Displaying items by tag: torpedo
Royal Navy Fires Torpedo at Own Base in Plymouth
#torpedo – An investigation is under way after a 9ft–missile was fired from HMS Argyll at high security Plymouth nuclear submarine dockyard during a training drill this week.
A Royal Navy spokesman said: "We can confirm an incident occurred onboard HMS Argyll on Wednesday, March 12, at 3.24pm, while the ship was alongside at Devonport Naval Base in Plymouth.
"During a training exercise, an inert Test Variant Torpedo (TVT) unexpectedly jettisoned onto the wharf. There was no explosion and no casualties.
A source said: "The torpedo came shooting out of the side of Argyll and flew through the air before going straight through a security fence.
"It's carried on going before hitting a storage container. If anyone was inside it they would have a had a nasty shock - the whole side of the container was stoved in.
The Telegraph has much more on the story here.
Taoiseach Honours Torpedo's Inventor Louis Brennan
#Torpedo - Taoiseach Enda Kenny had paid tribute to the Castlebar-born inventor of the steerable torpedo at the unveiling of a headstone on Louis Brennan's grave in London.
As the Irish Independent reports, Brennan - who lived from 1852 to 1932 - was a renowned inventor, credited with developing the world's first practical guided missile that he patented as the 'Brennan Torpedo', and tested at Fort Camden in Cork Harbour in the late 1870s.
Raised in Melbourne, Australia, Brennan spent much of his working life in Britain inventing for the military, developing such concepts as a revolutionary monorail system that attracted the attention of Winston Churchill.
However, following his death in a car accident in Switzerland, Brennan lay in an unmarked grave in Kensal Green, northwest London.
Now a group of history buffs from Brennan's Mayo birthplace have finally marked that spot with a headstone, as well as a plaque commemorating his life and achievements in the cemetery's oratory.
"I am pleased today that we have this opportunity to restore and publicly acknowledge the resting place of Louis Brennan," said the Taoiseach at the unveiling ceremony yesterday (11 March).
"But also, in a sense, to redeem ourselves in that we left him here alone unknown for so long."
The Irish Independent has more on the story HERE.
Fond Memories of Guinness Barges on the Liffey
#INLAND WATERWAYS - As Derek Evans writes in The Irish Times, the recent discovery of the first Guinness merchant vessel - sunk a century ago by a German torpedo in the Irish Sea - rekindled memories of the brewery's boats on the Liffey in the 1950s.
He writes: "Living close to Stoneybatter, I often took time to stand on Queen Street Bridge as the barges, filled with Guinness barrels, slowly made their way from James’s Gate to Sir John Rogerson’s Quay.
"I remember clearly the skipper standing beside the open wheelhouse in his navy blue polo-neck jumper, captain’s hat and pipe... The skipper always had a smile and a wave before he would disappear for a few moments under the white cloud."
He also recalls the hoisting of the barrells at Butt Bridge onto the Guinness cargo vessels - like the WM Barkley, the Lady Grania or Gwendolen Guinness - for transport to Liverpool.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the wreck of the WM Barkley was captured in high-resolution images taken from the national research vessel RV Celtic Voyager off the coast of Dublin.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Sonar Survey Reveals Torpedoed Guinness Ship
The detailed seabed images, which include deck features and complex sand wave structures, were recorded by towed sidescan sonar provided by the Moore Marine Group, and give a visual insight into the defensively armed ship that was sunk by a German torpedo in 1917, seven miles east of the Kish Bank off Dublin.
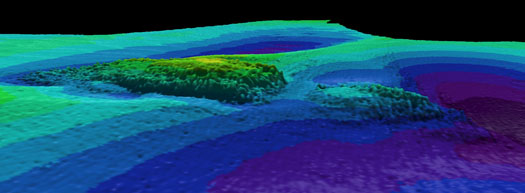
Photos above and below show topographic seafloor images in 3D, showing the partially buried wreck of the W M Barkley lying at a water depth of 56 metres; with deeper scouring around it down to 72 metres (darker colours indicate greater depths). The images were created from sonar data acquired onboard the Marine Institute's research vessel RV Celtic Voyager, during INFOMAR Programme mapping in 2010 and 2011 with data processed by INFOMAR's Fabio Sacchetti (University of Ulster) and Charise McKeon (Geological Survey of Ireland).
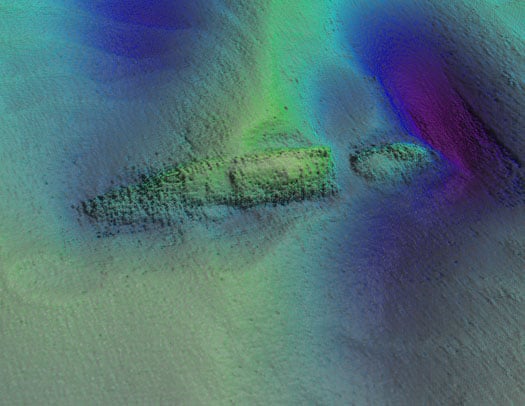
In May 2010, during a large scale mapping survey in the Irish Sea by INFOMAR, a national marine study run by the Marine Institute and the Geological Survey of Ireland, identified a seabed feature which, to the trained eye, was discernable as a potential shipwreck lying in the same position recorded on the Admiralty Chart, the EU wreck site and UK Hydrographic Office wreck site directories, as well as a survey conducted in the 1980s as the last known position of the W.M.Barkley.
Viewing the spectacular imagery of the shipwreck Minister for Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, Pat Rabbitte, said "I am delighted to note the continued excellence of the valuable work being carried out under the INFOMAR project. These images from the deep reveal a unique view of part of Ireland's marine heritage and I am delighted to announce details of INFOMAR''s annual seminar to be held in Galway on November 16 and 17th."

