The postponed date of Friday, July 31st is being considered as a feasible time to think of starting the ISORA-organised 160-mile Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race, which was originally planned for July 9th to link this summer’s celebration of the 150th Anniversary of Dun Laoghaire’s National Yacht Club with the massive Tricentenary Celebrations of the Royal Cork Yacht Club.
The COVID-19 lock-down and its aftermath may have wiped out or changed much of 2020’s keenly-anticipated major fixtures, with the SSE Renewables Round Ireland Race on 20th June from Wicklow postponed to August 22nd, while all the main Royal Cork regatta and championship events for July have been cancelled.
But now that the analyses of the disease and its treatment and progress are developing positively on a daily business, it has become a question of “when” rather than “if” on whether or not there can be a meaningful start of the 2020 sailing programme in the best of the summer months, while still adhering to nationwide health guidelines.
A port-to-port offshore race by its very nature involves much less shoreside infrastructure than a major regatta, and Dun Laoghaire’s Peter Ryan of the Irish Sea Offshore Racing Association, a key player in its renewed vitality in recent years, reckons ISORA can thus play a leading role in getting sailing going again, as the Association operates flexibly, and may even offer the slight possibility of a couple of shorter races earlier in July.
 In addition to his successful longtime involvement with ISORA, Peter Ryan was Commodore of the National Yacht Club when it won the Mitsubishi Motors Sailing Club of the Year Award for 2011.
In addition to his successful longtime involvement with ISORA, Peter Ryan was Commodore of the National Yacht Club when it won the Mitsubishi Motors Sailing Club of the Year Award for 2011.
Talking to Sailing on Saturday late this week, while Peter Ryan emphasised that his thoughts were speculative and entirely his own, he reckoned that thinking in terms of starting what would have been ISORA’s big one in 2020, the historic re-sailing of the path-finding 1860 offshore race from Dublin Bay to Cork, could be on the cards by Friday, July 31st.
“It gives a modern connection to such an extraordinarily historic event that running it would cheer everyone up after a period in which we’ve lost so much in so many ways,” says Ryan. “And it would fit in neatly with getting the Irish Sea fleets to Cork to be conveniently on station for the beginning of the four-day Calves Week at Schull on Tuesday, August 4th.
“Then too, it would still leave plenty of time for those who wish to return to the Irish Sea for the Welsh IRC Championship at Pwllheli from August 14th to 16th August. And it would provide a very useful qualifying race for those who need to build up their sea time for the SSE Renewables Round Ireland Race on August 22nd. So everything points to being ready to think in terms of the Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race on Friday, July 31st”.
 ISORA pre-start manoeuvres off Dun Laoghaire, with the successful Pwllheli-based J/109 Mojito (Peter Dunlop & Vicky Cox) in foreground. With a minimal requirement for shoreside infrastructure and organization, ISORA can be very flexible in modifying its programme. Photo: Afloat.ie/David O’Brien
ISORA pre-start manoeuvres off Dun Laoghaire, with the successful Pwllheli-based J/109 Mojito (Peter Dunlop & Vicky Cox) in foreground. With a minimal requirement for shoreside infrastructure and organization, ISORA can be very flexible in modifying its programme. Photo: Afloat.ie/David O’Brien
This is encouraging stuff, with the reassuring sense of quiet but thoughtful leadership at a time when it’s most needed. That said, the simple basic nature of ISORA’s functioning enables it to be nimble in adapting to changing circumstances. Yet in highlighting the significance of the Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race, Ryan definitely is associating his organisation and its revival of the sailing programme with sailing events of exceptional historical significance.
It was June 23rd 1861 when a distinctive 95ft schooner with markedly raked masts slipped into Cork Harbour and came to anchor off Cobh. She’d the look of a vessel which had recently sailed many offshore miles, but her congenial ship’s company were sailing under the burgee of the Royal Victoria Yacht of Ryde on the Isle of Wight, and they flew a well-used British ensign. So despite the absence of a properly-maintained ship’s log, the officials of this naval port accepted the schooner’s bona fides of being on an easygoing family cruise from the Solent to southwest Ireland, and accorded them the privileges which this conferred in terms of the waiving of harbour dues, while the Cobh-based Royal Cork Yacht and Royal Western of Ireland Yacht Clubs both made them welcome.
