Displaying items by tag: Galway Harbour
Marinas and public slipways around the coast are due to open next week as part of a phased lifting of Covid-19 restrictions.
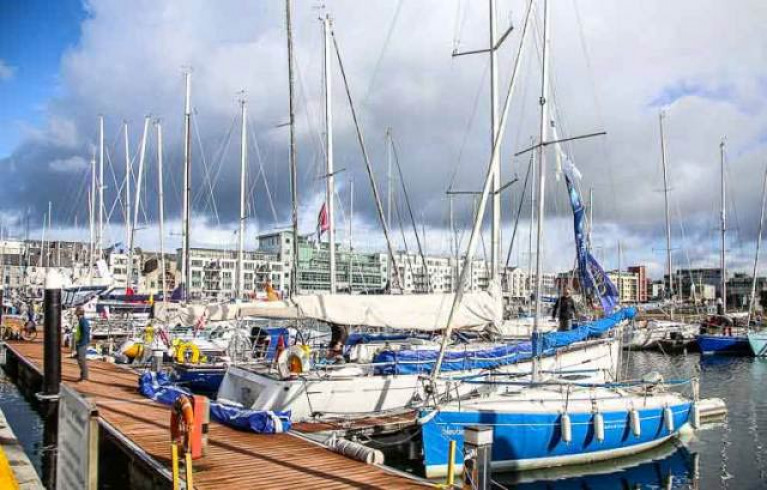
Port of Galway harbourmaster Capt Brian Sheridan has said the port’s public slipway and its marina will be open to those living within five kilometres.
Sailing is permitted within HSE guidelines, once landing ashore is not beyond five kilometres of a boat owner’s primary residence.
However, no visiting leisure craft are permitted to enter the marina under procedures drawn up to match HSE Covid-19 guidelines.
Hand sanitisers have been installed at the marina gangway, social distancing must be observed and any boat owners requiring the crane for boat lifts will have to complete a self-declaration of health, Capt Sheridan has said.
Galway City Council has opened up beaches, but car parks at all but Silver Strand remain closed.
Bathing water quality testing won’t begin until June 1st. Blackrock Diving Tower in Salthill remains closed until June 8th, when there will be restricted use. Salthill’s promenade will re-open with social distancing.
Galway City Council is also establishing a “city mobility team” to examine “wider footpaths, safer cycling facilities, traffic restrictions and supporting businesses who may need the use of public space for social distancing purposes”.
The Government has sanctioned re-opening of “outdoor public amenities and tourism sites, such as car parks, beaches and mountain walks” as part of phase one from Monday, May 18th.
This weekend the Irish Coast Guard lifted its advisory on staying off the water but urged people to observe the “current 2x5 rule, as in two-metre physical distance and five km travel distance”,
Irish Coast Guard spokesman Gerard O’Flynn thanked the public for its co-operation and warning that that there is still a Government focus on protection of frontline services and saving lives.
The new Irish Coast Guard statement was not issued with the RNLI, although both bodies issued joint statements over the last month advising people not to take to the water.
Atlantic Seaboard Harder Hit Than East Coast by Economic Affect of Pandemic, Report Says
Dublin may have the highest number of cases of Covid-19 infection, but it is least exposed of all Irish counties to the economic impacts, a new report says.
The Atlantic seaboard reliance on tourism and recreation, including the marine sector, and service industries is making it more vulnerable, with Kerry has been identified as the hardest hit, the report by the Northern and Western Regional Assembly says.
It identifies Galway as the city most likely to be severely affected, followed by Waterford, Limerick, Cork and Dublin in that order.
The report bases its information on numbers of commercial units operating in sectors which are likely to be worst affected, including mining and quarrying, construction, non-essential retail and wholesale services, food and accommodation, arts, recreation and entertainment, hairdressing, beauty and fitness.
It notes these are sectors which rely on human interaction and have been forced to close or downsize dramatically, due to social distancing measures. The nature of their business largely prevents them from operating remotely.
The report calculates that Kerry has 53.8 per cent of its commercial units operating in the sectors, and is likely to be hardest hit as a county.