Eibhlin Roche - Guinness Archivist, Guinness Storehouse with the model of the W.M. Barkley. Photo: Jason Clarke Photography
Ninety four years ago on the dark night of October 12th 1917 the W.M.Barkley was torpedoed without warning by the German submarine UC-75. Within minutes the ship, which was owned and operated by the Guinness Company of Dublin, broke in two and sank, taking with her to the bottom four men including her Captain and leaving the rest of her crew to face the sea in an open lifeboat. Now, the darkness where the ship has lain in pieces has been disturbed, probed by fingers of sound that are mapping the seabed in incredible details and bringing to light the position of this famous Irish shipwreck.
"As the first Guinness owned ship, the W.M. Barkley played an important role in the story of the transportation of GUINNESS beer overseas," said Eibhlin Roche, Guinness Archivist. The events of the night of 12th October 1917 are very much part of the history of Guinness that is recorded in the Guinness Archive. It is exciting to finally know the exact resting place of the W.M. Barkley."
A scale model of the W.M. Barkley is on display in the Transport Gallery of Guinness Storehouse remembering the lives of the Guinness men who both perished and survived the events of 12th October 1917. These are stories of tragedy and bravery portraying Irish traditional values, and how they were brought to light with the application of cutting-edge technology.

Koen Verbruggen (GSI), Minister Pat Rabbitte, Dr. Peter Heffernan (CEO, Marine Institute), Eibhlin Roche (Guinness Archivist, Guinness Storehouse) and David Smith (Country Director, Diageo Ireland) Photo: Jason Clarke Photography
What Happened to the Lusitania?
American Gregg Bemis is headed to Ireland for what may be the last major dive to the wreck of the Lusitania.
Bemis, who owns the wreck of the former Cunard cruise liner torpedoed off the Cork coast in 1915, told The Irish Times that hopes to discover once and for all what was in the cargo hold of the ship - and give an answer to rumours that precious art and munitions were part of the manifest.
The millionaire has fought with the Irish State over the rights to the wreck site, to which he has dived twice before, but now he has full licence and access to the latest technology to unveil the Lusitania's deepest secrets.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
German U-Boat Rediscovered in Cork Harbour
Scuba Divers have found a fully intact World War I U-Boat on the seabed just outside Cork harbour, some 93 years after it sank writes Timmy Carey.
During the First World War the menace provided by German U-Boats would prove deadly to the Allies and were responsible for sinking millions of tons of shipping; indeed German U-Boats almost changed the course of the war. Most allied ships sunk by U-boats were sunk by either torpedo, deck gunfire or explosives placed aboard the ship by U-boat crew. A smaller number of ships were also sunk by mine laying U-boats; one of these being UC42. On the 10th of September of 1917 UC42 was laying her deadly cargo of mines at the entrance to Cork harbour when a terrific explosion occurred which resulted in a grim death for all 27 German Submariners aboard.
As the submarine sank to the seabed the German submariners were trapped inside UC42, which would soon become their metal tomb.
On November 2nd of that year, hardhat divers from the Haulbowline dockyard dived the area and positively identified the U-boat as UC42, noting the stern damage to the submarine and the presence of the bodies of some of the German submariners. During 1918 the submarine was dived by Haulbowline and American divers in an effort to disarm all the mines and torpedoes still aboard, with USS Melville taking three of the mines. It was widely believed that in July 1919 divers using explosives from HMS Vernon torpedo school had destroyed the submarine with the remains being dispersed on the seabed by wire sweeps.
With the advent of scuba diving many divers have since searched for the scattered remains of UC42 around Cork harbour with no luck until a recent dive by two local divers Ian Kelleher and Niall O Regan descended a shot line to see the menacing sight of the hull of a German U-boat emerge from the shadows. Both divers were very surprised and ecstatic to find a fully intact World War I U-Boat in 27 meters of water just outside Cork harbour in good condition with little obvious explosive damage from the British naval dive team.
A local dive team of five divers had spent the previous 12 months carrying out a careful methodical search of the greater harbour area determined to find the remains of the submarine; their hard labours finally paying dividends when Niall and Ian identified the presence of the submarine. The dive team consisted of Ian Kelleher, Niall O Regan, Philip Johnston, Eoin Mc Garry and Timmy Carey.
Over the past few weeks the divers have carefully and methodically videoed and photographed the Submarine and taken various measurements to record the wrecks' condition. Over a number of dives the dive team carefully cleaned the growth from the propeller and after some methodical cleaning found the U-Boats number UC42 stamped into it; positively identifying the submarine.
As the submarine is a war grave and contains the remains of so many young German submariners the dive team also laid a plaque of remembrance, which was erected near the submarines propellers; to act as a memorial to the German submariners forever entombed in UC42. The plaque was kindly donated to the dive team by John O' Mahony of Complete Signs.

The image of the U-Boats propellor with the markings identifying the U-Boat. Photo: Timmy Carey

A badly decayed mine on UC42 still in the mine chute. Photo: Timmy Carey


































