At the time Cobh – or Queenstown as it then was – was very much the hub of Cork Harbour sailing. For although there was a nascent club across on the western shore at Monkstown, it was 1872 before it became the Royal Munster Yacht Club, while Crosshaven was a tiny fishing port, with one of the few yachts about the place being the Newenham family’s 25-ton cutter Mask, lying to her moorings upriver on the Owenabue River.
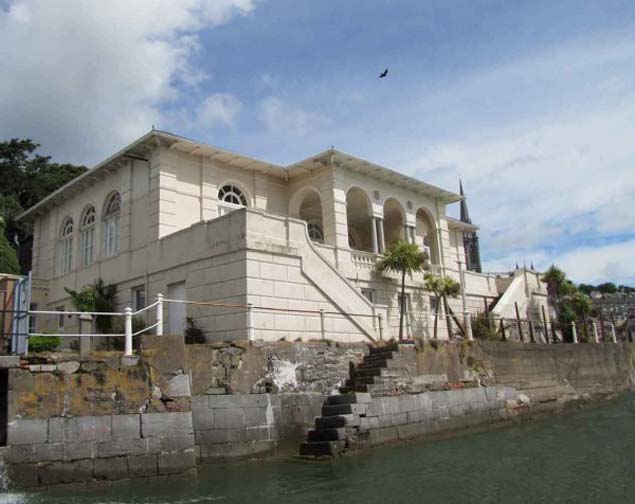 The Sirius Arts Centre in Cobh. Originally the 1854-completed Royal Cork YC clubhouse, it was here that the first Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race of 1860 finished, and where the crew of the mysterious schooner Camilla were made welcome on June 23rd 1861.
The Sirius Arts Centre in Cobh. Originally the 1854-completed Royal Cork YC clubhouse, it was here that the first Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race of 1860 finished, and where the crew of the mysterious schooner Camilla were made welcome on June 23rd 1861.
But Queenstown was buzzing, for in July 1860 the Royal Cork Yacht Club, under the enthusiastic guidance of its 80-year-old Admiral Thomas G French, had led the way in the inspiration for the first proper offshore race in British and Irish waters. The Royal St George Yacht Club in Dublin Bay had organized a week of regattas in early July, and after they’d concluded, no less than 16 boats – of very varied size and type – had accepted Admiral French’s challenge of racing the 160 miles to Cork, and it started on the 14th July.
 The Entry List for the second race of 1861 was very much an ad hoc affair, with RCYC Admiral Thomas French encouragingly visiting each boat pre-start in Kingstown, and confirming their entry and the fee paid on this list, believed to be written in his own hand. Image courtesy RCYC
The Entry List for the second race of 1861 was very much an ad hoc affair, with RCYC Admiral Thomas French encouragingly visiting each boat pre-start in Kingstown, and confirming their entry and the fee paid on this list, believed to be written in his own hand. Image courtesy RCYC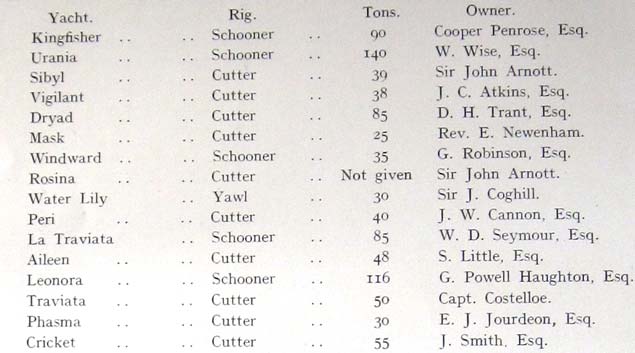 Printed version of the entry list for the first race of 1860 as it appeared in H P F Donegan’s History of Yachting in the South of Ireland, published 1908. Sir John Arnott certainly hedged his bets – he had two entries, and one of them, Sibyl helmed by the amateur Capt. Henry O’Bryen, was the winner
Printed version of the entry list for the first race of 1860 as it appeared in H P F Donegan’s History of Yachting in the South of Ireland, published 1908. Sir John Arnott certainly hedged his bets – he had two entries, and one of them, Sibyl helmed by the amateur Capt. Henry O’Bryen, was the winner
Much of it was raced in rugged windward conditions, but light airs prevailed at the finish off the Cobh waterfront for a real knife-edge conclusion, with Sir John Arnott’s 39-ton cutter Sybil – designed and built on Cork Harbour by Joseph Wheeler of Lower Glanmire – winning line honours and the race by three minutes from J.W.Cannon’s 40-ton cutter Peri, with Cooper Penrose’s 90-ton schooner Kingfisher another two minutes astern of Peri.
