Displaying items by tag: Incinerator
#CorkHarbour - Tánaiste Simon Coveney has echoed the concerns of locals in Ringaskiddy at the news that planning permission has been granted for an incinerator in their area.
RTÉ News reports on An Bord Pleanála’s approval of the €160 million waste-to-energy project, which went against its own inspector’s recommendation.
The decision was made after a lengthy series of deferrals, the most recent in February this year, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
In a statement, the Tánaiste and TD for Cork South-Central said: “I can understand that people will be very angry and frustrated at this announcement today and I share this sense with them.”
Meanwhile, the chair of the Cork Harbour Alliance for a Safe Environment (CHASE) said its fight was not over against the incinerator – plans for which Indaver, the company behind the project, says are “are fully in line” with planning regulations.
RTÉ News has more on the story HERE.
Dublin Bay Incinerator: The Pyramid of Poolbeg or Ziggurat Of Zandymount? You Tell Us...
Those of us who only occasionally head down the Sandymount seafront along the inner reaches of Dublin Bay will be driving carelessly if we give the attention it deserves to the impressive new structure which is taking shape on the Poolbeg Peninsula writes W M Nixon.
You’ve got to stop and get out and give it a proper look from as many angles as possible, for whatever it is, it’s quite something. And it doesn’t seem hostile. Yet so impressive is it that you could be forgiven for thinking that all the talk about building a giant film studio in the area has been simply a blind – the reality is that Hollywood-On-The-Bay is already nearing completion, and the first production will be Brexit – The Movie, starring Donald Trump’s friend Meryl Streep as Theresa May.
Not a bit of it, alas. We’ve been well aware from the other side of the river while sailing at Clontarf that the new Covanta Incinerator has been rapidly under construction. But it’s only when you see it from the south in recent days, in this extraordinary calm still silver grey light that denies we’re in the dark depths of January, that you realise it really is something quite remarkable.
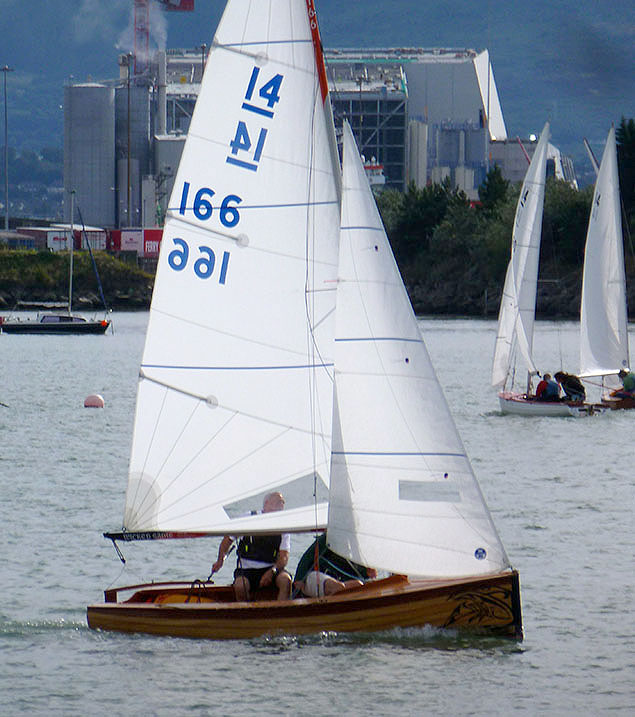 The new IDRA 14 Wicked Sadie racing at the class’s 70th Anniversary regatta at Clontarf last September. Construction of the incinerator (beyond) was already under way, but its full impact is lessened when seen from the north. Photo: W M Nixon
The new IDRA 14 Wicked Sadie racing at the class’s 70th Anniversary regatta at Clontarf last September. Construction of the incinerator (beyond) was already under way, but its full impact is lessened when seen from the north. Photo: W M Nixon
Whatever your views about an incinerator on the waterfront of a city (and don’t forget that the very beau ideal of a city, Copenhagen no less, has its own incinerator, and is none the worse for it) the reality is that this is an awesome structure in its own right, and I cheerfully admit to liking the look of it very much indeed.
It’s all of a piece. It makes some of the other industrial structures about it look very scruffy. And we’ll certainly have to get the old ESB twin smokestacks re-painted pronto. As for the Dubs, they’re going to have a fine old time giving it a nickname, if they haven’t done so already.
The Ziggurat of Sandymount (we’ll have to change it to Zandymount), or the Pyramid of Poolbeg spring readily to mind. Maybe the Apex of Ash might be a contender too. Whatever it gets called, there’s no escaping the fact that it’s here to stay.
Then after we’ve all been blown away in the inevitable nuclear holocaust which the present re-ordering of the world makes very likely, can’t you just imagine the archaeologists of 5,000 years hence earnestly analyzing it and proving beyond all doubt that it was a sacred temple for the worship of money, with its main corridor exactly in alignment with the point on the horizon beyond which the sun rises on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange on Midwinter’s Day?
