Displaying items by tag: wind energy
Minister for Environment and Climate Eamon Ryan has said that Ireland is “already a wind energy success story” on land and is “now looking to our seas.”
“We get 35% of our electricity from onshore wind farms, which is more than anywhere else in Europe,” he told the WindEurope 2024 conference in Bilbao, Spain.
“We’re world leaders in integrating renewables onto our electricity grid, which often sees 75% of total electricity demand come from wind farms,” he said.
“ For over 20 years, we have built a thriving national onshore wind industry, but now we are looking to our seas,” he said.
“Ireland has one of the best offshore wind resources in the world and we are moving towards the delivery of offshore wind energy at a rapid pace. More offshore wind capacity entered the planning system last year than ever before and we have a robust, and growing, pipeline of projects in place,” he continued..
“We have already set out a clear pathway to achieving our 2030 offshore wind targets and our new Future Framework for Offshore Renewable Energy, set to be published next month, identifies the key actions Ireland will take to deliver 20 gigawatts of offshore wind by 2040 and at least 37 gigawatts by 2050,” he said.
“We have invested a lot of time and resources in building the necessary legislative and regulatory base to develop a sustainable industry that delivers for Ireland and Europe. We look forward to working alongside the leading industry figures here today at WindEurope conference as we move closer to Ireland’s future as a global leader in renewable wind energy,” he said.
The ministerial panel discussion was just one of several high-profile Ireland-related events at WindEurope 2024.
Other events included:
- a dedicated “Ireland Markets Session”, focusing on the latest developments in terms of regulation, auctions, policy developments and business opportunities for companies interested in Irish market.
- a networking and information session hosted at the Ireland pavilion by members of the Government of Ireland’s cross-departmental Offshore Wind Delivery Taskforce.
- a panel discussion on grid access for wind farms, which featured EirGrid’s chief infrastructure officer Michael McMahon.
Irish Floating Offshore Wind Company Launches in Spain and Portugal
IberBlue Wind, a joint venture focused on the development of floating offshore wind farm projects, is commencing operations in Spain and Portugal with the aim of becoming one of the leading players in the offshore market off the Iberian Peninsula.
The company presented its strategic plans for the market today in Madrid. Its three backers - Global Irish company Simply Blue Group and the Spanish companies Proes Consultores and FF New Energy Ventures - have collectively extensive international experience in renewable project development. Thanks to this alliance, IberBlue Wind has the capacity to take on all phases of floating offshore wind farm development.
Simply Blue Group is a global developer of floating offshore wind farms with projects in Ireland, UK, US, Poland, and Sweden. Simply Blue Group currently has a pipeline of 10GW of projects under development. As part of its growth strategy, the company is now expanding into the Spanish and Portuguese markets.
Proes Consultores is the specialised engineering and architecture division of the Amper Group, with broad experience in the marine and coastal engineering sectors. Proes Consultores offers engineering, industrial and technological services and has participated in the design of Kincardine, a floating wind project in Scotland. Proes is one of the companies integrated into the Amper Group, a multidisciplinary group that also counts amongst its subsidiaries, Nervión Offshore, a global leader in the construction and assembly of offshore wind farms.
The third member is FF New Energy Ventures, a leader in the development, construction, and operation of solar photovoltaic and renewable energy plants in Spain, which has incorporated offshore wind energy into its portfolio. It is currently developing solar PV, wind and BESS projects in Spain and Portugal, having so far created a portfolio of 2 GW between the two countries, with more than 0.5 GW with connection rights already secured.
Supported by the alliance of these three leading companies, IberBlue Wind will participate in the public auctions for offshore sites off Spain and Portugal and will undertake the early development and design of the projects in advance of the construction and commissioning of wind turbines. To this end, its aim is to develop around 2 GW of floating offshore wind capacity off the Iberian Peninsula, comprising wind farms each of 500MW or more.
Initially, IberBlue Wind will focus on two strategically selected regions. In Spain, it will start in Andalusia, where it aspires to lead the promotion of offshore wind energy as a new economic engine for the region; and Galicia, one of the communities with the greatest potential for this form of renewable energy. In Portugal, IberBlue Wind will focus on the central and northern parts of the country where there is an excellent wind energy resource.
Iberian offshore wind market leadership potential
During the launch, Adrián de Andrés, Vice President of IberBlue Wind, highlighted "the potential for Spain and Portugal to become world leaders in offshore wind generation, as both countries have excellent wind resources, a long history in coastal engineering and first-class public works".