Sybil was skippered by the amateur ace Captain Henry O’Bryen, who had reputedly relinquished the helm for a total of only one hour during the race, a triumph for Corinthianism before it had became profitable or popular, if we may mix metaphors for a moment.
 The hand-written Race Instructions for 1860 were also on a “make it up as you go along” basis. It reads: “Ocean Race. A flag boat will be moored off the harbour, and no yacht may pass between her and the Light House on the East Pier until 11 am, when a gun will be fired from “Urania” as the signal for starting. The yachts may lie where they please provided they do not pass between the Light House and flag boat before the gun fires”.
The hand-written Race Instructions for 1860 were also on a “make it up as you go along” basis. It reads: “Ocean Race. A flag boat will be moored off the harbour, and no yacht may pass between her and the Light House on the East Pier until 11 am, when a gun will be fired from “Urania” as the signal for starting. The yachts may lie where they please provided they do not pass between the Light House and flag boat before the gun fires”.
But Sybil’s owner Sir John Arnott (1814-1898) was something else, a real go-getting Scottish-born entrepreneur who’d arrived into Cork in 1837 aged 23 and launched himself into a sometimes rocky commercial career which at various stages involved heavy investment in department stores in Ireland and Scotland, horse racing both as an owner of thoroughbreds and of noted race courses, steamship companies, railways, and for a while the inevitable newspapers, in his case The Northern Whig in Belfast and The Irish Times in Dublin.
 Victorian entrepreneur Sir John Arnott, who had two yachts entered in the first Kingstown to Queenstown Race of 1860
Victorian entrepreneur Sir John Arnott, who had two yachts entered in the first Kingstown to Queenstown Race of 1860
Arnott was always a man in a hurry, so it’s possible that he thought the distinguished flag officers of the Royal Cork were a bit conservative in their management. Thus he was one of a bunch of shaker-uppers who set up a new club in Cobh, the Queenstown Yacht Club, which they cleverly up-graded by taking on the tattered-remains of the old Royal Western of Ireland YC, founded in 1828 in Kilrush by Maurice O’Connell and his nephew Daniel of Derrynane among others, but wandering more or less homeless after the horrors of the Great Famine of 1845-47 had wiped out fripperies like yachting on Ireland’s Atlantic seaboard.
After a vague period in Dublin, suddenly the old Royal Western emerged re-born in 1861 in Cobh with Sir John Arnott as Commodore, and for their first season under this new arrangement, they showed nimbleness of foot by organising - at very short notice - a regatta to provide a race for this strange schooner which had suddenly arrived in their midst.
