said Matthias, “they simply couldn’t get out of the marina and obviously that’s a serious problem.”
Mr Hellstern said that already about 25% of the marina was not useable for keelboats at low tide.
 A KYC Marina pontoon at Kinsale Harbour Photo: David Forsythe
A KYC Marina pontoon at Kinsale Harbour Photo: David Forsythe
“At the moment we can move things around a bit. The berths furthest from the channel are most affected so we can put power boats, boats without keels in there for the time being but as the silting gets worse more and more of the marina will be affected.”
Cllr Kevin Murphy said that silting was affecting other users of the harbour as well across leisure, fishing and commercial sectors.
“We have to at all times ensure Kinsale continues being useable for leisure and also commercial and fishing, it’s all three. The Kinsale Yacht Club will help out with a survey that needs to be done on the silting and I would expect that the county council will also chip in if we can to help out in their endeavours to get that done as soon as possible.”
 (Above and below) The 200 berth Kinsale Yacht Club marina brings in some 3,500 visiting boat nights to the town every year contributing an estimated €525,000 to the local economy Photos: Bob Bateman
(Above and below) The 200 berth Kinsale Yacht Club marina brings in some 3,500 visiting boat nights to the town every year contributing an estimated €525,000 to the local economy Photos: Bob Bateman

Cllr Murphy said that he would put down a notice of motion at the next municipal district meeting to have all of the stakeholders attend a meeting at Kinsale Yacht Club, “to make sure this is addressed as soon as possible”.
Responding to Cllr Murphy, Kevin Morey, Director of Water Services at Cork County Council said, “We will engage just to take stock and see what is the issue there. From your description, it sounds like it might be quite a significant one and we are aware from other locations that that could bring us into quite complex and protracted processes. Let’s start looking first and take stock so we’ll get back to you on that and arrange some kind of assessment on site.”
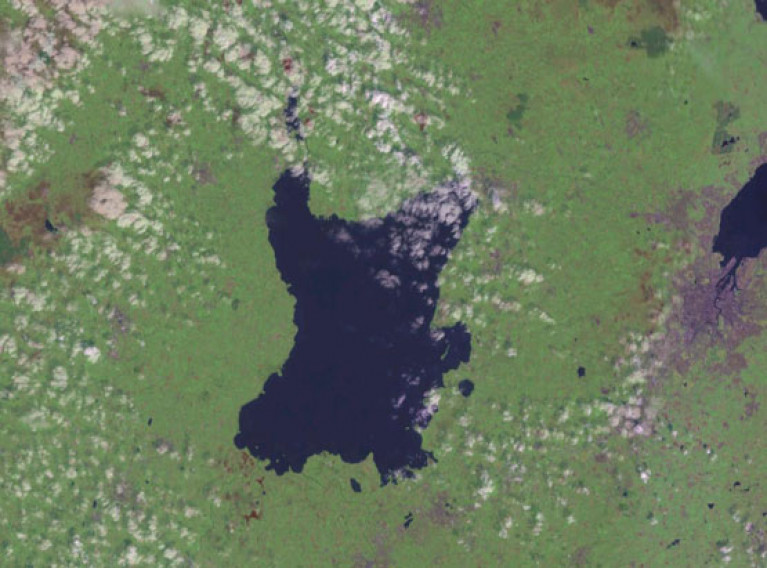
Campaigners Hit Out At Lough Neagh Sand Dredging Approval
Environmental campaigners have hit out at a Stormont decision to approve sand dredging in Lough Neagh, as the Belfast Telegraph reports.
Sand dredging has been practiced in Lough Neagh since the 1930s, with no permission needed until after the lough was designated as a Special Protection Area for wildlife in 1999.
Most recently the practice has been subject of a years-long legal battle, as previously reported on Afloat.ie, with Friends of the Earth claiming that as much as 1.5 million tonnes of sand are removed from the lough each year.
The final say on the matter was left to Northern Ireland’s Department of Infrastructure, whose minister Nichola Mallon signed off on the approval and said the decision was a “finely balanced” one “where I had to weigh up the various benefits with the potential for harm to the designation features of the lough”.
Among those criticising the move was Green Party NI leader Clare Bailey.
She said that sand dredging has “a devastating impact on the entire ecosystem of the lough”, and claimed the situation underscored the notion that “Northern Ireland is disintegrating into an environmental wasteland”.
The Belfast Telegraph has more on the story HERE.