IberBlue Wind can play a key role in delivering this goal because, as De Andrés said, "we can leverage our knowledge and experience acquired in floating offshore wind projects in Great Britain, Ireland and elsewhere, in the Iberian market.” In his speech, the Vice President also called for the Spanish government to be "more ambitious" in the tendering of offshore wind farms. In this context, he stated that the generation capacity of these facilities in Spain could reach more than 10GW in the long-term future.
This generation capacity is much higher than initially envisaged in the Roadmap for Offshore Wind and Marine Energy Development, which has set a target of between 1 and 3GW by 2030. The current draft of the Marine Spatial Plan assigns a space for offshore wind that only covers 0.8% of the available maritime space along its 8,000km of coastline; a density that he described as "conservative" if one considers that leading countries such as Scotland already allocate around 2.5%.
Regarding Portugal, Adrián de Andrés considers that its legislation "is ready to provide exclusive maritime space for wind energy, although a regulation is needed to establish the procedure for the auctioning of these development rights". In Portugal, which has 987 kilometres of coastline, the government has committed to producing 8GW of ocean renewable energy in the coming years, almost double the 5.6GW of current onshore wind power generation capacity.
Offshore energy, under discussion
The presentation also included the round table "Offshore wind: the challenge of blue energy in the Iberian market", with the participation of Juan Ramón Ayuso, Head of the Wind and Offshore Energy Department of the Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving (IDAE); Tomás Romagosa, Technical Director of the Spanish Wind Energy Association (AEE); Antonio Sarmento, President of WavEC Offshore Renewables of Portugal and Dorleta Marina, Portfolio Director of IberBlue Wind.
The experts analysed the current legislative context in Spain and Portugal and explained the main challenges facing the sector in the coming years.
About IberBlue Wind
IberBlue Wind is a joint venture developing offshore floating wind farm projects for the Iberian market. The partners are Simply Blue Group, a leader in offshore floating wind energy globally, and Spanish companies Proes Consultores, the engineering division of Grupo Amper, and FF New Energy Ventures (FF NEV), a developer of renewable projects. IberBlue’s objective is to help Spain and Portugal position themselves as leaders in this field of renewable energies.
Using its knowledge of the market and its extensive experience in the area of offshore wind farm development, IberBlue Wind will take advantage of the greater intensity of offshore wind to generate clean and efficient electricity from renewable sources.
To this end, IberBlue Wind aims to develop around 2GW of offshore wind energy capacity off the peninsula comprised of wind farms each of 500MW or more.
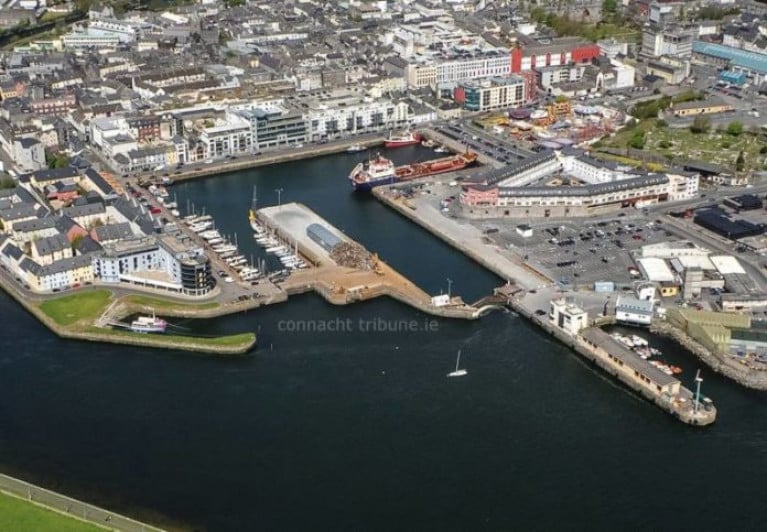
An increase in EU funding for Galway Port has been pushed for following a series of meetings in Brussels this week.
The meetings, facilitated by MEP for this region Colm Markey, took place between port representatives, officials from the European Commission and a number of MEPS.
The focus was on potential funding streams for the planned redevelopment of Galway Port, with a focus on supporting offshore wind capacity.
Advocates say the North-West has the best wind speeds in Europe, but it is the only maritime region not included in the Trans European Transport Network.
Connacht Tribune also has a podcast from the port's CEO and the role of TEN-T.