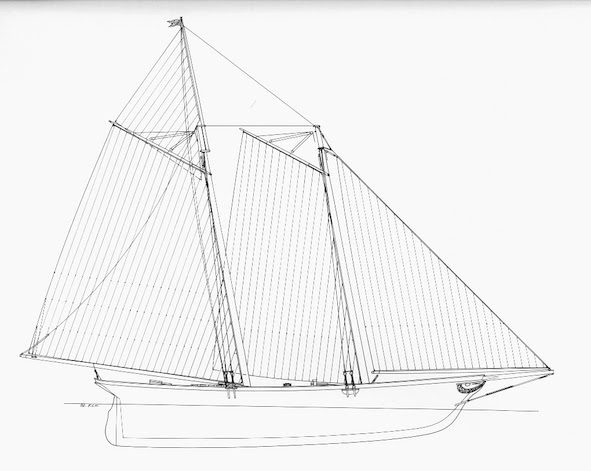
For although the schooner had the name of Camilla across her shapely transom, the dogs in the street in Queenstown knew that this was the one and only America, the 1851-built New York flyer which, by convincingly winning a rather hastily-assembled race round the Isle of Wight on the final day of Cowes Week 1851, had won a silver cup worth one hundred pounds sterling for her New York Yacht Club syndicate of owners.
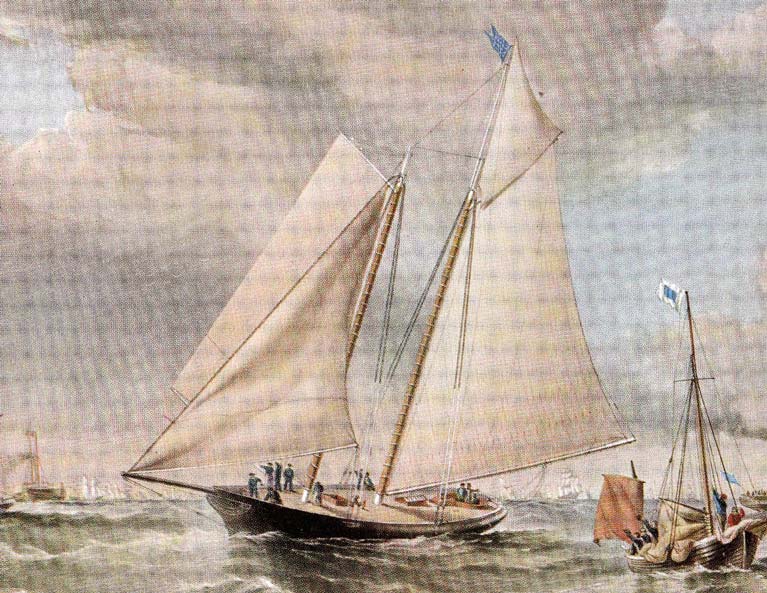 America wins, Friday, August 22nd 1851. Almost everything about her was different, including her notably flat-setting cotton sails, but she was soon being imitated
America wins, Friday, August 22nd 1851. Almost everything about her was different, including her notably flat-setting cotton sails, but she was soon being imitated The poster for Cowes Week 1851. The social pace was so hectic that they only had time for three races, and in the notice for Friday 22nd August, the inclusion of “yachts of the Clubs of all nations” was actually aimed at expected entries from the Imperial Yacht Club of St Petersburg in Russia. They failed to arrive, but in the meantime the schooner America had turned up, though she had to wait through the week until she could finally race on the Friday. From these only semi-planned beginnings, there emerged The America’s Cup.
The poster for Cowes Week 1851. The social pace was so hectic that they only had time for three races, and in the notice for Friday 22nd August, the inclusion of “yachts of the Clubs of all nations” was actually aimed at expected entries from the Imperial Yacht Club of St Petersburg in Russia. They failed to arrive, but in the meantime the schooner America had turned up, though she had to wait through the week until she could finally race on the Friday. From these only semi-planned beginnings, there emerged The America’s Cup.