It is followed by Westmeath at 51 per cent, Donegal at 50.6 per cent, Cavan at 50.5 per cent and Clare at 50.4 per cent, the report estimates.
The report says that exposure is “generally lower in more urban-based counties” as “such counties rely more on economic activities that are capable of operating remotely” – as in activities such as finance, ICT and professional and technical services.
It says the county with the lowest “Covid-19 exposure ratio” is Dublin, with 39.4 per cent of its commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected.
It calculates Cork is also cushioned, with 44.4 per cent of its commercial units in worst affected sectors, while Carlow is at 44.7 per cent, Waterford is at 45.8 per cent and Wicklow is at 46 per cent.
It says that in “absolute terms”, Dublin has the highest number of commercial units operating in the most exposed sectors at 14,360 units, followed by Cork at 8,144 units, Galway at 4,253 units, Kerry at 3,263 units and Donegal at three.
It says that Galway city and suburbs have 46.1 per cent of commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected, “in line with the corresponding ratio for the State as a whole”
The report for three regional assemblies by economist John Daly was prepared to identify which geographical areas in Ireland are more likely to be exposed to economic disruption caused by the necessary measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
It uses information from the GeoDirectory commercial database, as of September 2019.
Analysing the impact on a regional basis, it says the northern and western region has the highest “COVID-19 exposure ratio”, with 48.6 per cent of its commercial units operating in the worst affected sectors.#
The southern region has 47.2 per cent of its commercial units operating in the most affected sectors, while the eastern and midland region has the lowest “COVID-19 exposure ratio” at 43.6 per cent, the report says.
It notes that in absolute terms, the eastern and midland region had the highest number of commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected at 29,637 units, followed closely by the southern region at 27,583 units and the northern and western region at 16,515 units.
'Port Pilots are National Assets' - Galway Harbourmaster
The unsung role of port pilots has been highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Galway harbourmaster Capt Brian Sheridan.
“Without the pilots, everything would stop - they really are a national asset,” Capt Sheridan has said.
Capt Sheridan was commenting as he confirmed that key supply lines are being kept open by ports during the pandemic.
"Without the pilots, everything would stop"
He said there had been an overwhelmingly positive response to the light beamed from Galway city’s Nimmo’s pier last weekend as part of the Shine-A-Light initiative broadcast on RTÉ television.
An aerial view of the beam, and of the illuminated port and city, was filmed by Electric Skyline (see vid below)
Weather Forces Change of Venue from Ship to Shore for Sunrise Musical Performance as Part of Galway 2020
Near gale force and gusty south-west winds have forced a change of venue for a Galway 2020 International Women’s Day event on board the Naval Service patrol ship LÉ Niamh on Sunday morning.
The patrol ship was to have hosted “Ragadawn”, an outdoor sunrise performance by international poet and sound artist Caroline Bergvall.
However, due to the potential impact of the wind on the sound systems, the sell-out event will now take place in the Druid Theatre, Galway at 7 am on Sunday, March 8 th – within walking distance of the ship at Galway docks.
LÉ Niamh arrived into Galway under the command of Lieut Cdr Claire Murphy on Thursday in preparation for international women’s day.
It is almost 12 years since Lieut Cdr Roberta O’Brien became the first female commander of a navy patrol vessel – the LÉ Aisling - and that handover ceremony took place in Galway, the city which the ship had been twinned with.
Galway 2020 cultural producer Liz Kelly has paid tribute to the Naval Service and Galway harbourmaster Capt Brian Sheridan for agreeing to participate in the event.
“Ragadawn” is described as a unique outdoor sunrise performance by international poet and sound artist Caroline Bergvall.
It comprises a “multisensory composition for two live voices, a dawn chorus of multiple recorded languages, alongside a special vocal work for soprano by Gavin Bryars”, and it “invites audiences to follow the slow rising of day”.
The composition draws on “ancient and contemporary musical and literary sunrise traditions”, with “breath patterns, poetic voice, song, languages, electronic frequencies and passing sounds”
It aims to recall “the cyclical patterns that connect all beings both to nature and society, and the awakening of mind and body”, and is described as “a powerful and moving voice performance that reconnects audiences to time, place and to each other”.