Cork Harbour Where Wind Energy Can be As big as Pharma, Report Claims
Cork Harbour could see wind energy that would be as transformative as the biopharmaceutical industry, placing the region among the vanguard of Europe's transition to sustainable economies.
That is one of the conclusions of a major new report by a range of organisations and companies around Cork, who called for key policy changes within government, lest the region miss out on its potential as an "unparalleled hub for floating offshore wind energy in the Celtic Sea from 2025".
Firms such as Green Rebel Marine, Mainport, Doyle Shipping Group (DSG), Simply Blue Energy, DP Energy and the Port of Cork joined with Cork Chamber of Commerce and Cobh and Harbour Chamber to produce the Cork Harbour 2025: Ready to Float report.
"Offshore wind is leading the transformation of the global energy system, with a staggering growth rate of 19% — faster than any other industry," the report said.
"Cork Harbour is in the process of being transformed into an offshore renewables hub by the private sector, with circa €200m of investments and plans already underway," it said.
Cork can build on the maritime and energy infrastructure and capability that already exists, thereby positioning Cork Harbour as the de facto floating offshore wind hub in the Celtic Sea, its authors claimed.
Further reading from the Irish Examiner here
Each new wind turbine built in Europe generates €10 million worth of economic activity, according to a European industry network.
A new report by WindEurope also says investing in wind energy will help Europe’s economic recovery from the impacts of the Corona-19 virus pandemic.
The report says wind energy is generating 300,000 jobs in Europe and contributes €37bn to EU GDP every year.
It says that if governments fully implement their national energy and climate plans (NECPs), Europe will have over twice as much wind energy capacity as today by 2030.
It says that in this scenario, there would be 50% more jobs in wind by 2030 – as in a total of 450,000 employed.
It says wind energy would constitute 30% of Europe’s electricity consumption, up from 15% today, and it would be contributing €50bn to Europe’s GDP.
“But as they stand, the NECPs will struggle to deliver this,” the report says, as the plans “give insufficient visibility on when and how governments will auction new wind farms”.
“And they fail to simplify the process of getting permits for wind farms. If this doesn’t improve, Europe will not have enough new wind, and will actually lose 20,000 jobs compared to today,”the report says.
“Investing in wind energy will help Europe’s recovery,”it says and “each new turbine installed in Europe generates on average €10m of economic activity”.
“This is spread across the 248 factories in Europe that produce turbines and components – and all involved in planning, construction, logistics and R&D,”it says.
“Expanding wind energy will also help Europe strengthen its global leadership in wind. 5 of the world’s top 10 turbine manufacturers are European – and collectively they have a 42% global market share,” it says.
Wind farms benefit those who live near them, it says.
“Wind energy pays €5bn in taxes across Europe every year, often directly to deprived rural municipalities. Many wind farms also make direct payments to communities and local organisations, offer benefits-in-kind, and in many cases, communities participate in the ownership of the local wind farm,” it says.
WindEurope describes itself as “the voice of the wind industry, actively promoting wind power in Europe and worldwide”.
It has over 400 members, active in over 35 countries, extending from wind turbine manufacturers to component suppliers, research institutes, national wind and renewables associations, developers, contractors, electricity providers, finance and insurance companies, and consultants.
“Wind Energy and economic recovery in Europe – How wind energy will put communities at the heart of the European recovery”.
Round Table Discusses Ireland’s Offshore Wind Energy Ambitions
SSE Renewables recently hosted a virtual round table discussion with key stakeholders in the wind energy industry, examining their role in delivering on the Irish Government’s ambition for offshore wind energy.
Among those taking part was Paul Brewster of the Irish Marine Development Office (IMDO), who was involved in supporting the work of the Development Task Force nearly five years ago as part of Ireland’s integrated marine plan, Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth.
Offshore renewable energy was identified at the round table as a big growth area that could make a significant contribution to a step change in our ocean economy.
SSE Renewables, which is planning the expansion of Ireland’s first operating wind farm at Arklow Bank, says the policy and supports needed for the industry have now aligned.
And while all stakeholders had concerns about delays to foreshore licensing legislation, the industry has moved from hoping for progress to planning, and the conversations have become more commercially focused.
Read the full report from this round table discussion on pages 22-27 of the latest Eolas Magazine.
The Port of Waterford is highlighting a new report which identifies Belview Port on the River Suir as ideally places to serve Ireland’s growing offshore wind energy sector.
And it says strategic investment of €42 billion over the next 10 years could create 2,500 jobs in the sector.