In 1861 when the schooner was briefly in Cork, this rather unlovely cup – ewer is the technical name - was yet to become known as The America’s Cup, and there wasn’t to be a challenge to take it from the Americans until 1870. But ten years after her famous victory round the Isle of Wight, the myth and mystique of the schooner America was well established as part of world sailing lore, and the Young Turks in Cork sailing associated with John Arnott made the most of it, with this special schooner race quickly organised by the Royal Western of Ireland for June 28th, Camilla/America’s opposition being W D Seymour’s 85-ton La Traviata, W Wyse’s 140-ton Urania, and C H Smith’s “little” 66-ton Echo.
Camilla/America’s sails were tired and so were her crew, yet she still managed to take line honours in this slightly mysterious race. But it was by only one minute from the much-smaller La Traviata, which had been amateur-helmed by W D Seymour’s son to a clear handicap victory. After the finish, young Seymour was borne ashore shoulder-high by the cheering waterfront crowds to achieve a Cork Harbour sailing and sporting eminence to match that of Henry O’Bryen who – in a shrewd bit of window-dressing worthy of Arnott’s at their best - had been drafted in as Vice Commodore of the Royal Western of Ireland.
However, all these seemingly-rebellious Young Turks in the re-born RWIYC had retained their membership of the Royal Cork YC and would in time become part of its establishment lineup. But if they’d hoped to promote their “new” club by persuading the Camilla/America to take part in 1861’s staging of the Kingstown to Queenstown Race, they were disappointed, for as we shall see, the famous schooner had serious business elsewhere, and was soon gone.
 The Royal St George Yacht Club hosted the start of the first Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour race in 1860. Photo: Afloat.ie/David O’Brien
The Royal St George Yacht Club hosted the start of the first Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour race in 1860. Photo: Afloat.ie/David O’Brien
As it is, the 1861 race was started in Dublin Bay on 19th July, and once again mustered 16 starters with the winner being Colonel Huey’s slippy 62-ton cutter Osprey, with designer-builder Joseph Wheeler’s own 48-tonner Avalanche having to make do with second despite having led into Cork Harbour in light airs, while E J Saunderson of Lough Erne YC was third with another even smaller and slippy craft, the 34-ton cutter Phasma.
Admiral French’s own 61-ton yawl Spell took part this time (see first name on written entry list above), but although he was to continue as RCYC Admiral until his death in 1866, he’d already been 77 when he took over as Admiral in 1857, and his enthusiastic promotion of the Kingstown-Queenstown race’s first staging in 1860 suggested an old man in a hurry to promote an idea which he’d been carrying for some time.
Certainly, at its third staging on July 11th 1862, there’s a clear impression that others had taken it over, as the host club on Dublin Bay has become the Royal Irish YC from their impressive 1851-completed clubhouse, while the trophy is an expensive bit of silver plate presented by the Royal Western YC.
 The Royal Irish Yacht Club hosted the start of the third and final Kingstown to Queenstown Race in 1862
The Royal Irish Yacht Club hosted the start of the third and final Kingstown to Queenstown Race in 1862
For anyone seeking abstruse historical connections, it’s of interest that The Liberator, Daniel O’Connell of Derrynane (1775-1847) had been present at both the foundation of the Royal Western in Kilrush in 1828, and the meeting in Dublin on July 4th 1846 when the 1831-founded Royal Irish YC had been revived. Meanwhile, in 1862, the Kingstown-Queenstown Race once again attracted 16 starters (though there’s no note of any entry limit), and they ranged in size from three 35-ton cutters – Ariadne (G Higgins), Coolan (G Robinson) and Glance (A Duncan – to two 130-ton schooner, Galatea (T Broadwood) and Georgiana (Capt Smith Barry).
The clear winner was the 50-ton cutter Phosphorous owned by W Turner - who is doubtless immortalized in modern Cork by Turner’s Cross - while C J Tennant’s 90-ton cutter Clutha was second on the water, but Galatea won the schooners and was reckoned second on handicap.