The event is one of a number programmed by Galway 2020 over this weekend to mark international women’s day.
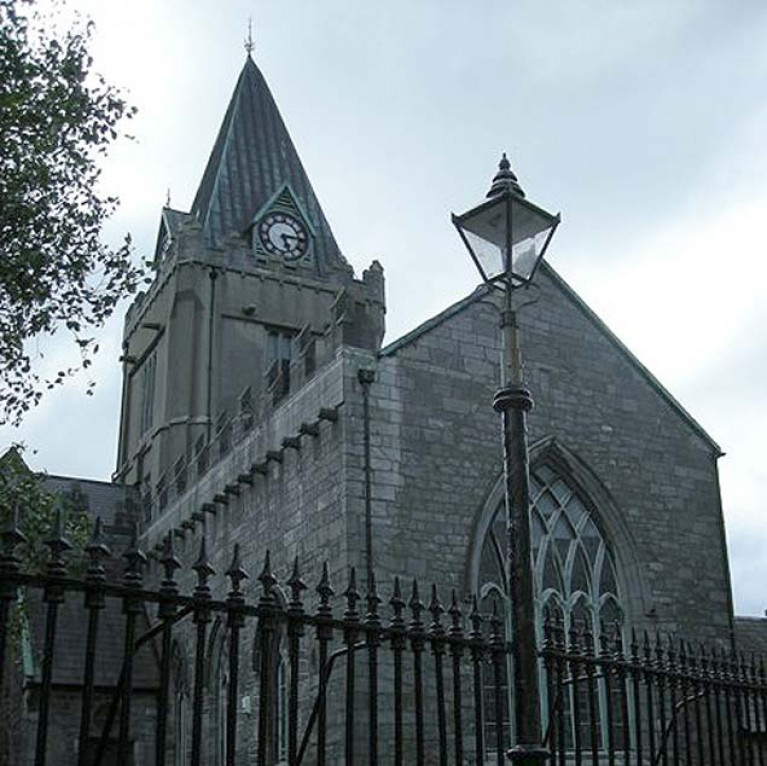
Galway Harbour Master Pays Tribute to Church Role as Navigational Aid & "Safe Haven" for Mariners
Galway’s harbourmaster Capt Brian Sheridan has paid tribute to the “safe haven” offered by the city’s St Nicholas’s medieval church as it marks its 700th anniversary writes Lorna Siggins
The illuminated clock tower was an aid to navigators, and the alignment of Nimmo’s pier and the St Nicholas church spire indicated the entrance point to the shipping channel over centuries, Capt Sheridan noted at a special service on Sunday evening.
Christopher Columbus is believed to have prayed there before setting sail to the Americas, and the church was named after St Nicholas of Myra, the patron saint of seafarers, Capt Sheridan said. Records from 1585 show that Galway was the busiest port on these islands then after London and Bristol.
"Christopher Columbus is believed to have prayed there before setting sail to the America"
He recalled how ships’ horns in Galway port responded this past new year’s eve when the church bells marked the beginning of the 700th-anniversary celebrations.
The bells rang again 700 times at the weekend, and President Michael D Higgins and deputy Galway mayor Cllr Donal Lyons were among hundreds of people welcomed by Rev Lynda Peilow to the anniversary service.
Participants included Bishop of Tuam Patrick Rooke, the Catholic bishop of Galway Dr Brendan Kelly, Rev Canon John Auchmuty of St Columba’s Parish church in Belfast, Fr Tudor Ghita of the Romanian Orthodox Church, Fr Des Foley of Galway’s Augustinian church, pupils of St Nicholas’s primary school and many parishioners.
The proceeds of the collection were divided equally between the RNLI and Galway OS, a local children’s charity.
A history of Galway market, which has traded outside the church for centuries, is among a number of events planned for both the Galway European capital of culture and the anniversary year, and 700 trees will be planted on Earth Day.
