Displaying items by tag: Shipwrecks
New predictive technology being developed in Estonia could help prevent the spread of pollution from shipwrecks.
Estonia’s public broadcaster ERR News reports on the monitoring system created by marine scientists at Tallinn University of Technology (TalTech) that may forecast where fuel will spread in the water from a hazardous wreck site.
Estonia’s coastline on the Gulf of Finland, Gulf of Riga and Baltic Sea has a large number of decades-old shipwrecks which are increasingly prone to fuel leaks as they age.
So far the results are promising, with TalTech’s predictive computer models — using current and wave data from Estonian waters — matching real-world data collected from smart buoys placed at a number of coastal sites.
ERR News has more on the story HERE.
‘Shipwrecks’ Discovered in INFOMAR Survey Off West Coast
Surveyors for the INFOMAR seabed mapping programme have reported the detection of two obstructions on the Atlantic floor some 30 nautical miles west of Co Galway.
Marine Institute research operations manager Aodán Fitzgerald told RTÉ News that these obstructions are likely shipwrecks.
“There are thousands of these in Irish waters,” he said. “However as these are fishing areas, we issued a notice to advise fishermen with towed fishing gear to avoid the areas.”
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, a series of seabed mapping surveys was launched in February this year, with the RV Tom Crean recruited to carry out operations west of west of Kerry, Clare and Galway outside the 30nm limit.
The State’s latest marine research vessel found one of the objects around 80km west of the Aran Islands in Galway Bay, and the other 70km west of Loop Head in Co Clare.
Coordinates for the obstructions are included in Marine Notice No 64 of 2023, attached below.
Shipwrecks With No Known Owner Will Become State Property Under Proposed New Legislation
Shipwrecks with no known owner will become State property under new legislation which Minister of State for Heritage Malcolm Noonan is proposing.
The legislation also proposes that commercial salvage law does not apply to historic wrecks.
The Monuments and Archaeological Bill intends to revise and replace the National Monuments Acts 1930 to 2014.
It was presented by Noonan on Thursday evening to the Joint Committee on Housing, Local Government and Heritage.
The Department of Housing said the proposed Bill seeks to introduce new measures to protect archaeological structures and sites.
 Minister of State for Heritage Malcolm Noonan
Minister of State for Heritage Malcolm Noonan
It will include the establishment of a single register of monuments, a statutory reporting scheme for newly discovered monuments and provisions to prevent the illicit import and possession of stolen cultural property.
“Another innovative element of the proposed Bill is to incorporate historic wrecks and underwater cultural archaeological objects into the new scheme for monument protection,” it said.
“The proposed Bill will also enable the State to ratify and give effect to several important international conventions relating to the protection of cultural heritage,” the department said.
Multiple amendments to the National Monuments Act 1930, along with multiple transfers of functions, have resulted in “fragmented legislation which is far from easily accessible and comprehensible”, it explained.
“The proposed legislation aims to address a range of structural issues, simplify terminology, as well as provide a single accessible piece of legislation,” the department said.
“This proposed Bill will modernise existing legislation protecting monuments and archaeology – some of this legislation dates back to the 19th century,” Noonan said.
“ If enacted, this legislation will substantially strengthen protection of archaeological heritage for the enjoyment of future generations and also represent major progress on the protection of our built heritage,” he said.
He referred to the department’s recent publication of a Vernacular Strategy to protect traditional buildings.
He said there were plans to launch “Heritage Ireland 2030” in the coming weeks, as in a “new national heritage plan to provide a vision and backdrop to realise our full set of ambitions for Ireland’s built, natural and archaeological heritage”.
The Department of Transport advises that a survey will take place at several offshore reefs and sandbanks off the North West Coast from next Friday 23 April to Tuesday 4 May.
Survey works with marine robots in support of the EU Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme will take place within a three-nautical-mile radius of six shipwrecks, the coordinates of which are included in Marine Notice No 24 of 2021 which can be downloaded below.
The survey will be conducted from the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will conduct acoustic surveying during the night using its hull mounted multibeam, with remotely operated vehicle (ROV) sampling during daylight hours.
In addition, the vessel will be used as a platform to deploy a range of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) and a series of six small (1.2m3) pyramidal landers, referred to as baited remote underwater video (BRUV).
At all times, the RV Celtic Explorer will display appropriate lights and signals.