They arrived into the finish at Cobh where the Royal Western of Ireland was now well-established as the second club with premises at Westbourne Place next the Queen’s Hotel, and a membership which by 1863 included the Lord Lieutenant, Lord Carlisle, as well as Sir Robert Peel, at that time Chief Secretary for Ireland. So heaven only knows what politicking was going on behind the scenes, for the Royal Cork, still with T G French as Admiral, had been well settled into its purpose-designed new clubhouse (now the Sirius Arts Centre in Cobh) since 1854, and no-one doubted its claim of seniority in its descent from the Water Club of 1720.
As it happened, 1863 was probably the high point of the RWIYC’s time in Cobh, for the rest of the decade saw a period of economic decline, and the Dublin Bay to Cork Harbour Race wasn’t staged again. While the Royal Cork came through the thin times as it had come through many others, in 1870 the Royal Western of Ireland YC was quietly wound up at Cobh. But in the west of Ireland, and particularly with the Glynn family of Kilrush and The Knight of Glin across the Shannon Estuary, enough of its memorabilia, artefacts and records survived for it to be revived with the opening of Kilrush Marina, with the club’s greatest modern success being Ger O’Rourke’s overall victory with the Cookson 50 Chieftain in the RORC Rolex Fastnet Race 2007.
This may all seem to be something of an impenetrable maze of history, but it’s perfectly straightforward by comparison with the story of the schooner America, and how she came to be in Cork.
Everyone knows that she was hurriedly built early in 1851 in New York by Brown’s Shipyard, to the designs of the 31-year-old George Steers, for a swashbuckling syndicate of New York Yacht Club members led by John Cox Stevens. The project was to send a challenger across the Atlantic to race the English in Cowes Week at a time when the Great Exhibition in London was signalling the global achievements of the British Empire and its worldwide commercial success and dominance.
 America as she was rigged when she won on August 22nd 1851. The boom on the jib broke during the race, which lost her about 15 minutes in repairs, but she was still well ahead at the finish.
America as she was rigged when she won on August 22nd 1851. The boom on the jib broke during the race, which lost her about 15 minutes in repairs, but she was still well ahead at the finish.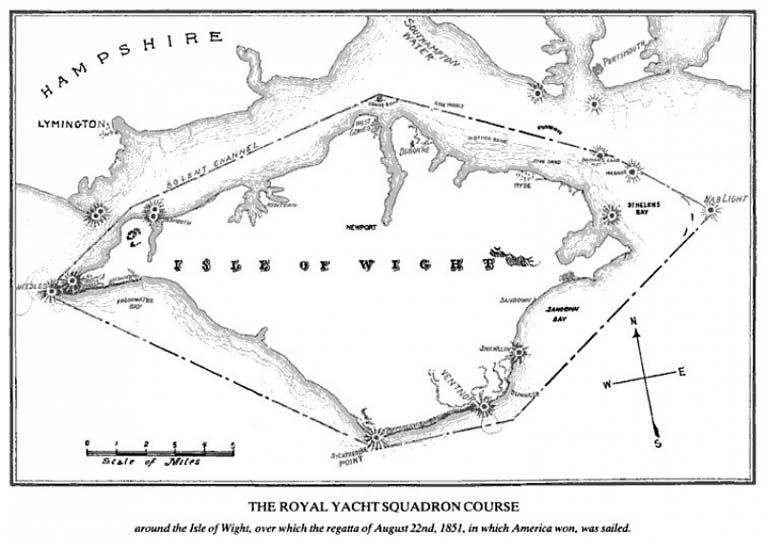 The 57-mile course for August 22nd 1851 – the Isle of Wight was rounded clockwise
The 57-mile course for August 22nd 1851 – the Isle of Wight was rounded clockwise
Not one of the top British racing yachts looked remotely like America, with her low rig and its raked masts, and her extremely hollow waterlines forward. But after she’d made her mark in a very distinctive fashion in just one race round the Isle of Wight on Friday, August 22nd 1851, several English racers were very expensively altered to take on board some of her ideas.