Galway capital of culture’s opening outdoor ceremony had to be cancelled due to Storm Ciara at the weekend, but Mayor of Galway Mike Cubbard received the European title at an indoor reception attended by EU Trade commissioner Phil Hogan.
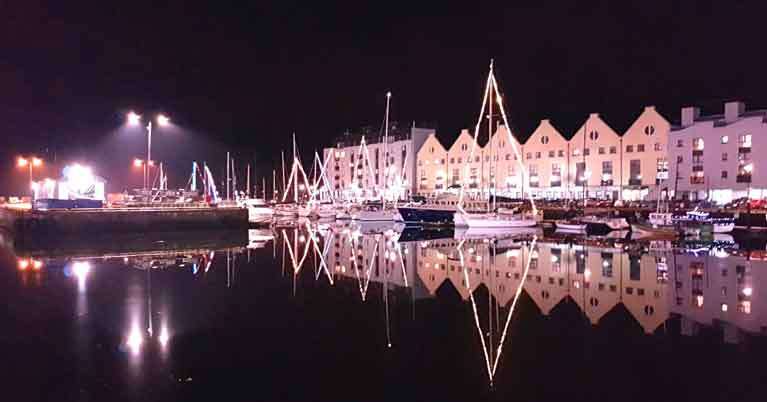
Galway Port Marina Celebrates Halcyon Calm of Mid-Winter Night
In ancient Greece, the Halcyon days of calm in time-honoured mythology occurred at the mid-winter solstice. Yet after Galway Port received such a battering from Storm Elsa as recently as last Wednesday night, most folk would have been more than content with a period of only reasonably normal wind strengths on this weekend of the Winter Solstice.
But the ancient traditions had their way - as is so often the case in the West of Ireland. As the turning of the astronomical year approached, a total calm came over the dock to provide mirror-like reflections of floodlit waterfront buildings and the seasonal decorations on boats in the marina.
We’re told that by Christmas Day itself, there’ll be more boats fully decked out with festive lights. But for now, the fact that it was flat calm on December 21st after they’d been experiencing winds of up to 73 knots on the night of December 18th is something of a miracle in itself.
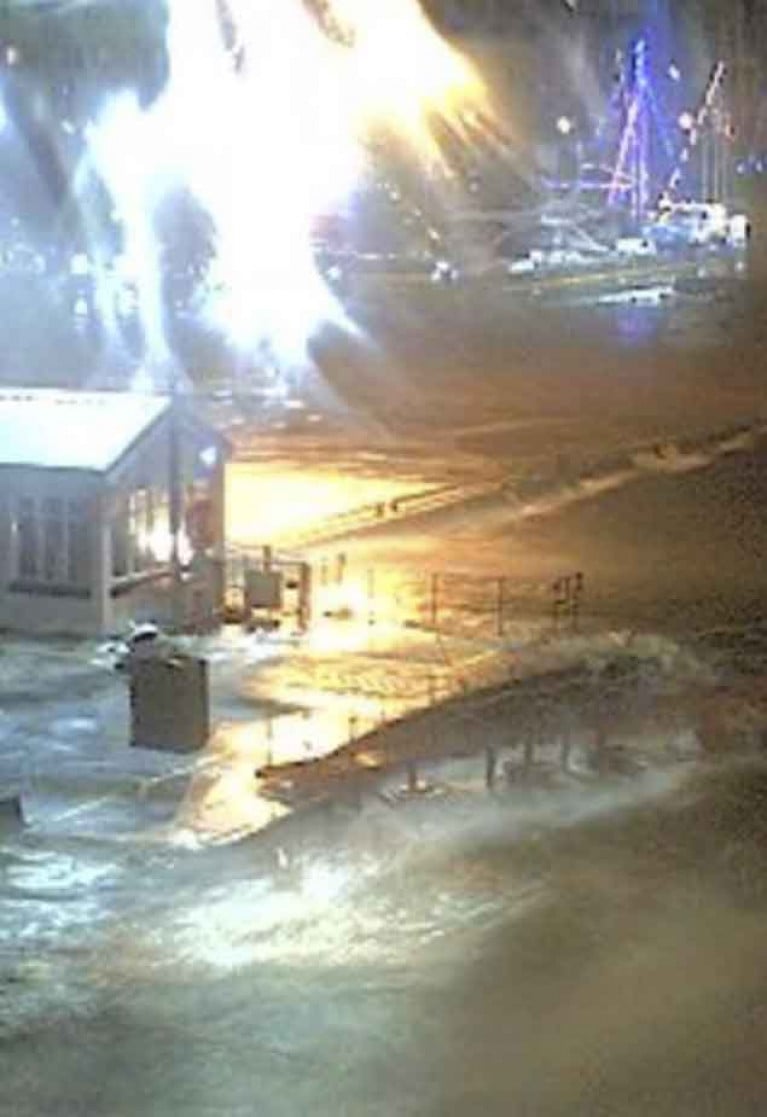
Galway Docks Hit by Localised Storm Surge