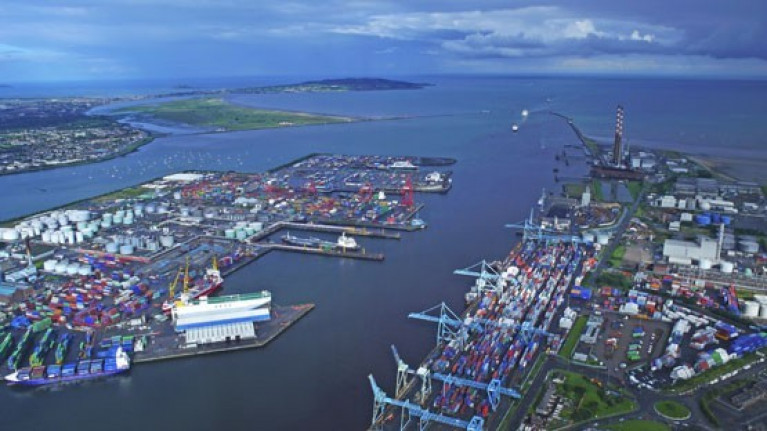
Dredging Works In Dublin Port Berths & Fairway
The Dublin Port Company has given notice that maintenance dredging will take place between Alexandra Basin and the Dublin Bay Buoy from tomorrow, Thursday 10 September.
Four weeks of dredging works are scheduled in the fairway and berth pockets from the buoy to a line drawn due south of berth OB1 and including Alexandra Basin East.
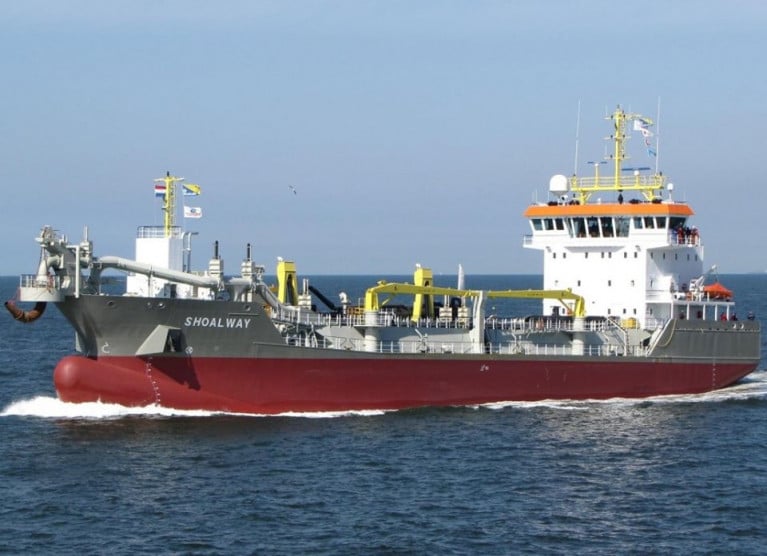
Three vessels will be involved in the dredging works: the trailing suction hopper dredger Shoalway; the survey vessel Smit Neyland; and Norma, a bed-levelling plough.
The three craft will maintain a listening watch on VHF Channel 12 and show the required lights and shapes.
All other vessels should pass at slow speed and make due allowance for their operations and restricted manoeuvrability.
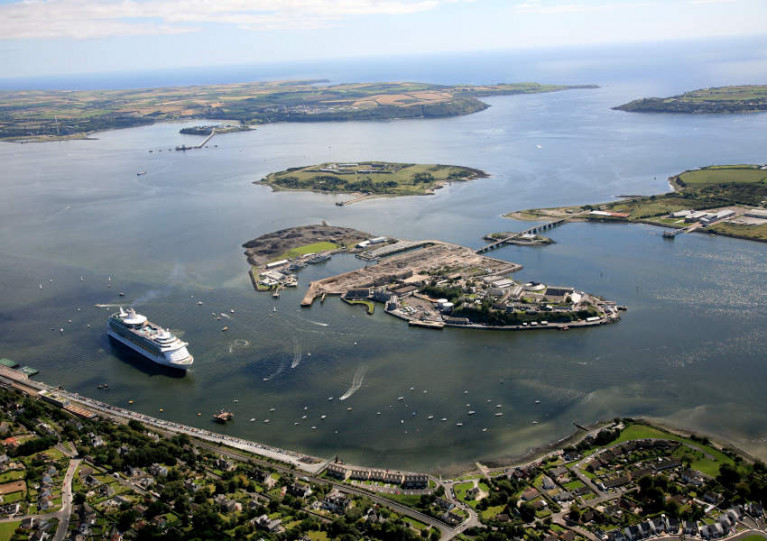
Port Of Cork Maintenance Dredging Begins This Week
The Port of Cork reminds mariners that maintenance dredging will be taking place in Cork Harbour on all main shipping channels and berths from this Wednesday 19 August.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the dredging campaign by the TSHD Taccola will progress 24 hours a day until late September.