As for her American owners, they were gamblers to a man, so they collected their winnings, and celebrated mightily in New York, supported by their fellow-citizens to such an extent that grinchy Manhattan lawyer George Templeton Strong confided to his diary: “Newspapers crowing over the victory of Stevens’s yacht, which has beaten everything in the British seas. Quite creditable to Yankee shipbuilding, certainly, but not worth the intolerable, vainglorious vaporings that make every newspaper I take up now ridiculous. One would think yacht building were the end of man’s existence on earth”.
Quite so. Henry James would have been pleased with that. But as for America’s owners, they dropped ideas of sailing her home, and sold her in the Solent for 25,000 dollars to an Irish army officer of French Huguenot extraction, John de Blaquiere, who was soon to become the fourth Baron de Blaquiere of Ardkill in County Derry, where the family had thousands of acres acquired through their skills in tax gathering for the government, while the title came from supporting the Act of Union in 1801.
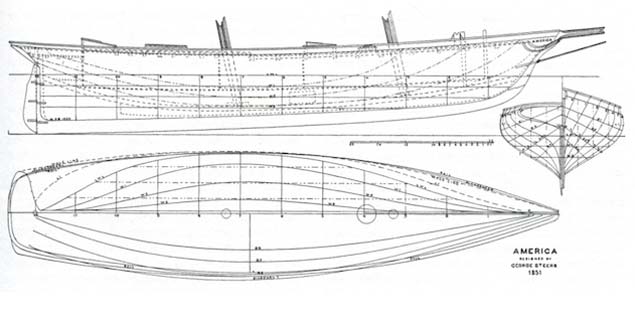 An amazingly well-balanced hull, with a rudder more like a trim tab. In her original form, America was steered by a small tiller, and the fact that her rudder stock had a very small rake forward may have helped her lightness of helm
An amazingly well-balanced hull, with a rudder more like a trim tab. In her original form, America was steered by a small tiller, and the fact that her rudder stock had a very small rake forward may have helped her lightness of helm
Despite these links, de Blaquiere never brought America to Ireland, but did some remarkable cruising to the Mediterranean, with the famous racing boat demonstrating her seagoing credentials by coming through a very severe storm off Malta in February 1852, while her legendary lightness of helm was eulogised by an experienced guest sailor: “Many yachtsmen will remember the almost mop-handle diminutiveness of her tiller, I steered her when going seven knots close-hauled and in some Bay of Naples swell, standing to leeward of the tiller and pressing against it with my little finger only”.
America’s hull was so sweetly balanced that her slim rudder was little more than a trim tab, but it was a trim tab made as effective as possible by being so vertical that the stock is almost inclined forward, unlike the unhealthy measurement-rule induced rudders of a later era, with their excessive and inefficient aft-raking of the stock.
Yet with all her virtues, as John Rousmaniere has commented in “The Low Black Schooner”, his brilliantly succinct account of this remarkable vessel, in the mid-1850s: “America was neglected because she had succeeded to the ambiguous status that is reserved for all trend-setters past their time.” However, in 1856 she was bought by yet another Irish peer from the north, this time Lord Templeton whose lands were in County Antrim, but he never brought America to Ireland either. In fact, he scarcely used her, though he did re-name her Camilla, and it was under this name that she was sold to ship-builder Henry Pitcher, who did extensive re-build work at his yard on the Thames.
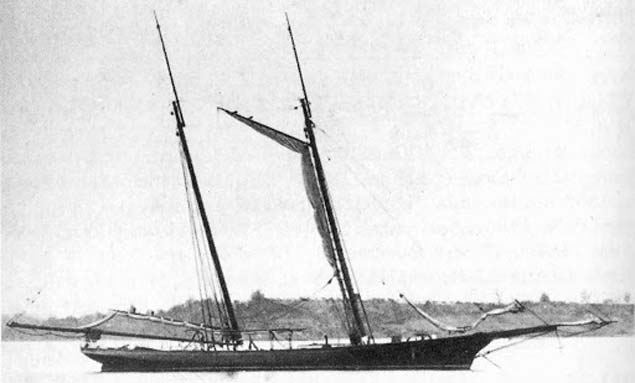 America’s rig underwent various forms in later life, and at one stage she had topmasts on both the main and fore masts, with the mainsail and the boomless foresail brailed up to their gaffs, the foresail’s gaff boom being left aloft. A retractable addition was also fitted to the bowsprit.