There were severe gales around much of Ireland on Wednesday night, but at Galway Docks, in particular, the localised effects of a storm surge on extreme high water – with southwest winds of more than 70 knots - caused the Aran ferry to break some of its mooring lines at its berth outside the dock gate at the Fishermen’s Layby, with the ship finally coming to rest across the RNLI launching berth, effectively closing off the rescue services until the vessel could be re-floated this morning.
As Afloat reported earlier, the situation prompted Galway’s Harbourmaster to hit out at the lack of a storm warning.
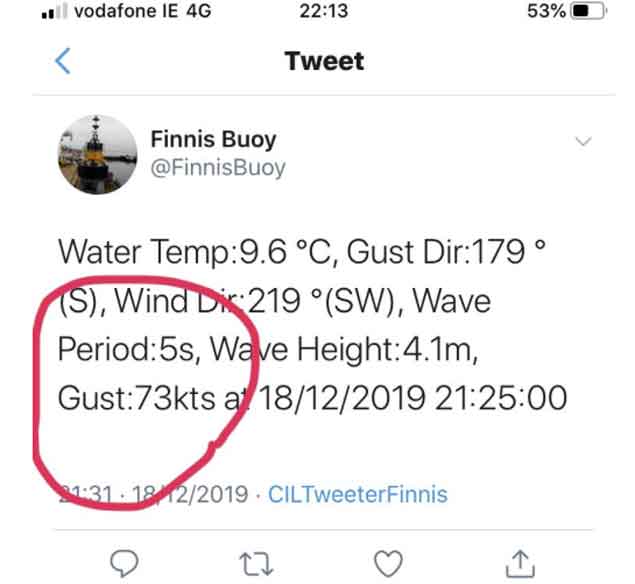 Precision measurement of a storm – in Galway Bay last night with south to southwest winds hitting 73 knots, the steep short waves on a period of 5 seconds were peaking at 4.1 metres.
Precision measurement of a storm – in Galway Bay last night with south to southwest winds hitting 73 knots, the steep short waves on a period of 5 seconds were peaking at 4.1 metres.
Conditions were such that the lock-gates themselves could not be closed until two hours after high water, while the ferry – having been freed today (Thursday) with the use of two mechanical diggers required to demolish part of a wall – has sustained quite substantial damage.
Experienced local sailors are saying that the night’s damage proved yet again that serious money needs to be spent, both to improve shelter and access to the entrance to Galway Docks, and provide better berthing generally for the most important port in Connacht.