It follows a prior survey conducted last week, and bed levelling operations which began yesterday, Sunday 16 August.
Mariners are requested to navigate with caution when in the vicinity of the work craft, to pass by as wide a margin as possible and proceed with minimum wash and speed.
Dredging Operations Underway at the Port of Waterford
A maintenance dredging campaign has begun in recent days at the Port of Waterford where activities will involve the waters of Duncannon Bar, Cheekpoint, and at the port's main terminal at Belview, writes Jehan Ashmore
Prior to the operations at the south-east port, the Cypriot flagged Shoalway, a trailing suction hopper dredger had been carrying out operations for the Dublin Port Company. Shoalway sailed from the capital to arrive on the Waterford Estuary on Sunday.
According to the Port of Waterford (click to consult campaign notice here), the dredger will dispose spoil at an approved site south west of Hook Head, Co. Wexford. Dredging will be followed by a bed levelling campaign by the vessels, Fastnet Sound and or the Glenesk.
Afloat adds that Irish Dredging which is a subsidiary of Royal Boskalis Westminster nv, the world’s largest dredging group, was given the contract from the Port of Waterford. The extensive fleet of the Dutch group provides Irish Dredging access to the use a of wide range of vessels for projects around the Irish coast.
Further tracking of the Shoalway since introduction on the Waterford Estaury has seen the 90m long dredger kept busy between Cheekpoint to the spoiling grounds out to sea.
The campaign according to the Port of Waterford is expected to last approximately 24 days.
Dredging Campaign Continues Operations at Port of Waterford
#Irishports - The Port of Waterford have issued a Marine Notice in recent days to advise all ship owners, shipmasters, agents, fishing vessels, pleasure craft users, seafarers and fishery organisations of a dredging campaign, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The dredging operation along Waterford Estuary began in mid-March and according to the south-east multi-modal Port the campaign will continue until around 6 April.
Carrying out these works is the task of trailing suction hopper dredger Freeway which will conduct dredging activities in the vicinity of Belview Port. The lo-lo facility located downriver of Waterford City is the main port along the estuary.
Freeway is operated by UK firm, Royal Boskalis Westminster based in Hampshire. They are no strangers to these waters having been contracted previously by the port and more recently from the Dublin Port Company. Due to berth capacity constraints the 92m dredger during December had to dock in Dun Laoghaire Harbour.
On this occasion, Freeway's role on Waterford Estuary will include duties carried off Cheekpoint and at the Duncannon Bar located further downriver and beyond where the Passage East ferry links to Ballyhack.
Disposal material from Freeway will take place at an approved site south west of Hook Head. Following such work a bed-levelling campaign will be assigned to the Waterford City based catamaran craft Fastnet Sound.
Howth Harbour Dredging Plans Move Forward With New Details
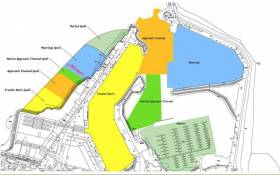
The Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine has updated local Fingal councillors on its proposals for the dredging of Howth Harbour.
On his Facebook page, Cllr Cian O’Callaghan says the meeting with the department and the Howth Harbour Master on Wednesday (6 March) detailed a plan to dredge five key areas of the harbour, namely:
- The fishing trawler basin between the West Pier and Middle Pier
- The approach channel at the mouth of the harbour
- The marina used by Howth Yacht Club
- The approach channel to the marina
- The outer moorings area which is used by the Howth Sailing and Boat Club
This would result in the extraction of 225,000 cubic metres of silt, the equivalent of up to 30,000 lorry loads, says Cllr O’Callaghan.
The detailed plan follows testing of material extracted from the harbour which confirms that while is it contaminated by general harbour activity, it is not considered hazardous.
It is being proposed that the spoil be treated and used to create a 100-metre-wide infill area along the west side of the present West Pier. Plans for the use of this new space have not yet been decided but it is expected there will be a relevant public consultation by year’s end.
Four months ago the tender period closed for engineering services related to these long-awaited dreading works in the North Co Dublin harbour.