Produced by the Carbon Trust for the Irish Wind Energy Association and part-funded by Green Tech Skillnet, ‘Harnessing Our Potential’ calls for strategic investment into one or more Irish ports to take advantage of the commercial opportunity of delivering 3.5GW of offshore wind by 2030. This is the level required by the State’s Climate Action Plan.
In a detailed readiness assessment of 16 Irish ports under physical characteristics and connectivity, Waterford was one of just two ports – along with Dublin, which is already regarded as at capacity – to meet all requirements.
Waterford also scored strongly for availability of additional land for development, proximity to existing offshore wind farm developments and access to the national road network.
The report’s authors say: “The [Port of Waterford’s] physical characteristics and connectivity mean it has good potential to serve the growth in offshore wind.
“t is currently one of the few ports in the Republic of Ireland capable of handling the weight of larger offshore wind turbines. Existing brownfield land at the port already in use for storing onshore wind turbines has the potential to accommodate staging with little investment or manufacturing with significant investment.
“Given the area available to the Port, it is well-placed to serve the construction stage of offshore wind with a certain level of investment. Redevelopment of other lands around Belview has also the potential for the Port to become an offshore wind cluster if the economic case can be proven.”
Commenting on the report, Port of Waterford chief executive Frank Ronan said: “There is clearly a huge commercial opportunity as Ireland moves more and more towards renewable energy to meet our international commitments to address climate change.
“This wide-ranging report puts clear data behind that opportunity and challenges all of us to seize the opportunity.
“From our own perspective at Waterford, we have been working for some time to position Belview as an ideal location for this type of activity over the coming decade and well beyond 2030. This is a central theme in both our Corporate Plan to 2023 and Masterplan to 2044.
“We look forward to further constructive engagement with multiple stakeholders to advance this ambition.”
The full report, which is available to read HERE, notes that Ireland currently lacks the ready infrastructure to build offshore wind farms, meaning that we would potentially lose “billions … unless strateguc investment decisions are made now”.
Floating Wind Project for Celtic Sea Welcomed as "Remarkable" by Marine Renewables Industry Spokesman
An Irish renewable energy company has partnered with French energy major Total to develop one of the world’s largest floating wind projects off the Welsh coast.
Marine Renewables Industry Association (MRIA) chairman Peter Coyle has described the Simply Blue Energy and Total partnership as a “remarkable achievement”.
As The Sunday Times reports, Simply Blue Energy, founded by Sam Roch-Perks, has secured Total’s support for a joint venture 96MW floating wind farm in 70 metres of water about 45km off Pembroke in the Celtic Sea.
The project is a “stepping stone” to a more ambitious operation and could be operating within the next five years if given approval by the British Crown Estate.
Floating platforms are regarded as the future for offshore wind, and a recent Crown Estate Scotland study predicted a potential yield of some 34 billion pounds sterling for the British economy by 2050.
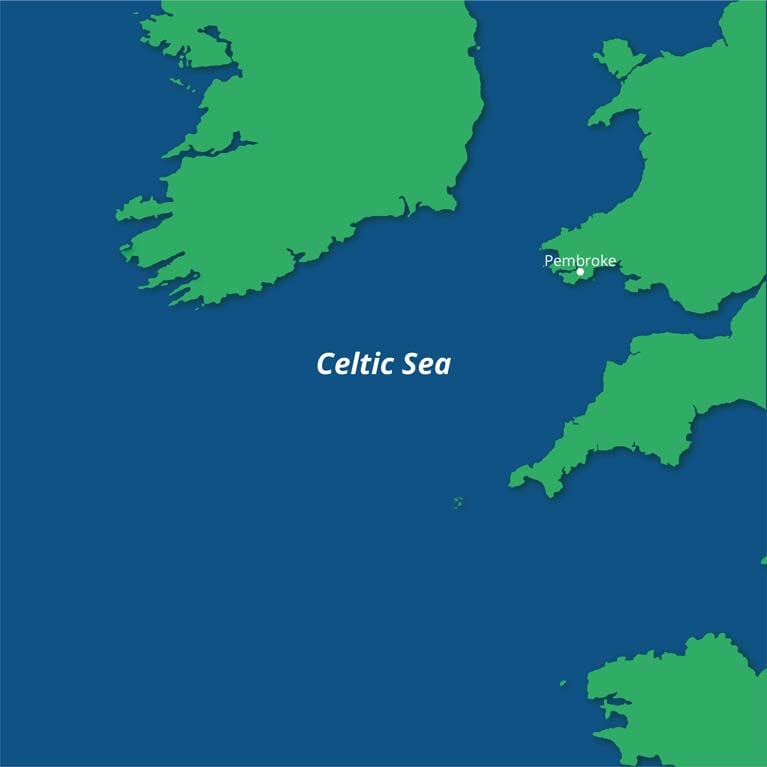 The Simply Blue Energy Celtic Sea 96MW floating wind farm is in 70 metres of water about 45km off Pembroke in the Celtic Sea
The Simply Blue Energy Celtic Sea 96MW floating wind farm is in 70 metres of water about 45km off Pembroke in the Celtic Sea
The world’s first commercial floating wind farm, the 30 MW Hywind Scotland project developed by Norwegian energy company Equinor (formerly Statoil) and Masdar off Aberdeen, was commissioned in 2017.