 The new Zandymount Ziggurat makes the other industrial structures in its neighbourhood look a bit scruffy. Photo: W M Nixon
The new Zandymount Ziggurat makes the other industrial structures in its neighbourhood look a bit scruffy. Photo: W M Nixon
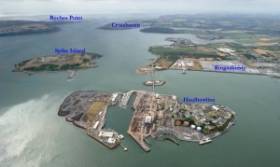
The Minister with Responsibility for Defence has stated that the operational requirements of the Defence Forces will be reviewed, depending on the outcome of Bord Pleanala’s decision on the application by Indaver to build an incinerator at Ringaskiddy in Cork Harbour close to Naval Service operational headquarters on Haulbowline Island.
The Department of Defence has warned that this has strategic implication for the State.
What the Minister means by his statement and what effect it could have on Naval Service operations at their headquarters is unclear.
The Minister was replying in a letter to Independent Dublin TD, Tommy Broughan, who questioned him about the “strategic implications for the Navy” and the impact on joint operations with the Air Corps, which were identified by the Department of Defence at the Bord Pleanala inquiry hearing into the Indaver planning application.
Mr.Kehoe said in his letter “As the planning application on the building of an incinerator in Ringaskiddy is currently under consideration by An Bord Pleanala it would not be useful at this time to consider what the outcome might be. The operational requirements of the Defence Forces will be reviewed in the context of the planning decision however it would be inappropriate to comment further on the matter at this time.”
In a previous response to Deputy Broughan and in a reply by the Taoiseach to Cork TD Mick Barry, Minister Kehoe and the Taoiseach, who is also Minister for Defence, had both acknowledged the Department of Defence concerns but had refused further comment pending the decision of Bord Pleanala.
Minister Kehoe’s second response, to Deputy Broughan, is the first indication that the operations of the Naval Service and Air Corps will be reviewed in the light of the Bord Pleanala decision.
“The boy stood on the burning deck,” is one of the most famous lines in literature and particularly relevant in the maritime sphere. Many people can quote the next line…”Whence all but he had fled…” But why was he there, on what ship and in what circumstances? On this week’s edition of THIS ISLAND NATION we tell you the full story. While listening to it, I compared it with a following story on the programme, the threat to the operations of the Irish Naval Service by a commercial company.
It seems ludicrous that a fully operational Naval Service is under threat, but so it is and the warning has come from the Department of Defence, so it is the opinion of Government.
“This cannot be an acceptable situation….for the necessary functioning of a fully operational Naval Base…..” Those words, from the Department of Defence, are blunt and were made in a major intervention at a public inquiry held by Bord Pleanala into the Indaver Ireland waste company’s third attempt to build a hazardous waste incinerator at Ringaskiddy in Cork Harbour, close to Naval Base headquarters. The Department went further, stating that the location of the incinerator would also affect Air Corps operations, which “may be forced to impose a ‘no-fly’ restriction” around Haulbowline Island. “In addition, Haulbowline Island is accessed by road as a sort of cul de sac to the Ringaskiddy Road. The proposed incinerator is to be built adjacent to this road, before Haulbowline. Therefore, in the event of any accident at the incinerator, road access to and from Haulbowline is threatened. For example, if an accident at the incinerator necessitated local area evacuation, the evacuation of Haulbowline would be denied.
“This cannot be an acceptable situation for those that work at or visit Haulbowline, nor for the necessary functioning of a fully operational Naval Base therein.”
That makes the threat to the Naval Service very clear. No nation can accept a restriction imposed on its Naval Service operations. That must be national policy. I am proud of our Naval Service. It is a professional, top-level maritime organisation. Its rescue work in Irish waters has been superb. Its performance on refugee rescue in the Mediterranean has raised the profile of Ireland as a maritime nation. I do not accept that its operations should be threatened. I live in the Cork Harbour area. Through my kitchen window I see three wind turbines and several chemical factories. So harbour industrial development is an accepted part of my daily life, but a threat to our Naval Service is not acceptable.
Also under threat, publicly stated by the Minister for the Marine, is €500m. of marine development investment in the harbour if the incinerator, which he has described as “wrong place, wrong time,” is built. Concern has been voiced about youth sailing close to the incinerator and, if Air Corps helicopter operations are affected, what about the effect on Coast Guard helicopter operations in the area?
This is the 50th edition of THIS ISLAND NATION so a somewhat unusual coincidence of two Naval stories on the programme - that of the legendary boy who stood on the burning deck of the flagship of Napoleon’s fleet at the Battle of the Nile, the three-decked, 120-gun L’Orient and the threat to Ireland’s Naval Service
• Listen to the programme below:
Waste Firm Drops Court Challenge Over Cork Harbour Incinerator
#CORK HARBOUR NEWS - A waste management firm has dropped its High Court challenge against the refusal of planning permission for an incinerator in Cork Harbour, the Irish Examiner reports.
Indaver last night pulled out of its legal challenge just days before a full judicial review of An Bord Pleanála's decision on the €140 million project in Ringaskiddy was set to begin.
However, a harbour residents group opposed to the incinerator proposals have given the "shock" move a cautious welcome.
Chase urged Indaver to "finally walk away" from the project as it has emerged the company is in pre-applications talks with An Bord Pleanála under its 'strategic infrastructure' process.
The Irish Examiner has more on the story HERE.