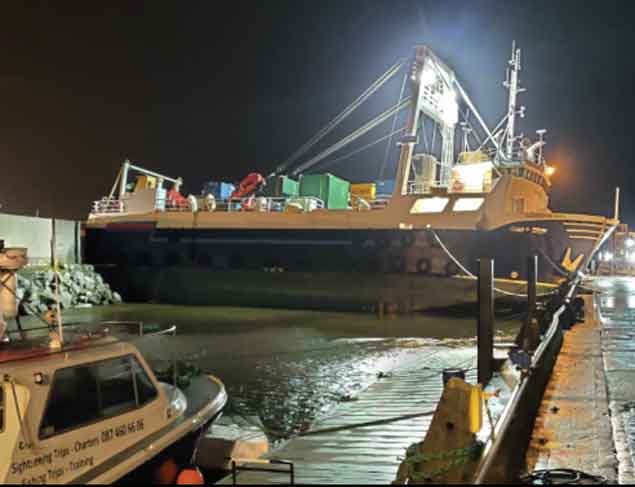 The Aran Islands ferry broke adrift from its alongside berth just outside the dock gates, and ended up aground across the entrance to the RNLI launching berth, with considerable damage sustained by the time the ship was refloated today (Thursday). Photo: Courtesy Pierce Purcell
The Aran Islands ferry broke adrift from its alongside berth just outside the dock gates, and ended up aground across the entrance to the RNLI launching berth, with considerable damage sustained by the time the ship was refloated today (Thursday). Photo: Courtesy Pierce Purcell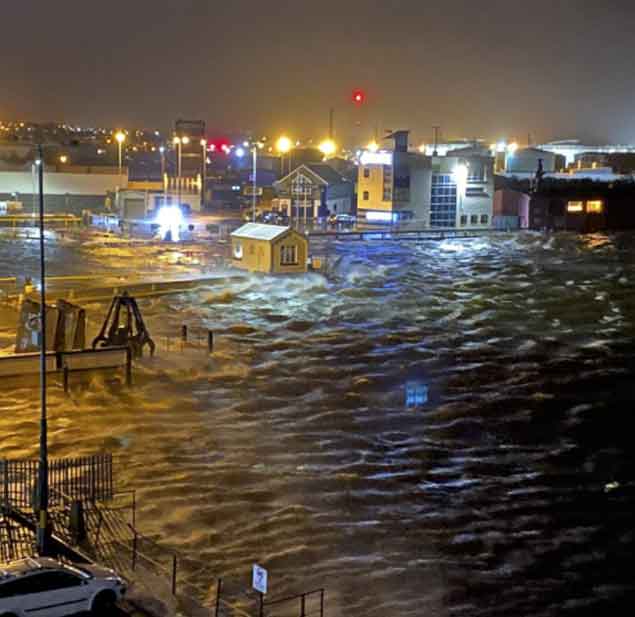 Collateral damage……some of the area immediately around the docks was flooded. Photo: Courtesy Pierce Purcell
Collateral damage……some of the area immediately around the docks was flooded. Photo: Courtesy Pierce Purcell
Galway’s Harbourmaster Hits Out at Lack of Storm Warning
Galway’s harbourmaster has hit out at the lack of warning for a severe storm which caused flooding in parts of the city and Salthill last night writes Lorna Siggins.
The city’s emergency plan was invoked after southerly winds forecast at 40 to 45 knots hit 73 knots, and there was a sea surge over quays in the docks and in Salthill.
A cargo ship making regular deliveries to the Aran Islands was thrown up on rock armour when it broke one of its moorings. The 39-metre Saoirse na Mara sustained considerable damage during the height of the winds at around 8 pm.
Capt Sheridan said Valentia Coast Guard had been informed last night, and there was no pollution from the ship and no injuries to crew. Efforts would be made to refloat the vessel at high tide this morning, he said.
Capt Sheridan said the city had “only dodged a bullet by a miracle”, but said he was furious at the lack of warning.
“With climate change and sea-level rise, we are only going to have more of these events and we need to be prepared,” he said.
“This inaccuracy of forecasting highlights our lack of ocean literacy and our need to focus on understanding what is actually going on in the ocean,” he said.
“We need to remind ourselves that the planet is 70 per cent water, and the ocean controls so much of our daily lives. Climate change is here and now,” Capt Sheridan emphasised.
The port had hosted an emergency training exercise for staff yesterday afternoon, and so Capt Sheridan said he had been particularly vigilant about weather forecasts.
“That exercise went off well, but at 3 pm it was forecast for 40 to 45-knot winds on Wednesday night. It reached 73 knots and was off the scale.”
The gusts caused widespread damage to trees on routes in and out of the city.