The Total/Simply Blue Energy project has been named Erebus – both the Greek mythological son of Chaos and name of one of Sir John Franklin’s ill-fated North-West passage ships which had been built in Pembroke dockyard in Wales and disappeared in 1848.
The project involves mounting 8 to 12MW turbines on semi-submersible “WindFloat” platforms supplied by Principle Power, with generated energy feeding into an established grid connection at Pembroke.
Simply Blue Energy was founded in 2011 by Roch-Perks, an engineer and property developer. It employs 12 people in energy and aquaculture projects and has offices in Cornwall, Pembroke, Edinburgh and Waterford.
MRIA chairman Peter Coyle said the Simply Blue Energy Erebus project is a “very significant development in the Irish business world for two reasons”.
“It is a remarkable achievement for a small Irish start-up to win the support and trust of Total, one of the world’s largest oil companies, and to do so for a project which will be the largest floating wind – a novel and demanding technology – project in the world to date,” Mr Coyle said.
“The success of Erebus in Welsh waters is vital to Irish offshore renewable energy ambitions as it will prove the technology and open up the scope for our enormous wind resource in deep waters to be harnessed to generate electricity for both local and export use,” he added.
“It is hugely significant that an accomplished Irish business person like Sam Roch Perks, CEO of Simply Blue Energy, who has had a stellar business track record in Asia and Sweden, should opt to focus on the new world of offshore energy rather than devote his resources to more fashionable and safe opportunities in areas such as software development,” Mr Coyle said.
“Our world-beating wind and wave resource for electricity generation is perhaps the biggest opportunity for income and job creation facing Ireland over the coming decades and the early success of Simply Blue Energy in this pioneering partnership with one of Europe’s largest companies will be a key milestone and a remarkable achievement”.
For more on The Sunday Times report, read here
Likely objections about “visual impact” would hamper any attempts to develop offshore wind farms in Northern Ireland for the time being, according to a new Stormont report.
As BBC News reports, the paper from the Department for the Economy highlights “significant issues” with regard to expected objections to wind farm projects within 13km of the shore.
As well as “visual impact”, there are also concerns relating to protected habitats around Northern Ireland’s coastline.
Northern Ireland has been exclused from the Crown Estate’s latest leasing round for such schemes. It had been hoped that the coast from Carlingford Lough to Belfast Lough would be considered for leasing.
BBC News has more on the story HERE.
Sailing Technology Inspires New Cloth Blades For Wind Farms
#SeaPower - Edinburgh-based ACT Blade has designed a textile blade for wind turbines that could increase energy production by nearly 10%.
The company, an offshoot of racing yacht sail specialist AMAR Azure, designed the blade as part of the Offshore Renewable Energy (ORE) Catapult’s Innovation Challenge.
ORE Catapult then led a study that identified the company’s technology could be used to produce a textile blade up to 50% lighter and 30% stiffer than conventional fibreglass equivalents, said ACT Blade’s Sabrina Malpede.
“I didn’t have knowledge of the renewable energy sector and needed to qualify my theory with sector experts,” she added.
“From these insights we were able to create the ACT Blade, the world’s first textile blade, capable of capturing more energy than a fibreglass blade by covering a larger swept area, significantly increasing annual production.”
ACT Blade says the design has the potential to increase energy production by 9.7% and reduce the levelised cost of energy by 8.7%.
ORE Catapult research and innovation project manager Vicky Coy said: “This is just one example of how technology can be adapted from one sector to create something genuinely groundbreaking in another industry.
“There are very few innovations in any field that deliver such a dramatic performance improvement with one fell swoop. This is a tremendous opportunity not just for ACT Blade, but for the UK to establish a new textile blade supply chain for the global marketplace.”