Dublin Bay Area’s Many Shipwrecks to be Brought into Focus
Dublin Bay Old Gaffers’ Association invites all to join their next Zoom session on Shipwrecks Around Dublin Bay, which will be given by Cormac Lowth on Thursday 25th February at 20.00hrs.
Following on from his extremely popular talk on the loss of the Palme and the tragic demise of the Kingstown Lifeboat in 1895, the renowned maritime archaeologist and historian Cormac Lowth will talk on “Shipwrecks Around Dublin Bay.” Based on historical research, hydrographic surveys, underwater photography and data from his own diving expeditions, Cormac will reveal the stories behind many of the shipwrecks hidden under the waves of Dublin Bay and the nearby coast.
Only partially protected by the offshore shoals of the Bennet and Kish Banks, Dublin Bay has proved to be a graveyard for many ships. Closer inshore the Burford and Rosbeg Banks lie in wait for the unwary.
The sinking of the Queen Victoria
Cormac will describe the sinking of the Queen Victoria in 1853, the Tayleur on Lambay in 1854, the Vanguard in 1875, the Palme in 1895 and the Bolivar in 1947 to name but a few. If you are interested in Dublin Bay and marine archaeology you will not want to miss this talk.
Please be early to be sure of getting a good seat!
DBOGA Fundraising for HOWTH RNLI: Pre-Covid, DBOGA listened to talks together at Poolbegwhile passing the Yellow Welly around for your €5 lifeboat donation. In Zoom Land we can’t do that, but the RNLI urgently needs funds. Please click on: www.justgiving.com/fundraising/DBOGAHowthLifeboat. Thank you - we are nearly halfway to our target of €4,000.
The details of this Zoom meeting are:
• Topic: Cormac Lowth Talk
• Time: February 25th 2021, at 20.00hrs
Donate to RNLI here
Zoom Link here
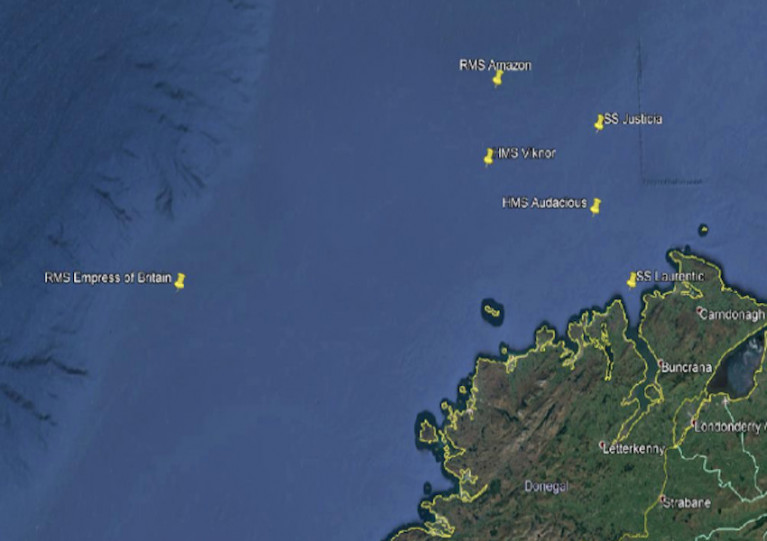
“Substantial progress” is being made in the recovery of gold bullion from a ship wrecked off Donegal nearly 80 years ago, as RTÉ News reports.
Atlantic Subsea Ventures is involved in the salvage operation at the Empress of Britain, a luxury ocean liner that was requisitioned for the war effort in 1939 and targeted by the Nazis the following year.
A number of such vessels are believed to lie in the depts around Ireland, with one in recent years — the SS Gairsoppa off Galway — giving up a record 48 tonnes of silver bullion seven years ago.
The Empress of Britain, which is believed to hold as much as €500 million in gold bullion, was found in 1995 but its location in deep waters precluded any salvage expedition, until now — thanks to remote-operated technology used in the oil and gas industry.
The massive “North Sea Giant” heading out from #killybegs #donegal in search of gold on a sunken WW11 wreck more on @rtenews @ 6 pic.twitter.com/VQeBHyfs30
— EileenMagnier (@EileenMagnier) May 28, 2019
What’s proving a bigger stumbling block for the salvage company, it says, is Ireland’s 7.5% levy on recovered cargo which must also be held for a year and a day before it can be moved on.