High Winds Cause Cruiseships to Cancel Calls During High Season
High winds played there part in determining cruiseship destinations among visiting vessels that were scheduled to call to Irish and Welsh ports, writes Jehan Ashmore.
Most recently to become subject to the conditions involved Princess Cruises smallest ship, the 670 capacity Pacific Princess which was unable yesterday to anchor safely offshore of Milford Haven in south Wales.
The Bermuda flagged cruiseship continued a passage to Dublin Port and where the 30,000 gross tonnage vessel arrived today. A fleetmate, Crown Princess is also today visiting the Irish capital but unlike the 'Pacific' is to remain in port overnight.
The cancelled call by Pacific Princess to the port in Pembrokeshire had prematurely ended a season which saw three ships visiting. Silverseas Silver Cloud called twice, once in May and June and Hapag Lloyd's Europa made an appearance last month.
A Silverseas fleetmate the 294 guest capacity Silver Wind was the other aptly named cruiseship affected by such weather conditions but which took place in Irish waters.
Silver Wind had arrived in Galway Bay in the early morning of last Friday and sheltered in the lee of Black Head, Co. Clare. Due to the prevailing winds, tenders could not take guests ashore to the Port of Galway forcing the 17,400 gross tonnage vessel to cancel the call.
Instead the Bahamas flagged Silver Wind proceeded to Lisahally (Foyleport) followed by Greenock, Scotland. By coincidence, Silver Wind is today also docked in Dublin Port having previously called to Belfast Harbour.
Despite the cancellation to the Port of Galway a further four cruiseships is scheduled with Fred. Olsen Lines Black Watch ending the season early next month.
The veteran Volvo Racer Green Dragon (back mast-less in her old home port of Galway since Sunday) has been sorted. Her spare mast will be stepped today, with the port’s adopted French supersailor Yannick Lemonnier playing a key role in getting this nautical heroine of many a campaign back in full seagoing trim.
Meanwhile, the exceptionally summery weather has provided a warm and welcoming mood for the assembly of fourteen-plus Galway Hookers of various sizes for the Claddagh Festival (which continues until Sunday). The two Viking longships from Ardglass have arrived and been put into full warship mode, the highlight of their visit being the Salthill Raid on Saturday, when they’ll be accompanied by the hookers and a fleet of local yachts.
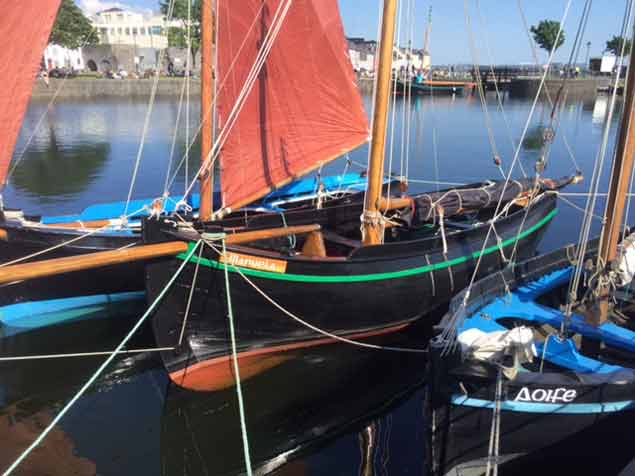 The standard of maintenance in the fleet of traditional craft gathered in Galway this weekend is impressively high. Photo: Pierce Purcell
The standard of maintenance in the fleet of traditional craft gathered in Galway this weekend is impressively high. Photo: Pierce Purcell
Afloat.ie’s man in Galway reports that huge credit is due to anchorman Peter Conneely and his team, led by Colin Hermon, who have put in a massive amount of behind-the-scenes work to bring this very special and successful show together. With the quayside thronged last night with Galway, Connemara, Claddagh and Ardglass folk, the festival mood was running very well.
 In the summery weather in Galway, the “raiding” Ardglass Viking longships from County Down seem to exude nothing but goodwill Photo: Pierce Purcell
In the summery weather in Galway, the “raiding” Ardglass Viking longships from County Down seem to exude nothing but goodwill Photo: Pierce Purcell