America’s rig underwent various forms in later life, and at one stage she had topmasts on both the main and fore masts, with the mainsail and the boomless foresail brailed up to their gaffs, the foresail’s gaff boom being left aloft. A retractable addition was also fitted to the bowsprit.
He then sold her in 1860 to a “mysterious character” called Henry Edward Decie, supposedly a 28-year-old former officer in the Royal Navy, where they’d been obliged to let him go, as they say in HR circles, because he’d been excessively zealous in chasing pirates on the coast of South America, and had knocked lumps out of a Brazilian warship by mistake.
Maybe so. At least that was his story, but we’re into murky waters here, and things were becoming even murkier in the USA with the Civil War looming. A dodgy character like Decie with a super-fast boat like Camilla ex-America - with her proven transatlantic capacity - was just what the Confederate States were looking for in assembling a fleet of fast blockade runners.
Henry Decie seems to have been Captain Cool, and he certainly loved sailing. Family cruising too. In August 1860, having won a race in a regatta at Plymouth, Camilla sailed away with Henry Decie and his wife or maybe she was his mistress and her six children and a crew of thirteen (nothing superstitious about our Henry), and after calling at several places including Lisbon and the Cape Verde Islands, on April 21st 1861 she fetched up on the other side of the Atlantic at Savannah, Georgia. There, the rebel Confederate Government had her bought within a month for 60,000 dollars on condition that Decie remained in charge, and undertook a voyage to Europe with a mission to purchase armaments and organize the building of warships.
So the former schooner America set off back to Europe still under the command of Henry Decie on the 25th May 1861 for her third Atlantic crossing, and on board with Decie and his shipmates were two Confederate Agents with Bills of Exchange to the tune of 600,000 dollars, plus Letters of Credit for much more. This was serious stuff. Yet on June 23rd it was as a light-hearted cruising vessel that she arrived into Cork Harbour, claiming the immunity and privileges conferred by her Royal Victoria Yacht Club burgee and British ensign, with Decie saying that he’d just strolled over from Cowes for a little competition.
 The modern port of Savannah in Georgia, USA. The schooner Camilla ex-America departed Transatlantic from here on 25th May 1861, but when she arrived in Cork Harbour on June 23rd, her skipper Henry Decie claimed they’d just sailed over from Cowes.
The modern port of Savannah in Georgia, USA. The schooner Camilla ex-America departed Transatlantic from here on 25th May 1861, but when she arrived in Cork Harbour on June 23rd, her skipper Henry Decie claimed they’d just sailed over from Cowes.
That was duly arranged in jig time by the Royal Western Yacht Club of Ireland in Cobh. We can only guess as to who really knew what was going on. The two Confederate agents soon disappeared into the bustle ashore and onward on their mission, and Henry Decie and the Cork Harbour schooners went yachting, but then he had to depart again within a day or to rendezvous with the agents.
In time, Camilla reverted to being America, and she finished the Civil War serving on the Union side. In various ownerships and eventually, in the charge of the US Navy, she survived until 1945. But the 100,000 dollars which President Franklin D Roosevelt had allocated for the maintenance of the old girl never reached her in the hectic end-of-war period, and in 1945 the roof of the shed she was housed in collapsed under a freak fall of snow, and that was the end of the wonderboat of 1851 which had briefly been a sensation when she sailed into Cork Harbour in 1861.
































