RTÉ News has more on the story HERE.
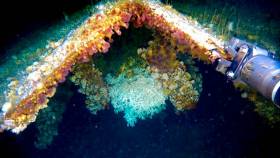
Shipwrecks off the Irish coast are acting as artificial reefs for corals usually found much deeper in the Atlantic.
That’s according to NUI Galway ocean scientist Anthony Grehan, who told the Irish Examiner about his recent surprising find at the wreck of a cargo vessel 160 metres below the surface.
Using the new submersible robot Étáin from the University of Limerick, Grehan and a team on the RV Celtic Explorer found examples of the stony coral species lophelia pertusa, which usually found at depths of 500 metres or more.
And the new discovery suggests that such wrecks may provide the necessary stability for deep-water corals to thrive in shallower waters.
The Irish Examiner has much more on the story HERE.
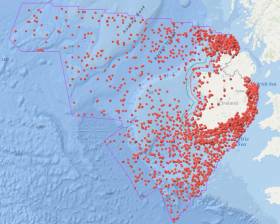
New Interactive Website Maps Ireland’s Historic Shipwrecks
#Shipwrecks - Heritage Minister Josepha Madigan yesterday (Wednesday 25 April) announced the launch of a new website with an interactive map of the thousands of historic shipwrecks in Irish waters.
The Wreck Viewer has been developed to facilitate free and easy access to the Wreck Inventory of Ireland Database compiled by the National Monuments Service of the Department of Culture, Heritage and the Gaeltacht.
The database holds information on over 18,000 known and likely wreck sites both off the Irish coast and in Ireland’s inland waterways.
These wrecks span the entirety of maritime travel around and within the island, from prehistoric logboats to medieval trading vessels, warships and ocean liners.
Detailed are exact locations for approximately 4,000 of the recorded wrecks. The map also provides summary information on individual wrecks and their history, voyage, cargo, passengers and, if known, the circumstances of their loss.
Information on the 14,000 wrecks in the database for which locations have yet to be fully confirmed can also be downloaded. Further details of these wrecks will be added to the database as they become available.
The Wreck Viewer complements the department’s Historic Environment Viewer, which provides information on archaeological sites across the country from the Sites and Monuments Record compiled under the National Monuments Acts and from the National Inventory of Architectural Heritage.
Speaking on the new Wreck Viewer yesterday, Minister Madigan said: “Of particular interest, in this decade of centenaries, are the stories of those wrecks from the First World War.
“Over 1,000 ships were lost off the coast of Ireland during that conflict, in effect bringing the Western Front to our shoreline and alerting the Irish people to both the grim realities of war and the scale of the tragic loss of life that took place on land and sea.”
The minister added that it’s hoped the website will “promote a much greater appreciation and awareness of our marine heritage and at the same time provide an essential tool to help the protection of this remarkable resource.”
Stormy Weather Exposes Shipwreck Near Killary Harbour
#Archaeology - With yet another stormy weekend comes news that continued coastal erosion on the West Coast has exposed the remains of a shipwreck at Killary Harbour.
According to The Irish Times, the wreck on Tallaghbaun Strand is already known to locals though its origins are as yet unclear.
But archaeologist Michael Gibbons believes it could date from the late medieval period, as wrecks from the Spanish Armada have been identified in the region.
Gibbons has also been researching what appear to be the remains of a late Bronze Age or early Christian monastic site on Kid Island in Broadhaven Bay. The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
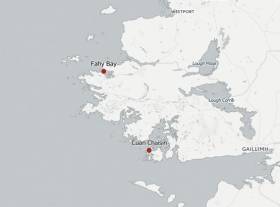
#Shipwrecks - Two new shipwrecks have been discovered in Connemara in areas known to be used by smugglers in centuries past, as The Irish Times reports.
Currach fisherman John Bhaba Jeaic Ó Conghaíle found the skeletal remains of what's thought to be an 18th-century vessel at Cuan Chaisín in Ceantar na nOileáin.
Elsewhere, Fahy Bay resident Michael Barry located a second wreck, believed to date from the 19th century, near his home on the northwest Connemara coast – inshore from the Spanish Armada wreck Falco Blanco Mediano.
The area is known as the birthplace of sea captain George O'Malley, one of the most notorious smugglers of his day.
The Irish Times has much more on the story HERE.